Related Research Articles

Breton is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of the insular branch instead of the continental grouping.
English orthography is the writing system used to represent spoken English, allowing readers to connect the graphemes to sound and to meaning. It includes English's norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalisation, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.

Persian, also known by its endonym Farsi, is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian, Dari Persian and Tajiki Persian. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivation of the Cyrillic script.

Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries.

The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian is a dead Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest written languages, first being recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4000 years. Its classical form is known as Middle Egyptian, the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt which remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era it had diversified into the Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic remains in use as the liturgical language of the Coptic Church.

Coptic is a language family of closely related dialects, representing the most recent developments of the Egyptian language, and historically spoken by the Copts, starting from the third-century AD in Roman Egypt. Coptic was supplanted by Arabic as the primary spoken language of Egypt following the Muslim conquest of Egypt and was slowly replaced over the centuries. Coptic has no native speakers today, although it remains in daily use as the liturgical language of the Coptic Orthodox Church and of the Coptic Catholic Church. Innovations in grammar, phonology, and the influx of Greek loanwords distinguish Coptic from earlier periods of the Egyptian language. It is written with the Coptic alphabet, a modified form of the Greek alphabet with several additional letters borrowed from the Demotic Egyptian script.

Middle English is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the Oxford English Dictionary specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages.
Bokmål is an official written standard for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is the preferred written standard of Norwegian for 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. Unlike, for instance, the Italian language, there is no nationwide standard or agreement on the pronunciation of Bokmål.
Modern Greek, generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek, refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the languages sometimes referred to as Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, beginning around the fourth century AD.

Burmese is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in Myanmar, where it is an official language, lingua franca, and the native language of the Burmans, the country's principal ethnic group. Burmese is also spoken by the indigenous tribes in Chittagong Hill Tracts in Bangladesh, and in Tripura state in Northeast India. Although the Constitution of Myanmar officially recognizes the English name of the language as the Myanmar language, most English speakers continue to refer to the language as Burmese, after Burma, the country's once previous and currently co-official name. Burmese is the common lingua franca in Myanmar, as the most widely-spoken language in the country. In 2007, it was spoken as a first language by 33 million, primarily the Burman people and related ethnic groups, and as a second language by 10 million, particularly ethnic minorities in Myanmar and neighboring countries. In 2022, the Burmese-speaking population was 38.8 million.
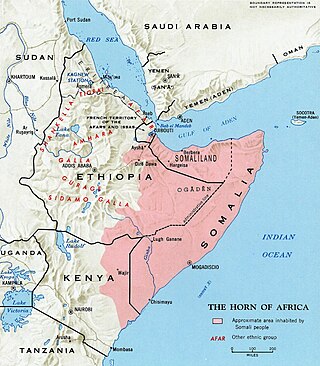
Somali is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken as a mother tongue by Somalis in Greater Somalia and the Somali diaspora. Somali is an official language in Somalia and Ethiopia, and a national language in Djibouti as well as in northeastern Kenya. The Somali language is written officially with the Latin alphabet although the Arabic alphabet and several Somali scripts like Osmanya, Kaddare and the Borama script are informally used.

Modern Hebrew, also known as Israeli Hebrew or Israeli, and generally referred to by speakers simply as Hebrew, is the standard form of the Hebrew language spoken today. Spoken in ancient times, Ancient Hebrew, a member of the Canaanite branch of the Semitic language family, was supplanted as the Jewish vernacular by the western dialect of Aramaic beginning in the third century BCE, though it continued to be used as a liturgical and literary language. It was revived as a spoken language in the 19th and 20th centuries and is the official language of Israel. Of the Canaanite languages, Modern Hebrew is the only language spoken today.

A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonological, grammatical or orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations.
In historical linguistics, grammaticalization is a process of language change by which words representing objects and actions become grammatical markers. Thus it creates new function words from content words, rather than deriving them from existing bound, inflectional constructions. For example, the Old English verb willan 'to want', 'to wish' has become the Modern English auxiliary verb will, which expresses intention or simply futurity. Some concepts are often grammaticalized, while others, such as evidentiality, are not so much.

The language known today as Spanish is derived from a dialect of spoken Latin, which was brought to the Iberian Peninsula by the Romans after their occupation of the peninsula that started in the late 3rd century BC. Influenced by the peninsular hegemony of Al-Andalus in the early middle ages, Hispano-Romance varieties borrowed substantial lexicon from Arabic. Upon the southward territorial expansion of the Kingdom of Castile, Hispano-Romance norms associated to this polity displaced both Arabic and the Mozarabic romance varieties in the conquered territories, even though the resulting speech also assimilated features from the latter in the process. The first standard norm of Spanish was brought forward in the 13th century by Alfonso X the Wise, probably drawing from the speech of the upper classes of Toledo. Features associated with the Castilian patterns of Hispano-Romance also spread west and east to the kingdoms of León and Aragón for the rest of the middle ages, owing to the political prestige achieved by the Kingdom of Castile in the peninsular context and to the lesser literary development of their vernacular norms. From the 1560s onward the standard written form followed Madrid's.
The Old Polish language was a period in the history of the Polish language between the 10th and the 16th centuries. It was followed by the Middle Polish language.

Old Burmese was an early form of the Burmese language, as attested in the stone inscriptions of Pagan, and is the oldest phase of Burmese linguistic history. The transition to Middle Burmese occurred in the 16th century. The transition to Middle Burmese included phonological changes as well as accompanying changes in the underlying orthography. Word order, grammatical structure and vocabulary have remained markedly comparable, well into Modern Burmese, with the exception of lexical content.

Middle Tamil is the form of the Tamil language that existed from the 8th to the 15th century. The development of Old Tamil into Middle Tamil, which is generally taken to have been completed by the 8th century, was characterised by a number of phonological and grammatical changes despite maintaining grammatical and structural continuity with the previous form of the language. In phonological terms, the most important shifts were the virtual disappearance of the aytam (ஃ), an old phoneme, the coalescence of the alveolar and dental nasals, and the transformation of the alveolar plosive into a rhotic.

Middle Khmer is the historical stage of the Khmer language as it existed between the 14th and 18th centuries, spanning the period between Old Khmer and the modern language. The beginning of the Middle Khmer period roughly coincides with the fall of the Angkorian Khmer Empire to the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom and the period of Cambodian history popularly referred to as the Post-Angkor Period. The Middle Khmer period was a stage of transition which saw relatively rapid and dramatic changes, especially in phonology, that ended with the emergence of a language recognizable as Modern Khmer approximately concurrent with the 1777 coronation of Ang Eng, the father of the poet-king Ang Duong.
Neo-Brittonic, also known as Neo-Brythonic, is a stage of the Insular Celtic Brittonic languages that emerged by the middle of the sixth century CE. Neo-Brittonic languages include Old, Middle and Modern Welsh, Cornish, and Breton, as well as Cumbric.
References
- 1 2 3 Herbert, Patricia; Anthony Crothers Milner (1989). South-East Asia: Languages and Literatures: a Select Guide. University of Hawaii Press. p. 5. ISBN 9780824812676.
- 1 2 3 Wheatley, Julian K. "43. Burmese". In Bernard Comrie (ed.). The World's Major Languages. Routledge. pp. 724–739. ISBN 9780203301524.
- ↑ LaPolla, Randy J.; Graham Thurgood (2013). Sino-Tibetan Languages. Routledge. ISBN 9781135797171.