Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HNO3. It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO3, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

Technetium is a chemical element with the symbol Tc and atomic number 43. It is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive. All available technetium is produced as a synthetic element. Naturally occurring technetium is a spontaneous fission product in uranium ore and thorium ore, the most common source, or the product of neutron capture in molybdenum ores. This silvery gray, crystalline transition metal lies between manganese and rhenium in group 7 of the periodic table, and its chemical properties are intermediate between those of both adjacent elements. The most common naturally occurring isotope is 99Tc, in traces only.

Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers.
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, use of radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments.

Group 7, numbered by IUPAC nomenclature, is a group of elements in the periodic table. They are manganese (Mn), technetium (Tc), rhenium (Re), and bohrium (Bh). All known elements of group 7 are transition metals.

In chemistry, a polyoxometalate is a polyatomic ion, usually an anion, that consists of three or more transition metal oxyanions linked together by shared oxygen atoms to form closed 3-dimensional frameworks. The metal atoms are usually group 6 or less commonly group 5 transition metals and Tc in their high oxidation states. Polyoxometalates are often colorless, orange or red diamagnetic anions. Two broad families are recognized, isopolymetalates, composed of only one kind of metal and oxide, and heteropolymetalates, composed of one metal, oxide, and a main group oxyanion. Many exceptions to these general statements exist.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C. Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.

A technetium-99m generator, or colloquially a technetium cow or moly cow, is a device used to extract the metastable isotope 99mTc of technetium from a decaying sample of molybdenum-99. 99Mo has a half-life of 66 hours and can be easily transported over long distances to hospitals where its decay product technetium-99m is extracted and used for a variety of nuclear medicine diagnostic procedures, where its short half-life is very useful.
Selenic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2SeO4. It is an oxoacid of selenium, and its structure is more accurately described as O2Se(OH)2. It is a colorless compound. Although it has few uses, one of its salts, sodium selenate is used in the production of glass and animal feeds.
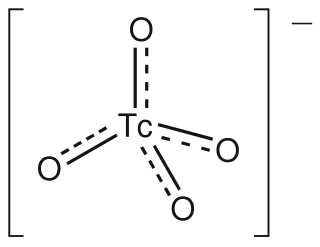
The pertechnetate ion is an oxyanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.

Technetium(VII) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Tc2O7. This yellow volatile solid is a rare example of a molecular binary metal oxide, the other examples being RuO4, OsO4, and the unstable Mn2O7. It adopts a centrosymmetric corner-shared bi-tetrahedral structure in which the terminal and bridging Tc−O bonds are 167pm and 184 pm respectively and the Tc−O−Tc angle is 180°.

Sodium pertechnetate is the inorganic compound with the formula NaTcO4. This colourless salt contains the pertechnetate anion, TcO−
4. The radioactive 99m
Tc
O−
4 anion is an important radiopharmaceutical for diagnostic use. The advantages to 99m
Tc
include its short half-life of 6 hours and the low radiation exposure to the patient, which allow a patient to be injected with activities of more than 30 millicuries. Na[99m
Tc
O
4] is a precursor to a variety of derivatives that are used to image different parts of the body.

Manganese(VII) oxide (manganese heptoxide) is an inorganic compound with the formula Mn2O7. This volatile liquid is highly reactive. It is a dangerous oxidizer and was first described in 1860. It is the acid anhydride of permanganic acid.
Technetium compounds are chemical compounds containing the chemical element technetium. Technetium can form multiple oxidation states, but often forms in the +4 and +7 oxidation states. Because technetium is radioactive, technetium compounds are extremely rare on Earth.
The Hammett acidity function (H0) is a measure of acidity that is used for very concentrated solutions of strong acids, including superacids. It was proposed by the physical organic chemist Louis Plack Hammett and is the best-known acidity function used to extend the measure of Brønsted–Lowry acidity beyond the dilute aqueous solutions for which the pH scale is useful.

Technetium-99m (99mTc) is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99, symbolized as 99mTc, that is used in tens of millions of medical diagnostic procedures annually, making it the most commonly used medical radioisotope in the world.
Organotechnetium chemistry is the science of describing the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organotechnetium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing carbon-to-technetium chemical bonds. The most common organotechnetium compounds are coordination complexes used as radiopharmaceutical imaging agents.

Technetium(IV) oxide, also known as technetium dioxide, is a chemical compound with the formula TcO2 which forms the dihydrate, TcO2·2H2O, which is also known as technetium(IV) hydroxide. It is a radioactive black solid which slowly oxidizes in air.
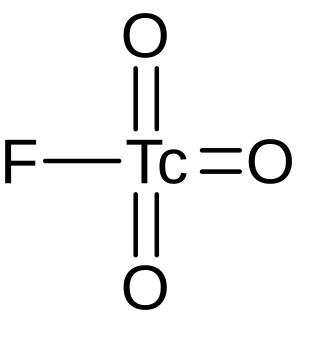
Pertechnetyl fluoride is an inorganic compound, a salt of technetium and hydrofluoric acid with the chemical formula TcO
3F. The compound was originally synthesized by H. Selig and G. Malm in 1963.














