
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.

Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange.

Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO2−
4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr
2O2−
7. They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.

Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can substitute for iron in variable amounts as it forms a solid solution with magnesiochromite (MgCr2O4). A substitution of the element aluminium can also occur, leading to hercynite (FeAl2O4). Chromite today is mined particularly to make stainless steel through the production of ferrochrome (FeCr), which is an iron-chromium alloy.
In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements.
Plating is a surface covering in which a metal is deposited on a conductive surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improve solderability, to harden, to improve wearability, to reduce friction, to improve paint adhesion, to alter conductivity, to improve IR reflectivity, for radiation shielding, and for other purposes. Jewelry typically uses plating to give a silver or gold finish.
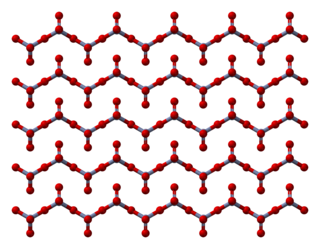
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions, bright orange when wet and which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser and a carcinogen.

Copper chromite is an inorganic compound with the formula Cu2Cr2O5. It is a black solid that is used to catalyze reactions in organic synthesis.

Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.

Chromium is a member of group 6, of the transition metals. The +3 and +6 states occur most commonly within chromium compounds, followed by +2; charges of +1, +4 and +5 for chromium are rare, but do nevertheless occasionally exist.

Ammonium dichromate is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Cr2O7. In this compound, as in all chromates and dichromates, chromium is in a +6 oxidation state, commonly known as hexavalent chromium. It is a salt consisting of ammonium ions and dichromate ions.

Sodium chromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CrO4. It exists as a yellow hygroscopic solid, which can form tetra-, hexa-, and decahydrates. It is an intermediate in the extraction of chromium from its ores.

Chromium(VI) peroxide or chromium oxide peroxide is an unstable compound with the formula CrO5. This compound contains one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands, making a total of five oxygen atoms per chromium atom.

In chemistry the term chromite has been used in two contexts. Under IUPAC naming conventions, chromate(III) is preferred to chromite.
- For compounds containing an oxyanion of chromium in oxidation state 3
- For other compounds of chromium(III) as a means of distinguishing a chemical species such as hexacyanochromite(III). [Cr(CN)6]3− from an analogous compound in which chromium is a different oxidation state.

In chemistry a molybdate is a compound containing an oxoanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxoanions which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxoanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxoanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.
A chromate ester is a chemical structure that contains a chromium atom (symbol Cr) in a +6 oxidation state that is connected via an oxygen (O) linkage to a carbon (C) atom. The Cr itself is in its chromate form, with several oxygens attached, and the Cr–O–C attachment makes this chemical group structurally similar to other ester functional groups. They can be synthesized from various chromium(VI) metal compounds, such as CrO3, chromium chloride complexes, and aqueous chromate ions, and tend to react via redox reactions to liberate chromium(IV).

The chromium cycle is the biogeochemical cycle of chromium through the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and lithosphere.
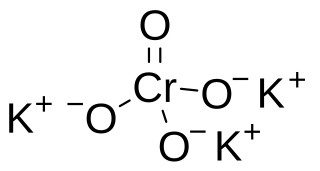
Potassium hypochromate is a chemical compound with the formula K3CrO4 with the unusual Cr5+ ion. This compound is unstable in water but stable in alkaline solution and was found to have a similar crystal structure to potassium hypomanganate.
Europium(III) chromate is an chemical compound composed of europium, chromium and oxygen with europium in the +3 oxidation state, chromium in the +5 oxidation state and oxygen in the -2 oxidation state. It has the chemical formula of EuCrO4.















