Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium and was thus named after the United States by analogy.
Berkelium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Curium is a transuranic, radioactive chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first intentionally made by the team of Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso in 1944, using the cyclotron at Berkeley. They bombarded the newly discovered element plutonium with alpha particles. This was then sent to the Metallurgical Laboratory at University of Chicago where a tiny sample of curium was eventually separated and identified. The discovery was kept secret until after the end of World War II. The news was released to the public in November 1947. Most curium is produced by bombarding uranium or plutonium with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains ~20 grams of curium.

Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, poisonous, pyrophoric, and capable of accumulating in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.

Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula HgO. It has a red or orange color. Mercury(II) oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The mineral form montroydite is very rarely found.

Lanthanum(III) oxide, also known as lanthana, chemical formula La2O3, is an inorganic compound containing the rare earth element lanthanum and oxygen. It is used in some ferroelectric materials, as a component of optical materials, and is a feedstock for certain catalysts, among other uses.

Curium(III) oxide is a compound composed of curium and oxygen with the chemical formula Cm2O3. It is a crystalline solid with a unit cell that contains two curium atoms and three oxygen atoms. The simplest synthesis equation involves the reaction of curium(III) metal with O2−: 2 Cm3+ + 3 O2− ---> Cm2O3. Curium trioxide can exist as five polymorphic forms. Two of the forms exist at extremely high temperatures, making it difficult for experimental studies to be done on the formation of their structures. The three other possible forms which curium sesquioxide can take are the body-centered cubic form, the monoclinic form, and the hexagonal form. Curium(III) oxide is either white or light tan in color and, while insoluble in water, is soluble in inorganic and mineral acids. Its synthesis was first recognized in 1955.

Uranium trioxide (UO3), also called uranyl oxide, uranium(VI) oxide, and uranic oxide, is the hexavalent oxide of uranium. The solid may be obtained by heating uranyl nitrate to 400 °C. Its most commonly encountered polymorph, γ-UO3, is a yellow-orange powder.

A uranate is a ternary oxide involving the element uranium in one of the oxidation states 4, 5 or 6. A typical chemical formula is MxUyOz, where M represents a cation. The uranium atom in uranates(VI) has two short collinear U–O bonds and either four or six more next nearest oxygen atoms. The structures are infinite lattice structures with the uranium atoms linked by bridging oxygen atoms.

Titanium hydride normally refers to the inorganic compound TiH2 and related nonstoichiometric materials. It is commercially available as a stable grey/black powder, which is used as an additive in the production of Alnico sintered magnets, in the sintering of powdered metals, the production of metal foam, the production of powdered titanium metal and in pyrotechnics.

Americium(III) chloride or americium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of americium and chlorine with the formula AmCl3. This salt forms pink hexagonal crystals. In the solid state each americium atom has nine chlorine atoms as near neighbours, at approximately the same distance, in a tricapped trigonal prismatic configuration.

Neodymium(III) oxide or neodymium sesquioxide is the chemical compound composed of neodymium and oxygen with the formula Nd2O3. It forms very light grayish-blue hexagonal crystals. The rare-earth mixture didymium, previously believed to be an element, partially consists of neodymium(III) oxide.

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.
Curium compounds are compounds containing the element curium (Cm). Curium usually forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state, although compounds with curium in the +4, +5 and +6 oxidation states are also known.
Einsteinium compounds are compounds that contain the element einsteinium (Es). These compounds largely have einsteinium in the +3 oxidation state, or in some cases in the +2 and +4 oxidation states. Although einsteinium is relatively stable, with half-lives ranging from 20 days upwards, these compounds have not been studied in great detail.

Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.
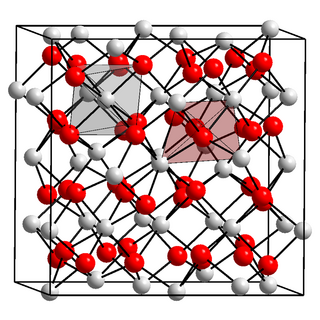
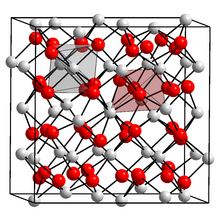
Berkelium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and oxygen with the chemical formula Bk
2O
3.