
Cat food is food specifically designed for consumption by cats. As obligate carnivores, cats have specific requirements for their dietary nutrients, namely nutrients found only in meat, such as taurine, arginine, and Vitamin B6. Certain nutrients, including many vitamins and amino acids, are degraded by the temperatures, pressures and chemical treatments used during manufacture, and hence must be added after manufacture to avoid nutritional deficiency.
Skin disorders are among the most common health problems in dogs, and have many causes. The condition of a dog's skin and coat is also an important indicator of its general health. Skin disorders of dogs vary from acute, self-limiting problems to chronic or long-lasting problems requiring life-time treatment. Skin disorders may be primary or secondary in nature, making diagnosis complicated.

Equine exertional rhabdomyolysis (ER) is a syndrome that affects the skeletal muscles within a horse. This syndrome causes the muscle to break down which is generally associated with exercise and diet regime. Depending on the severity, there are various types of ER, including sporadic and chronic.

Polioencephalomalacia (PEM), also referred to as cerebrocortical necrosis (CCN), is a neurological disease seen in ruminants that is caused by multiple factors, one of which is thiamine depletion in the body. Thiamine is a key chemical in glucose metabolism that, when deficient, is most threatening to neurological activity. In addition to altered thiamine status, an association with high sulfur intake has been observed as a potential cause of PEM. Other toxic or metabolic diseases can result in PEM as well. Cattle, sheep, goat, and other ruminants that are diagnosed with PEM or pre-PEM suffer opisthotonus, cortical blindness, disoriented movement, and eventually fatality, if left untreated. Current data shows that the onset of PEM can range from birth to late adulthood.

Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, resulting in a fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and leg swelling. Dry beriberi affects the nervous system, resulting in numbness of the hands and feet, confusion, trouble moving the legs, and pain. A form with loss of appetite and constipation may also occur. Another type, acute beriberi, found mostly in babies, presents with loss of appetite, vomiting, lactic acidosis, changes in heart rate, and enlargement of the heart.
Keshan disease is a congestive cardiomyopathy caused by a combination of dietary deficiency of selenium and the presence of a mutated strain of Coxsackievirus, named after Keshan County of Heilongjiang province, Northeast China, where symptoms were first noted. These symptoms were later found prevalent in a wide belt extending from northeast to southwest China, all due to selenium-deficient soil. The disease peaked in 1960–1970, killing thousands of people.
Equine polysaccharide storage myopathy is a hereditary glycogen storage disease of horses that causes exertional rhabdomyolysis. It is currently known to affect the following breeds American Quarter Horses, American Paint Horses, Warmbloods, Cobs, Dales Ponies, Thoroughbreds, Arabians, New Forest ponies, and a large number of Heavy horse breeds. While incurable, PSSM can be managed with appropriate diet and exercise. There are currently 2 subtypes, known as Type 1 PSSM and Type 2 PSSM.
Cat skin disorders are among the most common health problems in cats. Skin disorders in cats have many causes, and many of the common skin disorders that afflict people have a counterpart in cats. The condition of a cat's skin and coat can also be an important indicator of its general health. Skin disorders of cats vary from acute, self-limiting problems to chronic or long-lasting problems requiring life-time treatment. Cat skin disorders may be grouped into categories according to the causes.

Milk fever, postparturient hypocalcemia, or parturient paresis is a disease, primarily in dairy cattle but also seen in beef cattle and non-bovine domesticated animals, characterized by reduced blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia). It occurs following parturition, at onset of lactation, when demand for calcium for colostrum and milk production exceeds the body's ability to mobilize calcium. "Fever" is a misnomer, as body temperature during the disease is generally not elevated. Milk fever is more commonly seen in older animals and in certain breeds.

Equine nutrition is the feeding of horses, ponies, mules, donkeys, and other equines. Correct and balanced nutrition is a critical component of proper horse care.
Enterotoxemia is a condition induced by the absorption of large volumes of toxins produced by bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens from the intestines. There are several strains of C. perfringens that may lead to the development of this gastrointestinal condition.

Kashin–Beck disease (KBD) is a chronic, endemic type of osteochondropathy that is mainly distributed from northeastern to southwestern China, including 15 provinces. As of 2011, Tibet has the highest incidence rate of KBD in China. Southeast Siberia and North Korea are other affected areas. KBD usually involves children ages 5–15. To date, more than a million individuals have had KBD. The symptoms of KBD include joint pain, morning stiffness in the joints, disturbances of flexion and extension in the elbows, enlarged inter-phalangeal joints, and limited motion in many joints of the body. Death of cartilage cells in the growth plate and articular surface is the basic pathologic feature; this can result in growth retardation and secondary osteoarthrosis. Histological diagnosis of KBD is particularly difficult; clinical and radiological examinations have proved to be the best means for identifying KBD. Little is known about the early stages of KBD before the visible appearance of the disease becomes evident in the destruction of the joints.

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, and in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it.
Selenium deficiency occurs when an organism lacks the required levels of selenium, a critical nutrient in many species. Deficiency, although relatively rare in healthy well-nourished individuals, can have significant negative results, affecting the health of the heart and the nervous system; contributing to depression, anxiety, and dementia; and interfering with reproduction and gestation.

Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D deficiency can also be caused by inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D; disorders that limit vitamin D absorption; and disorders that impair the conversion of vitamin D to active metabolites, including certain liver, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone-softening diseases, such as rickets in children. It can also worsen osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults, increasing the risk of bone fractures. Muscle weakness is also a common symptom of vitamin D deficiency, further increasing the risk of fall and bone fractures in adults. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the development of schizophrenia.

Grass tetany is a metabolic disease involving magnesium deficiency, which can occur in such ruminant livestock as beef cattle, dairy cattle and sheep, usually after grazing on pastures of rapidly growing grass, especially in early spring.
Colitis X, equine colitis X or peracute toxemic colitis is a catchall term for various fatal forms of acute or peracute colitis found in horses, but particularly a fulminant colitis where clinical signs include sudden onset of severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, shock, and dehydration. Death is common, with 90–100% mortality, usually in less than 24 hours. The causative factor may be Clostridium difficile, but it also may be caused by other intestinal pathogens. Horses under stress appear to be more susceptible to developing colitis X, and like the condition pseudomembranous colitis in humans, an association with prior antibiotic use also exists. Immediate and aggressive treatment can sometimes save the horse, but even in such cases, 75% mortality is considered a best-case scenario.
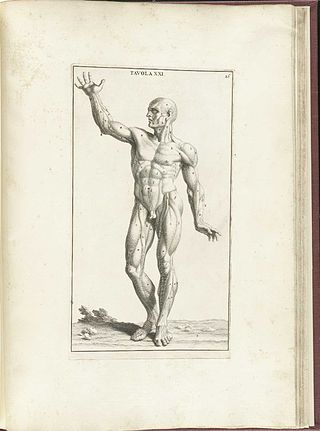
Acquired non-inflammatory myopathy (ANIM) is a neuromuscular disorder primarily affecting skeletal muscle, most commonly in the limbs of humans, resulting in a weakness or dysfunction in the muscle. A myopathy refers to a problem or abnormality with the myofibrils, which compose muscle tissue. In general, non-inflammatory myopathies are a grouping of muscular diseases not induced by an autoimmune-mediated inflammatory pathway. These muscular diseases usually arise from a pathology within the muscle tissue itself rather than the nerves innervating that tissue. ANIM has a wide spectrum of causes which include drugs and toxins, nutritional imbalances, acquired metabolic dysfunctions such as an acquired defect in protein structure, and infections.

As in the human practice of veganism, vegan dog foods are those formulated with the exclusion of ingredients that contain or were processed with any part of an animal, or any animal byproduct. Vegan dog food may incorporate the use of fruits, vegetables, cereals, legumes including soya, nuts, vegetable oils, as well as any other non-animal based foods.

Cobalt is essential to the metabolism of all animals. It is a key constituent of cobalamin, also known as vitamin B12, the primary biological reservoir of cobalt as an ultratrace element. Bacteria in the stomachs of ruminant animals convert cobalt salts into vitamin B12, a compound which can only be produced by bacteria or archaea. A minimal presence of cobalt in soils therefore markedly improves the health of grazing animals, and an uptake of 0.20 mg/kg a day is recommended because they have no other source of vitamin B12.
















