Related Research Articles

Niobium, also known as columbium, is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. Niobium is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a hardness similar to that of pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in the earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology, specifically Niobe, who was the daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, making them difficult to distinguish.

Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, it is named after Tantalus, a villain from Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as minor components in alloys. The chemical inertness of tantalum makes it a valuable substance for laboratory equipment, and as a substitute for platinum. Its main use today is in tantalum capacitors in electronic equipment such as mobile phones, DVD players, video game systems and computers. Tantalum, always together with the chemically similar niobium, occurs in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan. Tantalum is considered a technology-critical element.

Group 5 is a group of elements in the periodic table. Group 5 contains vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and dubnium (Db). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.

Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation.

Lithium niobate (LiNbO3) is a compound of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, piezoelectric sensors, optical modulators and various other linear and non-linear optical applications. It is a human-made dielectric material that does not exist in nature. Lithium niobate is sometimes referred to by the brand name linobate.

Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta
2O
5. It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. Ta
2O
5 is an inert material with a high refractive index and low absorption, which makes it useful for coatings. It is also extensively used in the production of capacitors, due to its high dielectric constant.

Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2O5. It is a colourless insoluble solid that is fairly unreactive. It is the main precursor to all materials made of niobium, the dominant application being alloys, but other specialized applications include capacitors, lithium niobate, and optical glasses.

Niobium monoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula NbO. It is a grey solid with metallic conductivity.

Niobium dioxide, is the chemical compound with the formula NbO2. It is a bluish black non-stoichiometric solid with a composition range of NbO1.94-NbO2.09 It can be prepared by reacting Nb2O5 with H2 at 800–1350 °C. An alternative method is reaction of Nb2O5 with Nb powder at 1100 °C.

Niobium(IV) chloride, also known as niobium tetrachloride, is the chemical compound of formula NbCl4. This compound exists as dark violet crystals, is highly sensitive to air and moisture, and disproportiates into niobium(III) chloride and niobium(V) chloride when heated.
Niobia may refer to:

Superconducting wires are wires made of superconductors. When cooled below their transition temperatures, they have zero electrical resistance. Most commonly, conventional superconductors such as niobium-titanium are used, but high-temperature superconductors such as YBCO are entering the market. Superconducting wire's advantages over copper or aluminum include higher maximum current densities and zero power dissipation. Its disadvantages include the cost of refrigeration of the wires to superconducting temperatures, the danger of the wire quenching, the inferior mechanical properties of some superconductors, and the cost of wire materials and construction. Its main application is in superconducting magnets, which are used in scientific and medical equipment where high magnetic fields are necessary.
Changbaiite (PbNb2O6) is a member of the oxide mineral class in which the mineral contains oxygen which is grouped along with one or two metal ion. Changbaiite is classified as a multiple Oxide XY2O6 and it generally has an ionic bond. Furthermore, it is also orthorhombic at a temperature of 25 °C and it changes to orthorhombic-tetragonal at 570 °C.
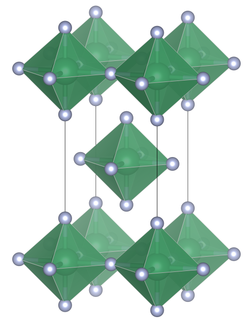
Niobium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula NbF4; it is a nonvolatile black solid. It absorbs vapor strongly. It turns into NbO2F in moist air. NbF4 reacts with water to form a brown solution and a brown precipitate whose components are unknown. It is stable between 275 °C and 325 °C when heated in a vacuum. However, it disproportionates at 350 °C rapidly to form niobium(V) fluoride and niobium(III) fluoride:

Niobium oxychloride is the inorganic compound with the formula NbOCl3. It is a white, crystalline, diamagnetic solid. It is often found as an impurity in samples of niobium pentachloride, a common reagent in niobium chemistry.

Niobium(V) ethoxide is an metalorganic compound with formula Nb2(OC2H5)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is mainly used for the sol-gel processing of materials containing niobium oxides.
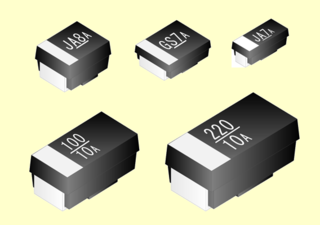
A niobium electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode electrode (+) is made of passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide on which an insulating niobium pentoxide layer acts as the dielectric of the niobium capacitor. A solid electrolyte on the surface of the oxide layer serves as the second electrode (cathode) (-) of the capacitor.

Niobium diselenide or niobium(IV) selenide is a layered transition metal dichalcogenide with formula NbSe2. Niobium diselenide is a lubricant, and a superconductor at temperatures below 7.2 K that exhibit a charge density wave (CDW). NbSe2 crystallizes in several related forms, and can be mechanically exfoliated into monatomic layers, similar to other transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Monolayer NbSe2 exhibits very different properties from the bulk material, such as of Ising superconductivity, quantum metallic state, and strong enhancement of the CDW.
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-carbon (Nb-C) bonds. Compared to the other group 5 transition metal organometallics, the chemistry of organoniobium compounds most closely resembles that of organotantalum compounds. Organoniobium compounds of oxidation states +5, +4, +3, +2, +1, 0, -1, and -3 have been prepared, with the +5 oxidation state being the most common.

Niobium diboride (NbB2) is a highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure. NbB2 is an ultra high temperature ceramic (UHTC) with a melting point of 3050 °C. This along with its relatively low density of ~6.97 g/cm3 and good high temperature strength makes it a candidate for high temperature aerospace applications such as hypersonic flight or rocket propulsion systems. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical conductivities (Electrical resistivity of 25.7 µΩ⋅cm, CTE of 7.7⋅10−6 °C−1), properties it shares with isostructural titanium diboride, zirconium diboride, hafnium diboride and tantalum diboride.
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |