Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States ; in Oceania, it is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo.

Apra Harbor, also called Port Apra, is a deep-water port on the western side of the United States territory of Guam. It is considered one of the best natural ports in the Pacific Ocean. The harbor is bounded by Cabras Island and the Glass Breakwater to the north and the Orote Peninsula in the south. Naval Base Guam and the Port of Guam are the two major users of the harbor. It is also a popular recreation area for boaters, surfers, scuba divers, and other recreationalists.

Asan-Maina is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The municipality combines the names of the coastal community of Asan with Maina, a community along the slopes of the Fonte River valley to the east. Asan was the northern landing site for United States Marines during Guam's liberation from the Japanese during World War II. Asan Beach Park is part of the War in the Pacific National Historic Park. The third community comprising Asan-Maina is Nimitz Hill Annex in the hills above Asan and Maina, which is the location of the Joint Region Marianas headquarters. Asan-Maina is located in the Luchan (Western) District.
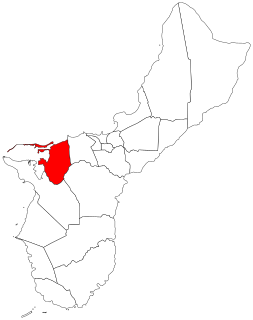
Piti is a village located on the central west coast of the United States territory of Guam. It contains northern and eastern coastlines of Apra Harbor, including Cabras Island, which has the commercial Port of Guam and the island's largest power plants. Piti was a pre-Spanish CHamoru village and, after Spanish colonization, became the primary port town on Guam. The town was largely destroyed during the 1944 liberation of Guam and the population relocated during the wartime construction of Apra Harbor.

The War in the Pacific National Historical Park is a multi-unit protected area in the United States territory of Guam, which was established in 1978 in honor of those who participated in the Pacific Theater of World War II. Uniquely among the National Park System, it honors the bravery and sacrifices of all those who participated in the Pacific Theater.

Agana Heights is one of the nineteen villages in the United States territory of Guam. It is located in the hills south of Hagåtña, in the central part of the island. United States Naval Hospital Guam is located in this largely residential village.
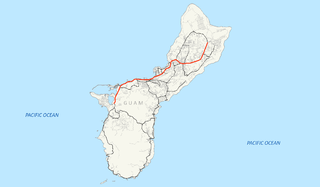
Guam Highway 1 (GH-1), also known as Marine Corps Drive, is one of the primary automobile routes in the United States territory of Guam. It runs in a southwest-to-northeast direction, from the main gate of Naval Base Guam in the southwestern village of Santa Rita in a northeasterly direction to the main gate of Andersen Air Force Base in the village of Yigo. It passes through Guam's capital, Hagåtña, as well as intersecting other territorial highways. The highway runs through tropical forest, urbanized commercial areas, and residential neighborhoods. The US military upgraded and extended the road starting in 1941. Construction ceased with the Japanese invasion in December 1941 and resumed after the Second Battle of Guam in 1944. The highway was formally dedicated to the U.S. Marine Corps by the governor in 2004.

The Battle of Guam was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II, and took place from 8 December to 10 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between Japan and the United States. The American garrison was defeated by Japanese forces on 10 December, which resulted in an occupation until the Second Battle of Guam in 1944.

The Asan River is a river in the United States territory of Guam that lies entirely within the village of Asan-Maina. It originates in the highlands of Nimitz Hill Annex and flows through the Asan Inland Unit of War in the Pacific National Historical Park (WAPA) and enters the community of Asan. It then briefly re-enters WAPA at its Asan Inland Unit, with the mouth at the eastern end of Asan Memorial Park into Asan Bay. The river was thus a significant geographical feature of the Asan Invasion Beach for U.S. forces during the initial landings on Guam in July 1944.
Guam Highway 6 (GH-6) is one of the primary automobile highways in the United States territory of Guam. It is known as Spruance Drive within Piti and Halsey Drive within Asan-Maina: both named for noteworthy US Navy Admirals that served in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II: Raymond A. Spruance and William Halsey Jr., respectively.

Joint Region Marianas' mission is to provide installation management support to all Department of Defense components and tenants through assigned regional installations on Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands in support of training in the Marianas; to act as the interface between the Department of Defense and the civilian community; to ensure compliance with all environmental laws and regulations, safety procedures, and equal opportunity policy; and perform other functions and tasks as may be assigned.

The Fonte River Dam is a historic dam on the Fonte River on the island of Guam. It is located in the upper third of the river's main valley, which is located between Nimitz Hill Annex and Agana Heights, and lies below and west of the Libugon scenic overlook on Nimitz Hill. The dam, built in 1910, was part of the first organized effort by the United States Navy to provide a reliable water supply to the island's major settlement, Hagåtña. It is a concrete structure 150 feet (46 m) long, 24 feet (7.3 m) high, and has a 17 feet (5.2 m) base. It is almost complete obscured by jungle overgrowth.

Typhoon Alice was a typhoon that brought severe flooding to Guam during the latter part of the 1953 Pacific typhoon season. The system was first tracked near the Marshall Islands on October 11 by the Fleet Weather Central (FWC) as a tropical storm, and the Central Meteorological Observatory (CMO) as a tropical depression. The CMO upgraded Alice to a tropical storm east of Guam on October 14. One day later, and the FWC reported that the storm had intensified to 65 knots, equivalent to a Category 1 typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Near Iwo Jima, the typhoon traveled northeastwards, reaching its peak of 100 kn late on October 18. Alice then steadily weakened down to a tropical storm on October 20. The storm became extratropical on October 23 near the International Date Line, and both agencies ceased tracking the cyclone.
Nimitz Hill may refer to:
Nimitz Hill is a community and census-designated place (CDP) in Piti, Guam. is located immediately west of the Nimitz Hill Annex CDP in Asan-Maina, which contains the geographic feature of Nimitz Hill. In normal conversation, the Nimitz Hill CDP and Nimitz Hill Annex CDP are often collectively referred to as "Nimitz Hill."

Adelup Point is limestone promontory in Hagåtña, Guam that extends into the Philippine Sea and separates Asan Bay from Hagåtña Bay. It has been the site of the Ricardo J. Bordallo Governor's Complex since 1990. Adelup is therefore a metonym for the Office of the Governor of Guam.

Asan is a community and census-designated place (CDP) along the western coast of the U.S. territory of Guam. Asan, along with Maina and Nimitz Hill Annex, are the three communities in the village of Asan-Maina. It is known for being the location of northern invasion beach used by the United States during the retaking of Guam in 1944.

Radio Barrigada, formally Communications Site Barrigada and previously Communications Annex Barrigada, refers to two adjacent U.S. military transmitter facilities located in the villages of Barrigada and Mangilao on the western Pacific territory of Guam. The larger facility is Naval Computer and Telecommunications Site (NCTS) Barrigada, operated by Naval Base Guam, located entirely within Barrigada. To its south, the Barrigada Transmitter Site, operated by Andersen Air Force Base, lies partially within Mangilao. The installation itself is managed by Joint Region Marianas. Radio Barrigada is the counterpart to the telecommunications receiving site Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station Guam, located to the north in Finegayan, Dededo. Located near the high point of Mount Barrigada, Radio Barrigada comprises 1,800 acres (7.3 km2).
Nimitz Hill is a hill in Asan-Maina, Guam. It lies within the Nimitz Hill Annex CDP. The US Navy headquarters for Guam lie near the crest of the hill. The hill is named after American admiral Chester W. Nimitz who was Commander in Chief of the Pacific Ocean Areas during World War 2 with his headquarters in Guam.