Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the 32 Federal Entities of the United Mexican States. It is divided into 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.

Villahermosa is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Tabasco, and serves as the municipal seat of the state. Located in Southeast Mexico, Villahermosa is an important city because of its cultural history, natural resources, commercial development, and modern industrialization.

Tabasco is a state in Southeast Mexico that is divided into 17 municipalities. According to the 2020 Mexican census, it has the 20th largest population with 2,402,598 inhabitants and is the 24th largest by land area spanning 24,738 square kilometres (9,551 sq mi).

Comalcalco is a city located in Comalcalco Municipality about 45 miles (60 km) northwest of Villahermosa in the Mexican state of Tabasco. Near the city is the Pre-Columbian Maya archaeological site of Comalcalco. The literal English translation of "Comalcalco" is "In the house of the comals". A comal is a pan used to prepare food.

Metepec is a municipality in the State of Mexico in Mexico and is located directly to the east of the state capital, Toluca, at an altitude of 2,635 metres (8,645 ft) above sea level. The center of Mexico City lies some 50 km further to the east. The city of Metepec also form part of the Greater Toluca. The name Metepec comes from Náhuatl meaning hill of the agave plants. However, it is also known in the Matlatzinca language as "Nepinta-Tuhi" meaning 'people of corn land' and in the Otomi language as "Ntaguada".

Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco is a public institution of higher learning located in Villahermosa, Tabasco, Mexico. The mission of the university is "to prepare professionals with broad and deep expertise in their area of study to fill the needs of Tabasco and the country at large." UJAT is the largest and most prominent university in the state of Tabasco. During the 2007-2008 academic year the university enrolled 35,271 students and had a teaching staff of over 2,000. For the same school year the university offered bachelor's degrees in 36 disciplines, master's degrees in 26 areas, three doctoral degrees, and post-graduate Certificates (Especialidades) in 17 graduate areas of specialization. The university grants law, education, management, engineering, medicine, architecture, nursing, and dentistry degrees, plus some 30 additional degrees in other fields of study.
XHCPBS-FM, known as La Voz de los Chontales, is an indigenous community radio station on 98.7 FM broadcasting in Spanish, Chontal Maya (yokot'an), Ch'ol and Ayapa Zoque from Nacajuca in the Mexican state of Tabasco. The station will form part of the Indigenous Cultural Broadcasting System (SRCI), part of the National Institute of Indigenous Peoples (INPI).

Cunduacán is a municipality in the central portion of the Mexican state of Tabasco, in Mexico. It is located at about 18°4'0"North, 93°10'0"West.

Tlacotalpan is a municipality located in the eastern coastal region of the Mexican state of Veracruz. It covers a total surface area of 646.51 km2 (250 sq mi), accounting for 0.89% of the state total. The municipal seat is the city of Tlacotalpan, Veracruz, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Escárcega is one of the 13 municipalities in the Mexican state of Campeche. The municipal seat, and largest settlement, is the city of Escárcega.

Paraíso is a town and municipality located in the north of the Mexican state of Tabasco, about 75 km due north of the state capital of Villahermosa on the Gulf of Mexico. Much of the area is traditionally dedicated to fishing and agriculture. Today, it is also an oil-producing area with the mostly oil-dedicated port of Dos Bocas. There is also some tourism connected to the area's beaches and natural attractions, and the area is promoted under the state's Cacao Route tourism program.

Pahuatlán, officially Pahuatlán del Valle, is a town and municipality located in the northwest of the state of Puebla in central Mexico. The municipality is part of the Sierra Norte region of the state, a steep mountainous area which receive significant moisture from the Gulf of Mexico, and borders the states of Hidalgo and Veracruz.

Zacatlán Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Puebla in south-eastern Mexico. Its administrative centre is the city of Zacatlán.

Jalpa de Méndez Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Tabasco in south-eastern Mexico.

Pinal de Amoles Municipality is a municipality in the Mexican state of Querétaro in central Mexico.

Jalpa de Méndez is a city in Jalpa de Méndez Municipality located in the north of the Mexican state of Tabasco, Mexico. It is considered part of the Chontal Maya region of the state, known for its production of decorated dried gourds traditionally used for drinking chocolate and cured meats. Although there is some oil production and tourism, its main economic activity is agriculture, producing cacao, coconut and livestock.

Nacajuca is a city in Nacajuca Municipality in the state of Tabasco, Mexico. It is part of the Chontalapa region in the north center of the state and a major center of Tabasco's Chontal Maya population. Although the local economy is still based on agriculture and livestock, oil production, handcrafts and some tourism are important aspects as well. The environment of the area is low-lying flat land susceptible to flooding including being hard hit by the 2007 Tabasco flood and more recent flooding in 2011.
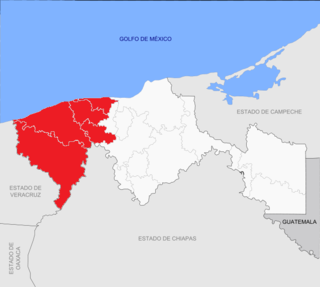
Chontalpa is an area in the Mexican state of Tabasco, which consists of four municipalities in the northwest of the state. Although the name refers to the state's Chontal Maya population, modern Chontalpa is a subregion of the Grijalva Region, and formed with economic concerns in mind. A large percentage of the state's Chontal Maya population does live here, with the municipality of Nacajuca having the largest concentration of indigenous, with the next largest concentration found just east of the region in the Villahermosa area. The subregion's economy is based on agriculture, especially livestock production as well as oil drilling, which have been at odds with each other because of severe degradation of the environment since the mid 20th century. Chontalpa is also home to Tabasco's two main archeological sites, La Venta and Comalcalco, along with numerous smaller sites.

Eduardo González Arévalo was a Spanish-born Imperial Mexican General during the Second French intervention in Mexico. He was known for being the Imperial Governor of Tabasco from June 18, 1863 to January 20, 1864 as well as being a major participant of the French intervention in Tabasco.

Paraíso is a municipality in Tabasco in south-eastern Mexico.



















