Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish.

Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, it is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as components of strong high-melting-point alloys. It is a group 5 element, along with vanadium and niobium, and it always occurs in geologic sources together with the chemically similar niobium, mainly in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan.
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.

Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula SO. It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. These compounds are produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green.

Niobium(V) chloride, also known as niobium pentachloride, is a yellow crystalline solid. It hydrolyzes in air, and samples are often contaminated with small amounts of NbOCl3. It is often used as a precursor to other compounds of niobium. NbCl5 may be purified by sublimation.

Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta
2O
5. It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. Ta
2O
5 is an inert material with a high refractive index and low absorption, which makes it useful for coatings. It is also extensively used in the production of capacitors, due to its high dielectric constant.

Metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand.

The dioxygenyl ion, O+
2, is a rarely-encountered oxycation in which both oxygen atoms have a formal oxidation state of +1/2. It is formally derived from oxygen by the removal of an electron:

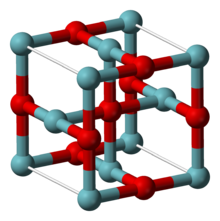
Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2O5. A colorless, insoluble, and fairly unreactive solid, it is the most widespread precursor for other compounds and materials containing niobium. It is predominantly used in alloying, with other specialized applications in capacitors, optical glasses, and the production of lithium niobate.

Silicon monoxide is the chemical compound with the formula SiO where silicon is present in the oxidation state +2. In the vapour phase, it is a diatomic molecule. It has been detected in stellar objects and has been described as the most common oxide of silicon in the universe.

Niobium dioxide, is the chemical compound with the formula NbO2. It is a bluish-black non-stoichiometric solid with a composition range of NbO1.94-NbO2.09. It can be prepared by reducing Nb2O5 with H2 at 800–1350 °C. An alternative method is reaction of Nb2O5 with Nb powder at 1100 °C.

Niobium(IV) chloride, also known as niobium tetrachloride, is the chemical compound of formula NbCl4. This compound exists as dark violet crystals, is highly sensitive to air and moisture, and disproportiates into niobium(III) chloride and niobium(V) chloride when heated.
Boron monofluoride or fluoroborylene is a chemical compound with formula BF, one atom of boron and one of fluorine. It was discovered as an unstable gas and only in 2009 found to be a stable ligand combining with transition metals, in the same way as carbon monoxide. It is a subhalide, containing fewer than the normal number of fluorine atoms, compared with boron trifluoride. It can also be called a borylene, as it contains boron with two unshared electrons. BF is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and dinitrogen; each molecule has 14 electrons.
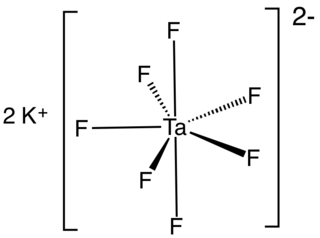
Potassium heptafluorotantalate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2[TaF7]. It is the potassium salt of the heptafluorotantalate anion [TaF7]2−. This white, water-soluble solid is an intermediate in the purification of tantalum from its ores and is the precursor to the metal.

Niobium(V) ethoxide is an metalorganic compound with formula Nb2(OC2H5)10. It is a colorless liquid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is mainly used for the sol-gel processing of materials containing niobium oxides.
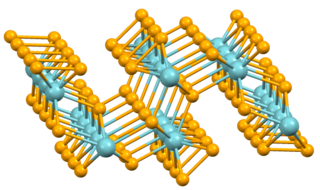
Niobium triselenide is an inorganic compound belonging to the class of transition metal trichalcogenides. It has the formula NbSe3. It was the first reported example of one-dimensional compound to exhibit the phenomenon of sliding charge density waves. Due to its many studies and exhibited phenomena in quantum mechanics, niobium triselenide has become the model system for quasi-1-D charge density waves.
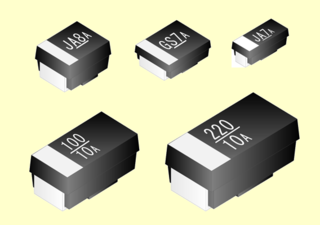
A niobium electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor whose anode (+) is made of passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide, on which an insulating niobium pentoxide layer acts as a dielectric. A solid electrolyte on the surface of the oxide layer serves as the capacitor's cathode (−).

Niobium diselenide or niobium(IV) selenide is a layered transition metal dichalcogenide with formula NbSe2. Niobium diselenide is a lubricant, and a superconductor at temperatures below 7.2 K that exhibit a charge density wave (CDW). NbSe2 crystallizes in several related forms, and can be mechanically exfoliated into monatomic layers, similar to other transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Monolayer NbSe2 exhibits very different properties from the bulk material, such as of Ising superconductivity, quantum metallic state, and strong enhancement of the CDW.
Niobium(III) chloride also known as niobium trichloride is a compound of niobium and chlorine. The binary phase NbCl3 is not well characterized but many adducts are known.