Related Research Articles

Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.

A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, from Latin sudor 'sweat', are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species:

Sweet's syndrome (SS), or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a skin disease characterized by the sudden onset of fever, an elevated white blood cell count, and tender, red, well-demarcated papules and plaques that show dense infiltrates by neutrophil granulocytes on histologic examination.
Pityriasis alba is a skin condition, a type of dermatitis, commonly seen in children and young adults as dry, fine-scaled, pale patches on the face. It is self-limiting and usually only requires use of moisturizer creams.

Chemotherapy-induced acral erythema is reddening, swelling, numbness and desquamation on palms of the hands and soles of the feet that can occur after chemotherapy in patients with cancer. Hand-foot syndrome is also rarely seen in sickle-cell disease. These skin changes usually are well demarcated. Acral erythema typically disappears within a few weeks after discontinuation of the offending drug.

Hidrocystoma is an adenoma of the sweat glands.

Uremic frost is a colloquial description for crystallized urea deposits that can be found on the skin of those affected by chronic kidney disease. In states of prolonged kidney failure and subsequent uremia, the high level of urea in the bloodstream leads to high levels of urea secreted by eccrine sweat glands as a component of sweat. As water evaporates off of the skin, it results in crystallization of the remaining urea.
Florid cutaneous papillomatosis (FCP), is an obligate paraneoplastic syndrome.
Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH), first described by Lotzbeck in 1859, is a rare benign vascular hamartoma characterized histologically by a proliferation of eccrine and vascular components. EAH exists on a spectrum of cutaneous tumors that include eccrine nevus, mucinous eccrine nevus and EAH. Each diagnostic subtype is characterized by an increase in the number as well as size of mature eccrine glands or ducts, with EAH being distinguished by the added vascular component.
Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis (NEH) usually is a cutaneous complication of chemotherapy, but it can also occur for other reasons. It consists of fever and non specific skin lesions. It is rare, and self-limited.
Cutaneous amoebiasis, refers to a form of amoebiasis that presents primarily in the skin. It can be caused by Acanthamoeba or Entamoeba histolytica. When associated with Acanthamoeba, it is also known as "cutaneous acanthamoebiasis". Balamuthia mandrillaris can also cause cutaneous amoebiasis, but can prove fatal if the amoeba enters the bloodstream

Syringocystadenoma papilliferum is a benign apocrine tumor.

A sebaceous adenoma, a type of adenoma, a cutaneous condition characterized by a slow-growing tumor usually presenting as a pink, flesh-coloured, or yellow papule or nodule.

Eccrine carcinoma is a rare skin condition characterized by a plaque or nodule on the scalp, trunk, or extremities. It originates from the eccrine sweat glands of the skin, accounting for less than 0.01% of diagnosed cutaneous malignancies. Eccrine carcinoma tumors are locally aggressive with a high rate of recurrence. Lack of reliable immunohistochemical markers and similarity to other common tumors has made identification of eccrine carcinoma difficult.
Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a tumor that usually presents on the chest, scalp, or vulva of middle- to older-aged persons.
Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus is a skin lesion that resembles a comedonal nevus, but it occurs on the palms and soles where pilosebaceous follicles are normally absent. It is probably transmitted by paradominant transmission.
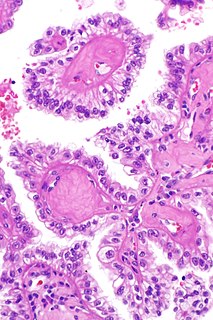
Reed’s syndrome is a rare inherited condition characterised by multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and, in women, uterine leiomyomas. It predisposes for renal cell cancer, an association denominated hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer, and it is also associated with increased risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fumarate hydratase gene, which leads to an accumulation of fumarate. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Laxmisha C, Thappa DM, Jayanthi S (2004). "Papillary eccrine adenoma". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 70 (6): 370–2. PMID 17642667.
- ↑ Blasini W, Hu S, Gugic D, Vincek V (2007). "Papillary eccrine adenoma in association with cutaneous horn". Am J Clin Dermatol. 8 (3): 179–82. doi:10.2165/00128071-200708030-00005. PMID 17492846.
- ↑ Guccion JG, Patterson RH, Nayar R, Saini NB (1998). "Papillary eccrine adenoma: an ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study". Ultrastruct Pathol. 22 (3): 263–9. doi:10.3109/01913129809033478. PMID 9793207.