| Trichodiscoma | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Oncology, dermatology |
A trichodiscoma is a cutaneous condition, a benign, usually skin-colored tumor most often affecting the face and upper trunk. [1] :674 [2]
| Trichodiscoma | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Oncology, dermatology |
A trichodiscoma is a cutaneous condition, a benign, usually skin-colored tumor most often affecting the face and upper trunk. [1] :674 [2]

Kindler syndrome is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.

Pili torti is characterized by short and brittle hairs that appear flattened and twisted when viewed through a microscope.
Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa is a distinctive skin condition of generalized hyperkeratosis and polycyclic and serpiginous erythematous plaques with a characteristic, migratory, double-edged scale at the margins, and is the typical cutaneous manifestation of Netherton's syndrome.
Keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome presents at birth/infancy and is characterized by progressive corneal opacification, either mild generalized hyperkeratosis or discrete erythematous plaques, and neurosensory deafness.
Alezzandrini syndrome is a very rare syndrome characterized by a unilateral degenerative retinitis, followed after several months by ipsilateral vitiligo on the face and ipsilateral poliosis. Deafness may also be present.
Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition with punctate symmetric palmoplantar keratoderma, with the keratoderma and fragility of the nails beginning around age 12. In addition to palmoplantar keratoderma, other symptoms include hypodontia, hypotrichosis, nail dystrophies, and eyelid cysts. Patients may also develop syringofibroadenoma and squamous cell carcinomas.
Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome type 2 is a genetic disorder consisting of fine and sparse scalp hair, thin nails, pear-shaped broad nose, and cone-shaped epiphyses of the middle phalanges of some fingers and toes.
Epidermal nevus syndrome is a rare disease that was first described in 1968 and consists of extensive epidermal nevi with abnormalities of the central nervous system (CNS), skeleton, skin, cardiovascular system, genitourinary system and eyes. However, since the syndrome's first description, a broader concept for the "epidermal nevus" syndrome has been proposed, with at least six types being described:
Gougerot–Blum syndrome is a variant of pigmented purpuric dermatitis, a skin condition characterized by minute, rust-colored to violaceous, lichenoid papules that tend to fuse into plaques of various hues. Relative to other variants, it is characterized clinically by a male predominance, pruritus, with a predilection for the legs, and histologically, it features a densely cellular lichenoid infiltrate.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

A sebaceous adenoma, a type of adenoma, a cutaneous condition characterized by a slow-growing tumor usually presenting as a pink, flesh-coloured, or yellow papule or nodule.

Spiradenoma, also spiroma or eccrine spiradenoma, is a cutaneous condition that is typically characterized, clinically, as a solitary, deep-seated dermal nodule of approximately one centimeter, occurring on the ventral surface of the body. Spiradenoma lesions are benign sudoriferous tumors, and have also been described as cystic epitheliomas of the sweat glands.

Pilomatricoma, is a benign skin tumor derived from the hair matrix. These neoplasms are relatively uncommon and typically occur on the scalp, face, and upper extremities. Clinically, pilomatricomas present as a subcutaneous nodule or cyst with unremarkable overlying epidermis that can range in size from 0.5-3.0 cm, but the largest reported case was 24 cm.

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
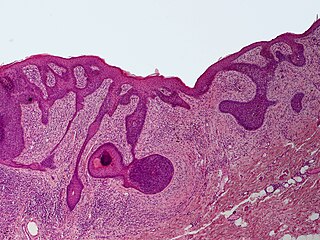
Perifollicular fibroma is a cutaneous condition, a benign tumor usually skin colored, most often affecting the face and upper trunk.
Brooke–Fordyce syndrome is a condition characterized by multiple trichoepitheliomas.
| Classification |
|---|
| This Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, cysts article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |