
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HNO3. It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO3, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%.

An oxide is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 that protects the foil from further oxidation.
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.

Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturally as the mineral magnetite. As the mineral known as hematite, Fe2O3 is the main source of iron for the steel industry. Fe2O3 is readily attacked by acids. Iron(III) oxide is often called rust, since rust shares several properties and has a similar composition; however, in chemistry, rust is considered an ill-defined material, described as hydrous ferric oxide.

Basic copper carbonate is a chemical compound, more properly called copper(II) carbonate hydroxide. It is an ionic compound consisting of the ions copper(II) Cu2+
, carbonate CO2−
3, and hydroxide OH−
.

Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O. It is one of the principal oxides of copper, the other being copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide (CuO). Cuprous oxide is a red-coloured solid and is a component of some antifouling paints. The compound can appear either yellow or red, depending on the size of the particles. Copper(I) oxide is found as the reddish mineral cuprite.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO2−
4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr
2O2−
7. They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.
Cuprates are a class of compounds that contain copper (Cu) atom(s) in an anion. They can be broadly categorized into two main types:

Barium nitrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba(NO3)2. It, like most barium salts, is colorless, toxic, and water-soluble. It burns with a green flame and is an oxidizer; the compound is commonly used in pyrotechnics.
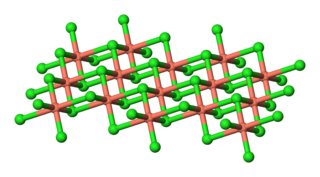
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.
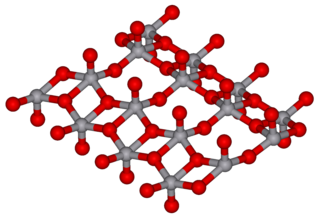
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

Copper(II) hydroxide is the hydroxide of copper with the chemical formula of Cu(OH)2. It is a pale greenish blue or bluish green solid. Some forms of copper(II) hydroxide are sold as "stabilized" copper(II) hydroxide, although they likely consist of a mixture of copper(II) carbonate and hydroxide. Cupric hydroxide is a strong base, although its low solubility in water makes this hard to observe directly.
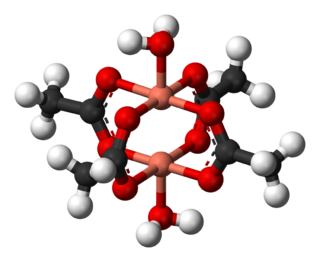
Copper(II) acetate, also referred to as cupric acetate, is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(OAc)2 where AcO− is acetate (CH
3CO−
2). The hydrated derivative, Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2, which contains one molecule of water for each copper atom, is available commercially. Anhydrous copper(II) acetate is a dark green crystalline solid, whereas Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2 is more bluish-green. Since ancient times, copper acetates of some form have been used as fungicides and green pigments. Today, copper acetates are used as reagents for the synthesis of various inorganic and organic compounds. Copper acetate, like all copper compounds, emits a blue-green glow in a flame.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry is a systematic method of naming inorganic chemical compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. Ideally, every inorganic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous formula can be determined. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry.
In ore deposit geology, supergene processes or enrichment are those that occur relatively near the surface as opposed to deep hypogene processes. Supergene processes include the predominance of meteoric water circulation (i.e. water derived from precipitation) with concomitant oxidation and chemical weathering. The descending meteoric waters oxidize the primary (hypogene) sulfide ore minerals and redistribute the metallic ore elements. Supergene enrichment occurs at the base of the oxidized portion of an ore deposit. Metals that have been leached from the oxidized ore are carried downward by percolating groundwater, and react with hypogene sulfides at the supergene-hypogene boundary. The reaction produces secondary sulfides with metal contents higher than those of the primary ore. This is particularly noted in copper ore deposits where the copper sulfide minerals chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu18S10), and djurleite (Cu31S16) are deposited by the descending surface waters.

Copper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2. They can be regarded as the cupric salts of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate and a trihydrate are blue solids.
Dicopper chloride trihydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cu2(OH)3Cl. It is often referred to as tribasic copper chloride (TBCC), copper trihydroxyl chloride or copper hydroxychloride. It is a greenish crystalline solid encountered in mineral deposits, metal corrosion products, industrial products, art and archeological objects, and some living systems. It was originally manufactured on an industrial scale as a precipitated material used as either a chemical intermediate or a fungicide. Since 1994, a purified, crystallized product has been produced at the scale of thousands of tons per year, and used extensively as a nutritional supplement for animals.

Compounds of lead exist with lead in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.

A transition metal nitrate complex is a coordination compound containing one or more nitrate ligands. Such complexes are common starting reagents for the preparation of other compounds.





















