
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.

The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ob, "behind", and caput, "head".

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar are the nuclei located in the thalamus. As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus, usually just called the pulvinar.
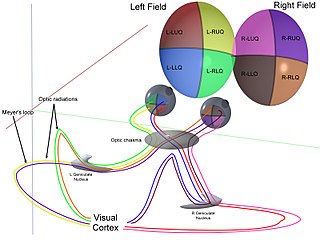
In neuroanatomy, the optic radiation are axons from the neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus to the primary visual cortex. The optic radiation receives blood through deep branches of the middle cerebral artery and posterior cerebral artery.

The fusiform gyrus, also known as the lateral occipitotemporal gyrus,is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia.

In neuroanatomy, the arcuate fasciculus is a bundle of axons that generally connects the Broca's area and the Wernicke's area in the brain. It is an association fiber tract connecting caudal temporal cortex and inferior frontal lobe.

The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.

The angular gyrus is a region of the brain lying mainly in the posteroinferior region of the parietal lobe, occupying the posterior part of the inferior parietal lobule. It represents the Brodmann area 39.

The inferior temporal gyrus is one of three gyri of the temporal lobe and is located below the middle temporal gyrus, connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of objects, places, faces, and colors. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers and words.

The superior parietal lobule is bounded in front by the upper part of the postcentral sulcus, but is usually connected with the postcentral gyrus above the end of the sulcus. The superior parietal lobule contains Brodmann's areas 5 and 7.

The middle cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of the brain. It connects the pons to the cerebellum, with fibres originating from the pontine nucleus and travelling to the opposite hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex. It is supplied by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and branches from the basilar artery. It conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.

The uncinate fasciculus is a white matter association tract in the human brain that connects parts of the limbic system such as the temporal pole, anterior parahippocampus, and amygdala in the temporal lobe with inferior portions of the frontal lobe such as the orbitofrontal cortex. Its function is unknown though it is affected in several psychiatric conditions. It is one of the last white matter tracts to mature in the human brain.

The superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) is an association tract in the brain that is composed of three separate components. It is present in both hemispheres and can be found lateral to the centrum semiovale and connects the frontal, occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes. This bundle of tracts (fasciculus) passes from the frontal lobe through the operculum to the posterior end of the lateral sulcus where they either radiate to and synapse on neurons in the occipital lobe, or turn downward and forward around the putamen and then radiate to and synapse on neurons in anterior portions of the temporal lobe.

The inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) is traditionally considered one of the major occipitotemporal association tracts. It is the white matter backbone of the ventral visual stream. It connects the ventral surface of the anterior temporal lobe and the extrastriate cortex of the occipital lobe, running along the lateral and inferior wall of the lateral ventricle.

In human neuroanatomy, brain asymmetry can refer to at least two quite distinct findings:
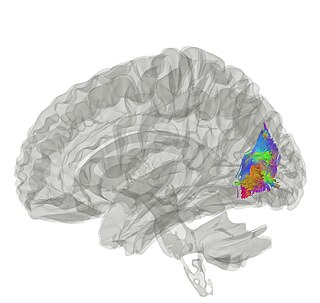
The vertical occipital fasciculus is a fascicle of white matter running vertically in the rear of the brain. It is found at least in primates. It "is the only major fiber bundle connecting dorsolateral and ventrolateral visual cortex."
Heinrich Sachs was a late 19th and early 20th century German neurologist and neuroanatomist best known for his atlas of the brain's white matter.

The occipital gyri (OcG) are three gyri in parallel, along the lateral portion of the occipital lobe, also referred to as a composite structure in the brain. The gyri are the superior occipital gyrus, the middle occipital gyrus, and the inferior occipital gyrus, and these are also known as the occipital face area. The superior and inferior occipital sulci separates the three occipital gyri.

















