
TIROS, or Television InfraRed Observation Satellite, is a series of early weather satellites launched by the United States, beginning with TIROS-1 in 1960. TIROS was the first satellite that was capable of remote sensing of the Earth, enabling scientists to view the Earth from a new perspective: space. The program, promoted by Harry Wexler, proved the usefulness of satellite weather observation, at a time when military reconnaissance satellites were secretly in development or use. TIROS demonstrated at that time that "the key to genius is often simplicity". TIROS is an acronym of "Television InfraRed Observation Satellite" and is also the plural of "tiro" which means "a young soldier, a beginner".

Landsat 4 is the fourth satellite of the Landsat program. It was launched on July 16, 1982, with the primary goal of providing a global archive of satellite imagery. Although the Landsat Program is managed by NASA, data from Landsat 4 was collected and distributed by the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat 4 science operations ended on December 14, 1993, when the satellite lost its ability to transmit science data, far beyond its designed life expectancy of five years. The satellite housekeeping telemetry and tracking continued to be maintained by NASA until it was decommissioned on June 15, 2001.

ESSA-8 was a weather satellite launched by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) on December 15, 1968, from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

The Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA) was a United States Federal executive agency created in 1965 as part of a reorganization of the United States Department of Commerce. Its mission was to unify and oversee the meteorological, climatological, hydrographic, and geodetic operations of the United States. It operated until 1970, when it was replaced by the new National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).

ESSA-1 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA-9, also known as TOS-G, was a meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA). ESSA-9 replaced the ESSA-7 satellite.
Intelsat II F-2, also known as Lani Bird, was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat. Launched in 1967, it was operated in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 174 degrees east until 1969.

USA-239, also known as GPS IIF-3, GPS SVN-65, and Navstar-67 is an American navigation satellite which forms part of the Global Positioning System. It was the third of twelve Block IIF satellites to be launched.
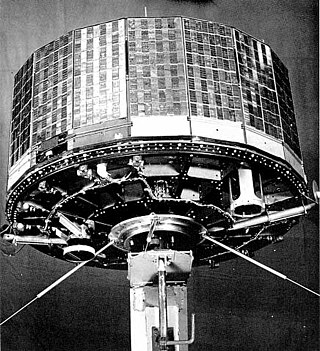
TIROS 4 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the fourth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.

TIROS 6 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the sixth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.

TIROS-7 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the seventh in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.

TIROS-8 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the eighth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.

TIROS-9 was a spin-stabilized meteorological satellite. It was the ninth in a series of Television Infrared Observation Satellites.
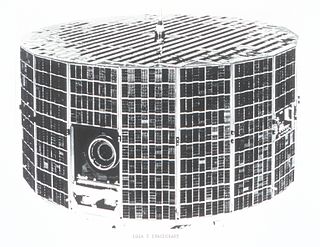
ESSA-2 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
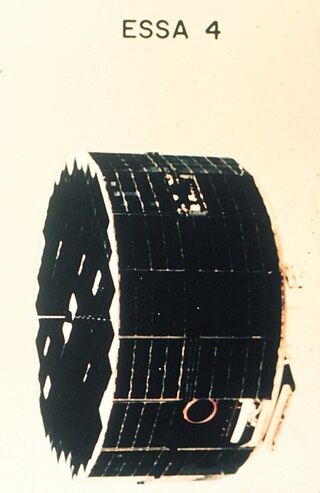
ESSA-4 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA-5 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

ESSA-6 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).
ESSA-7 was a spin-stabilized operational meteorological satellite. Its name was derived from that of its oversight agency, the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA).

Nimbus 6 was a meteorological satellite. It was the sixth in a series of the Nimbus program.

TIROS-M, also known as ITOS-1 was a weather satellite operated by the Environmental Science Services Administration (ESSA). It was part of a series of satellites called ITOS, or improved TIROS. TIROS-M was launched on a Delta rocket on January 23, 1970. The launch carried one other satellite, Australis-OSCAR 5. It was deactivated on June 18, 1971.

















