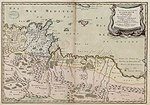
Tunisia is a country in Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, having a western border with Algeria (965 km) and south-eastern border with Libya (459 km) where the width of land tapers to the south-west into the Sahara. The country has north, east and complex east-to-north coasts including the curved Gulf of Gabès, which forms the western part of Africa's Gulf of Sidra. Most of this greater gulf forms the main coast of Libya including the city of Sirte which shares its root name. The country's geographic coordinates are 34°00′N9°00′E. Tunisia occupies an area of 163,610 square kilometres, of which 8,250 are water. The principal and reliable rivers rise in the north of the country with a few notable exceptions from north-east Algeria and flow through the northern plain where sufficient rainfall supports diverse plant cover and irrigated agriculture.

Tunisian culture is a product of more than three thousand years of history and an important multi-ethnic influx. Ancient Tunisia was a major civilization crossing through history; different cultures, civilizations and multiple successive dynasties contributed to the culture of the country over centuries with varying degrees of influence. Among these cultures were the Carthaginian – their native civilization, Roman, Vandal, Jewish, Christian, Arab, Islamic, Turkish, and French, in addition to native Amazigh. This unique mixture of cultures made Tunisia, with its strategic geographical location in the Mediterranean, the core of several civilizations of Mare Nostrum.

Muhammad VII al-Munsif, ) commonly known as Moncef Bey was the Bey of Tunis between 19 June 1942 and 14 May 1943. He was the penultimate ruler of the Husainid dynasty.

The Bourse des Valeurs Mobilières de Tunis (BVMT) or Bourse de Tunis is a stock exchange based in Tunis, Tunisia. It was founded in 1969, and currently lists around 50 stocks.
Métouia, also spelled El Méthouia, is a town and commune in the Gabès Governorate, Tunisia. As of 2004 it had a population of 9,946. In summer, it increases to nearly 50 000 inhabitants due to the return of summer residents living abroad. Administratively, it has a municipality seat of 9,946 inhabitants and a delegation attached to the governorate of Gabès.

Presidential elections were held in Tunisia on 23 November 2014, a month after parliamentary elections. They were the first free and fair presidential elections since the country gained independence in 1956, and the first direct presidential elections after the Tunisian Revolution of 2011 and the adoption of a new Constitution in January 2014.

Beji Caid Essebsi was a Tunisian politician who served as the sixth president of Tunisia from 31 December 2014 until his death on 25 July 2019. Previously, he served as the minister of foreign affairs from 1981 to 1986 and as the prime minister from February 2011 to December 2011.
The mass media in Tunisia is an economic sector. Under the authoritarian regimes of Habib Bourguiba, and then Zine el-Abidine Ben Ali, it saw periods of liberalization and then challenges, notably due to Tunisian censorship. The 2010-2011 Tunisian protests and the subsequent change in government may bring significant change in this domain.

The Kingdom of Tunisia was a short-lived country established as a monarchy on 20 March 1956 after Tunisian independence and the end of the French protectorate period. It lasted for a period of one year and five months between 20 March 1956, the day of the independence, until 25 July 1957, the day of the declaration of the republic. Its sole monarch, titled Bey of Tunis, was Muhammad VIII al-Amin who appointed the Prime Ministers Tahar Ben Ammar and Habib Bourguiba.
The Turks in Tunisia, also known as Turco-Tunisians and Tunisian Turks, are ethnic Turks who constitute one of the minority groups in Tunisia.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Tunis, Tunisia.

Parliamentary elections were held in Tunisia on 26 October 2014. Campaigning started on 4 October 2014. They were the first free regular legislative elections since independence in 1956, and the first elections held following the adoption of the new constitution in January 2014, which created a 217-seat Assembly of the Representatives of the People. According to preliminary results, Nidaa Tounes gained a plurality of votes, winning 85 seats in the 217-seat parliament, beating the Ennahda Movement and many smaller parties.

Othman Battikh was a Tunisian Islamic scholar and Grand Mufti of Tunisia from 2008 to 2013. He also served as member of the Tunisian government.

Moez Chakchouk, born in Sousse on 12 July 1975, is the Director of Government Affairs and Regulatory Policy at Packet Clearing House, the international organization responsible for providing operational support and security to critical internet infrastructure, including Internet exchange points and the core of the domain name system. Chakchouk was previously the Transport Minister of Tunisia (2020-2021), Assistant Director-General for Communication and Information at UNESCO (2018-2020), Chairman and CEO of the Tunisian Post (2015-2018), and chairman and CEO of Agence Tunisienne d'Internet.
The 1987 Tunisian coup d'état involved the bloodless ousting of the aging President of Tunisia Habib Bourguiba on 7 November 1987, and his replacement as President by his recently appointed Prime Minister, Zine El Abidine Ben Ali. The action was justified by reference to Bourguiba's failing health and Article 57 of the country's constitution. Reports later surfaced to indicate that the Italian intelligence services had been involved in planning it.

Bahri Guiga was a Tunisian lawyer and politician.

Dar Lasram is one of the palaces of the medina of Tunis. It is located at 24 Tribunal Street.

Chedly Ayari was a Tunisian politician, economist, and diplomat. He served in several ministerial positions under the government of Habib Bourguiba and was President of the Central Bank of Tunisia from 24 July 2012 to 16 February 2018.
In Tunisia, makhzen was the term used to designate the political and administrative establishment of the Beylik of Tunis before the proclamation of the republic in 1957. The makhzen consisted of families of Turkish origin, or Turkish-speaking mamluks of European origin, intermarried with indigenous Tunisian families who were great merchants or landowners. This network of families dominated the high offices of state, the leadership of the army and the positions of rank and power in the regions outside the capital. They were also closely connected with the senior ulema. These were known as “makhzen families”. Outside of the capital and the major towns, the term 'makhzen' designated not the leading families close to the regime, but those of the interior tribes which had a trusted relationship with the ruling family. Together the great families and the loyal tribes made up the country's 'establishment'.