
Satellite temperature measurements are inferences of the temperature of the atmosphere at various altitudes as well as sea and land surface temperatures obtained from radiometric measurements by satellites. These measurements can be used to locate weather fronts, monitor the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, determine the strength of tropical cyclones, study urban heat islands and monitor the global climate. Wildfires, volcanos, and industrial hot spots can also be found via thermal imaging from weather satellites.

The advanced microwave sounding unit (AMSU) is a multi-channel microwave radiometer installed on meteorological satellites. The instrument examines several bands of microwave radiation from the atmosphere to perform atmospheric sounding of temperature and moisture levels.
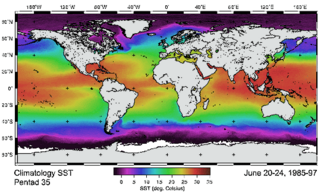
The Advanced Very-High-Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) instrument is a space-borne sensor that measures the reflectance of the Earth in five spectral bands that are relatively wide by today's standards. AVHRR instruments are or have been carried by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) family of polar orbiting platforms (POES) and European MetOp satellites. The instrument scans several channels; two are centered on the red (0.6 micrometres) and near-infrared (0.9 micrometres) regions, a third one is located around 3.5 micrometres, and another two the thermal radiation emitted by the planet, around 11 and 12 micrometres.

NOAA-19, known as NOAA-N' before launch, is the last of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series of weather satellites. NOAA-19 was launched on 6 February 2009. NOAA-19 is in an afternoon Sun-synchronous orbit and is intended to replace NOAA-18 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.

NOAA-17, also known as NOAA-M before launch, was an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-17 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-L series and a new launch vehicle.

NOAA-16, also known as NOAA-L before launch, was an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-16 continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft that began with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983; but it had additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-K series and a new launch vehicle. It was launched on 21 September 2000 and, following an unknown anomaly, it was decommissioned on 9 June 2014. In November of 2015 it broke up in orbit, creating more than 200 pieces of debris.

NOAA-18, also known as NOAA-N before launch, is an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-18 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-M series and a new launch vehicle. NOAA-18 is in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and replaced NOAA-17 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.

NOAA-15, also known as NOAA-K before launch, is an operational, polar-orbiting of the NASA-provided Television Infrared Observation Satellite (TIROS) series of weather forecasting satellite operated by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-15 was the latest in the Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) series. It provided support to environmental monitoring by complementing the NOAA/NESS Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite program (GOES).
The Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite (POES) is a constellation of polar orbiting weather satellites funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) with the intent of improving the accuracy and detail of weather analysis and forecasting. The spacecraft were provided by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center oversaw the manufacture, integration and test of the NASA-provided TIROS satellites. The first polar-orbiting weather satellite launched as part of the POES constellation was the Television Infrared Observation Satellite-N (TIROS-N), which was launched on 13 October 1978. The final spacecraft, NOAA-19, was launched on 6 February 2009. The ESA-provided MetOp satellite operated by EUMETSAT utilize POES-heritage instruments for the purpose of data continuity. The Joint Polar Satellite System, which was launched on 18 November 2017, is the successor to the POES Program.
NOAA-13, also known as NOAA-I before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the operational, polar orbiting, meteorological satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite System (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the series (fifth) of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983. NOAA-I was in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and was intended to replace the NOAA-11 (NOAA-H) as the prime afternoon (14:00) spacecraft.

NOAA-7, known as NOAA-C before launch, was an American operational weather satellite for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for the support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978-1984. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment. An earlier launch, NOAA-B, was scheduled to become NOAA-7, however NOAA-B failed to reach its required orbit.
NOAA-6, known as NOAA-A before launch, was an American operational weather satellite for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for the support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978-1984. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA B was an American operational weather satellite for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for the support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978-1984. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.

GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). GOES-16 serves as the operational geostationary weather satellite in the GOES East position at 75.2°W, providing a view centered on the Americas. GOES-16 provides high spatial and temporal resolution imagery of the Earth through 16 spectral bands at visible and infrared wavelengths using its Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI). GOES-16's Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) is the first operational lightning mapper flown in geostationary orbit. The spacecraft also includes four other scientific instruments for monitoring space weather and the Sun.

The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) is a sensor designed and manufactured by the Raytheon Company on board the polar-orbiting Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership, NOAA-20, and NOAA-21 weather satellites. VIIRS is one of five key instruments onboard Suomi NPP, launched on October 28, 2011. VIIRS is a whiskbroom scanner radiometer that collects imagery and radiometric measurements of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans in the visible and infrared bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.

NOAA-9, known as NOAA-F before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the second of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-10, known as NOAA-G before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the third of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-11, known as NOAA-H before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978–1984. It was the fourth of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-12, also known as NOAA-D before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an operational meteorological satellite for use in the National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service (NESDIS). The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-14, also known as NOAA-J before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-14 continued the third-generation operational, Polar Orbiting Environmental Satellite (POES) series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-14 continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983.













