
Gabbro is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is chemically equivalent to rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt. Much of the Earth's oceanic crust is made of gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridges. Gabbro is also found as plutons associated with continental volcanism. Due to its variant nature, the term gabbro may be applied loosely to a wide range of intrusive rocks, many of which are merely "gabbroic". By rough analogy, gabbro is to basalt as granite is to rhyolite.

Bytownite is a calcium rich member of the plagioclase solid solution series of feldspar minerals with composition between anorthite and labradorite. It is usually defined as having between 70 and 90%An. Like others of the series, bytownite forms grey to white triclinic crystals commonly exhibiting the typical plagioclase twinning and associated fine striations.

Dunite, also known as olivinite, is an intrusive igneous rock of ultramafic composition and with phaneritic (coarse-grained) texture. The mineral assemblage is greater than 90% olivine, with minor amounts of other minerals such as pyroxene, chromite, magnetite, and pyrope. Dunite is the olivine-rich endmember of the peridotite group of mantle-derived rocks.

Anorthosite is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic minerals most commonly present.

Nepheline syenite is a holocrystalline plutonic rock that consists largely of nepheline and alkali feldspar. The rocks are mostly pale colored, grey or pink, and in general appearance they are not unlike granites, but dark green varieties are also known. Phonolite is the fine-grained extrusive equivalent.

Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can substitute for iron in variable amounts as it forms a solid solution with magnesiochromite (MgCr2O4). A substitution of the element aluminium can also occur, leading to hercynite (FeAl2O4). Chromite today is mined particularly to make stainless steel through the production of ferrochrome (FeCr), which is an iron-chromium alloy.

Peridotite ( PERR-ih-doh-tyte, pə-RID-ə-) is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock consisting mostly of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene. Peridotite is ultramafic, as the rock contains less than 45% silica. It is high in magnesium (Mg2+), reflecting the high proportions of magnesium-rich olivine, with appreciable iron. Peridotite is derived from Earth's mantle, either as solid blocks and fragments, or as crystals accumulated from magmas that formed in the mantle. The compositions of peridotites from these layered igneous complexes vary widely, reflecting the relative proportions of pyroxenes, chromite, plagioclase, and amphibole.

In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a concordant intrusive sheet, meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existing bedding planes, concordant fracture zone, or foliations.

Pyroxenite is an ultramafic igneous rock consisting essentially of minerals of the pyroxene group, such as augite, diopside, hypersthene, bronzite or enstatite. Pyroxenites are classified into clinopyroxenites, orthopyroxenites, and the websterites which contain both types of pyroxenes. Closely allied to this group are the hornblendites, consisting essentially of hornblende and other amphiboles.

Charnockite is any orthopyroxene-bearing quartz-feldspar rock formed at high temperature and pressure, commonly found in granulite facies’ metamorphic regions, sensu stricto as an endmember of the charnockite series.
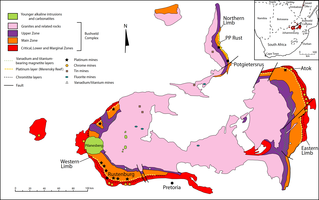
The Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) is the largest layered igneous intrusion within the Earth's crust. It has been tilted and eroded forming the outcrops around what appears to be the edge of a great geological basin: the Transvaal Basin. It is approximately 2 billion years old and is divided into four different limbs: the northern, southern, eastern, and western limbs. The Bushveld Complex comprises the Rustenburg Layered suite, the Lebowa Granites and the Rooiberg Felsics, that are overlain by the Karoo sediments. The site was first publicised around 1897 by Gustaaf Molengraaff who found the native South African tribes residing in and around the area.

A layered intrusion is a large sill-like body of igneous rock which exhibits vertical layering or differences in composition and texture. These intrusions can be many kilometres in area covering from around 100 km2 (39 sq mi) to over 50,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi) and several hundred metres to over one kilometre (3,300 ft) in thickness. While most layered intrusions are Archean to Proterozoic in age, they may be any age such as the Cenozoic Skaergaard intrusion of east Greenland or the Rum layered intrusion in Scotland. Although most are ultramafic to mafic in composition, the Ilimaussaq intrusive complex of Greenland is an alkalic intrusion.

Cumulate rocks are igneous rocks formed by the accumulation of crystals from a magma either by settling or floating. Cumulate rocks are named according to their texture; cumulate texture is diagnostic of the conditions of formation of this group of igneous rocks. Cumulates can be deposited on top of other older cumulates of different composition and colour, typically giving the cumulate rock a layered or banded appearance.

Troctolite is a mafic intrusive rock type. It consists essentially of major but variable amounts of olivine and calcic plagioclase along with minor pyroxene. It is an olivine-rich anorthosite, or a pyroxene-depleted relative of gabbro. However, unlike gabbro, no troctolite corresponds in composition to a partial melt of peridotite. Thus, troctolite is necessarily a cumulate of crystals that have fractionated from melt.

Harzburgite, an ultramafic, igneous rock, is a variety of peridotite consisting mostly of the two minerals olivine and low-calcium (Ca) pyroxene (enstatite); it is named for occurrences in the Harz Mountains of Germany. It commonly contains a few percent chromium-rich spinel as an accessory mineral. Garnet-bearing harzburgite is much less common, found most commonly as xenoliths in kimberlite.

A lopolith is a large igneous intrusion which is lenticular in shape with a depressed central region. Lopoliths are generally concordant with the intruded strata with dike or funnel-shaped feeder bodies below the body. The term was first defined and used by Frank Fitch Grout during the early 1900s in describing the Duluth gabbro complex in northern Minnesota and adjacent Ontario.

The Merensky Reef is a layer of igneous rock in the Bushveld Igneous Complex (BIC) in the North West, Limpopo, Gauteng and Mpumalanga provinces of South Africa which together with an underlying layer, the Upper Group 2 Reef (UG2), contains most of the world's known reserves of platinum group metals (PGMs) or platinum group elements (PGEs)—platinum, palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium. The Reef is 46 cm thick and bounded by thin chromite seams or stringers. The composition consists predominantly of cumulate rocks, including leuconorite, anorthosite, chromitite, and melanorite.

The Stillwater igneous complex is a large layered mafic intrusion (LMI) located in southern Montana in Stillwater, Sweet Grass and Park Counties. The complex is exposed across 30 miles (48 km) of the north flank of the Beartooth Mountain Range. The complex has extensive reserves of chromium ore and has a history of being mined for chromium. More recent mining activity has produced palladium and other platinum group elements.
The Skaergaard intrusion is a layered igneous intrusion in the Kangerlussuaq area of East Greenland and is composed of various rocks and minerals including gabbro, olivine, apatite, and basalt.



















