Human spaceflight programs have been conducted, started, or planned by multiple countries and companies. Until the 21st century, human spaceflight programs were sponsored exclusively by governments, through either the military or civilian space agencies. With the launch of the privately funded SpaceShipOne in 2004, a new category of human spaceflight programs – commercial human spaceflight – arrived. By the end of 2022, three countries and one private company (SpaceX) had successfully launched humans to Earth orbit, and two private companies had launched humans on a suborbital trajectory.

The Brazilian Space Agency is the civilian authority in Brazil responsible for the country's space program. It operates a spaceport at Alcântara, and a rocket launch site at Barreira do Inferno. It is the largest and most prominent space agency in Latin America.

The Canadian Space Agency is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the Canadian Space Agency Act.

A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered gliders.

Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane developed by Sierra Space. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the Dream Chaser Cargo System cargo variant is operational. The crewed variant is planned to carry up to seven people and cargo to and from low Earth orbit.

The Romanian Space Agency is a public institution that coordinates Romania's national space technology research programs and activities related to space research. ROSA, established in 1991, is subordinate to the Romanian Ministry of Education.

Thales Alenia Space is a joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%). The company is headquartered in Cannes, France.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. It currently supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, the Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station.

Rocket Lab USA, Inc. is a publicly traded aerospace manufacturer and launch service provider that operates and launches lightweight Electron orbital rockets used to provide dedicated launch services for small satellites as well as a suborbital variant of Electron called HASTE. The company plans to build a larger Neutron rocket as early as 2024. Electron rockets have launched 44 times from either Rocket Lab's Launch Complex 1 in New Zealand or at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport in Wallops Island, Virginia, United States. Rocket Lab has launched one HASTE rocket to date from Wallops Island, Virginia.

The Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment is the public service department of New Zealand charged with "delivering policy, services, advice and regulation" which contribute to New Zealand's economic productivity and business growth.

Artemis 1, officially Artemis I and formerly Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), was an uncrewed Moon-orbiting mission. As the first major spaceflight of NASA's Artemis program, Artemis 1 marked the agency's return to lunar exploration after the conclusion of the Apollo program five decades earlier. It was the first integrated flight test of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, and its main objective was to test the Orion spacecraft, especially its heat shield, in preparation for subsequent Artemis missions. These missions seek to reestablish a human presence on the Moon and demonstrate technologies and business approaches needed for future scientific studies, including exploration of Mars.
The Polish Space Agency is the space agency of Poland, administered by the Ministry of Development, Labour and Technology. It is a member of the European Space Agency. The agency is focused on developing satellite networks and space technologies in Poland. It was established on 26 September 2014, and its headquarters are located in Gdańsk, Poland.

EQUULEUS is a nanosatellite of the 6U CubeSat format that will measure the distribution of plasma that surrounds the Earth (plasmasphere) to help scientists understand the radiation environment in that region. It will also demonstrate low-thrust trajectory control techniques, such as multiple lunar flybys, within the Earth-Moon region using water steam as propellant. The spacecraft was designed and developed jointly by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the University of Tokyo.

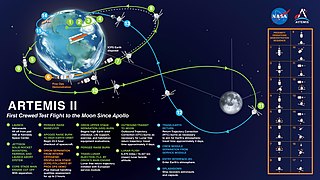
The Artemis program is a Moon exploration program that is led by the United States' NASA and was formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The Artemis program is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since Apollo 17 in 1972. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a permanent base on the Moon to facilitate human missions to Mars.

CAPSTONE is a lunar orbiter that is testing and verifying the calculated orbital stability planned for the Lunar Gateway space station. The spacecraft is a 12-unit CubeSat that is also testing a navigation system that is measuring its position relative to NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) without relying on ground stations. It was launched on 28 June 2022, arrived in lunar orbit on 14 November 2022, and was scheduled to orbit for six months. On 18 May 2023, it completed its primary mission to orbit in the near-rectilinear halo orbit for six months, but will stay on this orbit, continuing to perform experiments during an enhanced mission phase.
This article documents expected notable spaceflight events during the year 2025.

The Artemis Accords is a series of non-binding bilateral arrangements between the United States government and other world governments that elaborates on the norms expected to be followed in outer space. The accords are related to the Artemis program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2026, with the ultimate goal of expanding space exploration to Mars and beyond. As of February 9, 2024, thirty-five countries have signed the accords, including fifteen in Europe, eight in Asia, four in South America, three in North America, two in Oceania and four in Africa.
MethaneSAT is an American-New Zealand space mission launched in 2024 aboard SpaceX's Transporter 10 rideshare mission. It is an Earth observation satellite that will monitor and study global methane emissions in order to combat climate change. The spacecraft will carry a high performance spectrometer methane sensing system, which will allow the spacecraft to take high resolution measurements of global methane emissions from roughly 50 major regions across Earth.
The Luxembourg Space Agency (LSA) is the national space agency of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. It was founded on September 12, 2018, by Luxembourg's Economy Minister Étienne Schneider.
Dawn Aerospace is a space transportation company building both in-space propulsion systems and a space launch vehicle. The company currently manufactures satellite propulsion systems with lower greenhouse potential and nontoxic materials, as well as an uncrewed suborbital spaceplane with rapidly reusable flight characteristics.

















