Windows Media Audio (WMA) is a series of audio codecs and their corresponding audio coding formats developed by Microsoft with the composer Stan LePard. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs. The original WMA codec, known simply as WMA, was conceived as a competitor to the popular MP3 and RealAudio codecs. WMA Pro, a newer and more advanced codec, supports multichannel and high resolution audio. A lossless codec, WMA Lossless, compresses audio data without loss of audio fidelity. WMA Voice, targeted at voice content, applies compression using a range of low bit rates. Microsoft has also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store audio encoded by WMA.

Windows Media Player (WMP) is a media player and media library application developed by Microsoft that is used for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Video (WMV) is a series of video codecs and their corresponding video coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows Media framework. WMV consists of three distinct codecs: The original video compression technology known as WMV, was originally designed for Internet streaming applications, as a competitor to RealVideo. The other compression technologies, WMV Screen and WMV Image, cater for specialized content. After standardization by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), WMV version 9 was adapted for physical-delivery formats such as HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc and became known as VC-1. Microsoft also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store video encoded by Windows Media Video.
Windows Media is a discontinued multimedia framework for media creation and distribution for Microsoft Windows. It consists of a software development kit (SDK) with several application programming interfaces (API) and a number of prebuilt technologies, and is the replacement of NetShow technologies.
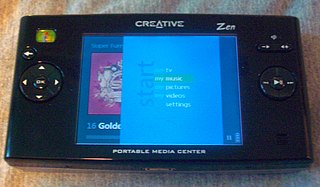
Portable Media Center (PMC) is a portable media player (PMP) platform developed by Microsoft. Announced at the 2003 Consumer Electronics Show (CES), and released in early 2004, it was originally positioned as a competitor to Apple's iPod. All its hard drive-based players use a graphical user interface (GUI) modeled after Media Center, a software portal bundled with Windows XP Media Center Edition. Manufacturers of PMC devices included Creative, Philips, iriver, Samsung, and Toshiba.
Digital Living Network Alliance was founded by a group of PC and consumer electronics companies in June 2003 to develop and promote a set of interoperability guidelines for sharing digital media among multimedia devices under the auspices of a certification standard. DLNA certified devices include smartphones, tablets, PCs, TV sets and storage servers.
Windows Media DRM or WMDRM, is a Digital Rights Management service for the Windows Media platform. It is designed to provide delivery of audio or video content over an IP network to a PC or other playback device in such a way that the distributor can control how that content is used.
Janus is the codename for a portable version of Windows Media DRM for portable devices, whose marketing name is Windows Media DRM for Portable Devices introduced by Microsoft in 2004 for use on portable media devices which store and access content offline. Napster To Go was the first online music store to require the Janus technology. Supporting Janus often implies that the device also make use of the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP).

MSN Music was a part of MSN's web services. It delivered music news, music videos, spotlights on new music, artist information, and live performances of artists. The website also served as a digital music store from 2004 to 2008.

SonicStage is a discontinued software from Sony that is used for managing portable devices when they are plugged into a computer running Microsoft Windows. It comprises a music player and library manager, similar to iTunes, Windows Media Player and RealPlayer. It is used to manage the library of ATRAC and MP3 recordings on a PC. It was first used in VAIO PCs put on the Japanese market in October 2001, and superseded OpenMG Jukebox. Version 2 was found on 2004 model products, and Version 3 on 2005 model products. SonicStage was required to transfer and manage music on all Network Walkman, NetMD and Hi-MD players, and the Clie handheld, before the software was dropped entirely outside of Japan in 2007.

Windows Media Center (WMC) is a defunct digital video recorder and media player created by Microsoft. Media Center was first introduced to Windows in 2002 on Windows XP Media Center Edition (MCE). It was included in Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista, as well as all editions of Windows 7 except Starter and Home Basic. It was also available on Windows 8 Pro and Windows 8.1 Pro as a paid add-on, before being discontinued in Windows 10, although it can reportedly be unofficially reinstalled using a series of Command Prompt commands.
Urge was an discontinued online music distribution service run by MTV Networks. Urge was integrated into Windows Media Player 11.

Zune is a discontinued line of digital media products and services marketed by Microsoft from November 2006 until its discontinuation in June 2012. Zune consisted of a line of portable media players, digital media player software for Windows PCs, a music subscription service known as a "Zune Music Pass", music and video streaming services for the Xbox 360 game console via the Zune Software, music, TV and movie sales, and desktop sync software for Windows Phone. Zune was also the provider of music streaming for United Airlines in-flight, after a partnership in 2010.
SpiralFrog was a very early music streaming service based in New York City that launched in the United States and Canada on September 17, 2007. SpiralFrog offered free and legal music downloads, all supported by advertising, and was the largest site of its kind in North America. On March 19, 2009, SpiralFrog terminated operations due to loan recalls. While SpiralFrog was not successful in the end, it nonetheless helped shaped the digital music industry shift from the purchase to streaming models, and its ultimate revenue recovery
Zune is a discontinued media management software for Microsoft Windows that functions as a full media player application with a library, an interface to the Zune Marketplace, and as a media streaming server. The software is used to sync with all devices with Zune functionality including the Zune 4, 8, 16, 30, 80, 120, Zune HD, Windows Phone 7, and Microsoft Kin. Zune devices work exclusively with the Zune software, which applies many design principles of Microsoft's Metro design language.
PassAlong Networks, also known as Tennessee Pacific Group, LLC, was a developer of digital media innovations and services located in Franklin, Tennessee. The company had a digital music library of three million licensed songs, two million of which were raw MP3 music files, and provided a series of products and services in the digital media marketplace.

The Gmini is a series of portable audio and video players released by Archos in 2004 and 2005.
PlayReady is a media file copy prevention technology from Microsoft that includes encryption, output prevention and digital rights management (DRM). It was announced in February 2007.
inMusic was a Canadian music news portal and an online music store. The music store had over 2 million tracks in English and French from various genres. Samples of 30 seconds for each song were offered at no charge. Purchases and downloads could be transferred to a CD or compatible digital music device.

The Zune HD is a portable media player in the Zune product family released on September 15, 2009 by Microsoft. It was a direct competitor with Apple's iPod Touch series of mobile devices. It was initially released in 16 and 32 GB capacities. A 64 GB version was released on April 9, 2010. It has a touchscreen interface for navigation and included Wi-Fi for synchronization, access to the Zune Marketplace and Web browsing.









