Chemical structures
- Phalloidin
- Prophalloin
- Phalloin
- Phallisin
- Phallacidin
- Phallacin
- Phallisacin
The phallotoxins consist of at least seven compounds, all of which are bicyclic heptapeptides (seven amino acids), isolated from the death cap mushroom (Amanita phalloides). They differ from the closely related amatoxins by being one residue smaller, both in the final product and the precursor protein. [1]
Phalloidin had been isolated in 1937 by Feodor Lynen, Heinrich Wieland's student and son-in-law, and Ulrich Wieland of the University of Munich. [2] [3] The remaining six are prophalloin, phalloin, phallisin, phallacidin, phallacin and phallisacin. Though highly toxic to liver cells, phallotoxins have since been found to have little contribution to the death cap's toxicity because they are not absorbed through the gut. Reports of phalloidin in the edible (and sought after) Blusher (Amanita rubescens) [4] have not been confirmed by later researchers [5]

Amanita phalloides, commonly known as the death cap, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Widely distributed across Europe, but now sprouting in other parts of the world, A. phalloides forms ectomycorrhizas with various broadleaved trees. In some cases, the death cap has been introduced to new regions with the cultivation of non-native species of oak, chestnut, and pine. The large fruiting bodies (mushrooms) appear in summer and autumn; the caps are generally greenish in colour with a white stipe and gills. The cap colour is variable, including white forms, and is thus not a reliable identifier.

The name destroying angel applies to several similar, closely related species of deadly all-white mushrooms in the genus Amanita. They are Amanita bisporigera and A. ocreata in eastern and western North America, and A. virosa in Europe. Another very similar species, A. verna or fool's mushroom, was first described in France.

α-Amanitin (alpha-Amanitin) is a cyclic peptide of eight amino acids. It is possibly the most deadly of all the amatoxins, toxins found in several species of the mushroom genus Amanita, one being the death cap as well as the destroying angel, a complex of similar species, principally A. virosa and A. bisporigera. It is also found in the mushrooms Galerina marginata and Conocybe filaris. The oral LD50 of amanitin is 100 μg/kg for rats.
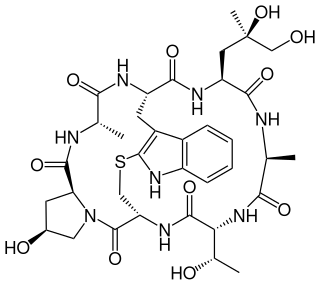
Phalloidin belongs to a class of toxins called phallotoxins, which are found in the death cap mushroom (Amanita phalloides). It is a rigid bicyclic heptapeptide that is lethal after a few days when injected into the bloodstream. The major symptom of phalloidin poisoning is acute hunger due to the destruction of liver cells. It functions by binding and stabilizing filamentous actin (F-actin) and effectively prevents the depolymerization of actin fibers. Due to its tight and selective binding to F-actin, derivatives of phalloidin containing fluorescent tags are used widely in microscopy to visualize F-actin in biomedical research.

Heinrich Otto Wieland was a German chemist. He won the 1927 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research into the bile acids.

Mushroom poisoning is poisoning resulting from the ingestion of mushrooms that contain toxic substances. Its symptoms can vary from slight gastrointestinal discomfort to death in about 10 days. Mushroom toxins are secondary metabolites produced by the fungus.

Feodor Felix Konrad Lynen was a German biochemist. In 1964 he won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine together with Konrad Bloch for their discoveries concerning the mechanism and regulation of cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism while he was director of the Max-Planck Institute for Cellular Chemistry in Munich.

Amanita virosa, commonly known in Europe as the destroying angel or the European destroying angel amanita, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in Europe, A. virosa associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. The large fruiting bodies appear in summer and autumn; the caps, stipes and gills are all white in colour.
Amatoxin is the collective name of a subgroup of at least nine related toxic compounds found in three genera of poisonous mushrooms and one species of the genus Conocybe. From the amanita, the most notably is the death cap. Amatoxins are lethal in even small doses, as little as half a mushroom, including the immature 'egg' form which appears quite different from the fully-grown mushroom.

Amanita verna, commonly known as the fool's mushroom, destroying angel, mushroom fool or the spring destroying angel amanita, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in Europe in spring, A. verna associates with various deciduous and coniferous trees. The caps, stipes and gills are all white in colour.

Galerina marginata, known colloquially as funeral bell, deadly skullcap, autumn skullcap or deadly galerina, is a species of extremely poisonous mushroom-forming fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae of the order Agaricales. It contains the same deadly amatoxins found in the death cap. Ingestion in toxic amounts causes severe liver damage with vomiting, diarrhea, hypothermia, and eventual death if not treated rapidly. About ten poisonings have been attributed to the species now grouped as G. marginata over the last century.

Amanita ocreata, commonly known as the death angel, destroying angel, angel of death or more precisely western North American destroying angel, is a deadly poisonous basidiomycete fungus, one of many in the genus Amanita. Occurring in the Pacific Northwest and California floristic provinces of North America, A. ocreata associates with oak trees. The large fruiting bodies generally appear in spring; the cap may be white or ochre and often develops a brownish centre, while the stipe, ring, gill and volva are all white.

Amanita brunnescens, also known as the brown American star-footed amanita or cleft-footed amanita is a native North American mushroom of the large genus Amanita. Originally presumed to be the highly toxic Amanita phalloides by renowned American mycologist Charles Horton Peck, it was described and named by George F. Atkinson of Cornell University. He named it after the fact that it bruised brown. It differs from the death cap by its fragile volva and tendency to bruise brown. It is considered probably poisonous.

Antamanide is a cyclic decapeptide isolated from a fungus, the death cap: Amanita phalloides. It is being studied as a potential anti-toxin against the effects of phalloidin and for its potential for treating edema. It contains 1 valine residue, 4 proline residues, 1 alanine residue, and 4 phenylalanine residues with a structure of c(Val-Pro-Pro-Ala-Phe-Phe-Pro-Pro-Phe-Phe). It was isolated by determining the source of the anti-phalloidin activity from a lipophillic extraction from the organism. It has been shown that antamanide can react to form alkali metal ion complexes. These include complexes with sodium and calcium ions. When these complexes are formed, the cyclopeptide structure undergoes a conformational change.

Amanullinic acid is a cyclic nonribosomal peptide. It is an amatoxin, all of which are found in several members of the mushroom genus Amanita. Amanullinic acid is relatively non-toxic( oral LD50 >20 mg/kg in mice).

Amaninamide is a cyclic peptide. It is one of the amatoxins, all of which are found in several members of the mushroom genera Amanita, Lepiota and Galerina. It differs from alpha-amanitin in lacking the hydroxyl group on tryptophan. This alters its UV absorption spectrum but not its toxicity.

Amanita bisporigera is a deadly poisonous species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. It is commonly known as the eastern destroying angel amanita, the eastern North American destroying angel or just as the destroying angel, although the fungus shares this latter name with three other lethal white Amanita species, A. ocreata, A. verna and A. virosa. The fruit bodies are found on the ground in mixed coniferous and deciduous forests of eastern North America south to Mexico, but are rare in western North America; the fungus has also been found in pine plantations in Colombia. The mushroom has a smooth white cap that can reach up to 10 cm (4 in) across, and a stipe, up to 14 cm (5.5 in) long by 1.8 cm (0.7 in) thick, that has a delicate white skirt-like ring near the top. The bulbous stipe base is covered with a membranous sac-like volva. The white gills are free from attachment to the stalk and crowded closely together. As the species name suggests, A. bisporigera typically bears two spores on the basidia, although this characteristic is not as immutable as was once thought.

Amanita exitialis, also known as the Guangzhou destroying angel, is a mushroom of the large genus Amanita. It is distributed in eastern Asia, and probably also in India where it has been misidentified as A. verna. Deadly poisonous, it is a member of section Phalloideae and related to the death cap A. phalloides. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) are white, small to medium-sized with caps up to 7 cm (2.8 in) in diameter, a somewhat friable ring and a firm volva. Unlike most agaric mushrooms which typically have four-spored basidia, the basidia of A. exitialis are almost entirely two-spored. Eight people were fatally poisoned in China after consuming the mushroom in 2000, and another 20 have been fatally poisoned since that incident. Molecular analysis shows that the species has a close phylogenetic relationship with three other toxic white Amanitas: A. subjunquillea var. alba, A. virosa and A. bisporigera.
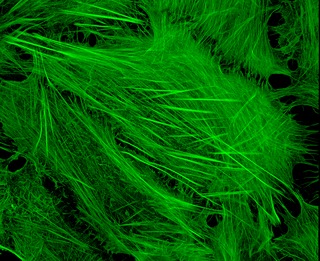
Cytoskeletal drugs are small molecules that interact with actin or tubulin. These drugs can act on the cytoskeletal components within a cell in three main ways. Some cytoskeletal drugs stabilize a component of the cytoskeleton, such as taxol which stabilizes microtubules or Phalloidin which stabilizes actin filaments. Others such as Cytochalasin D bind to actin monomers and prevent them from polymerizing into filaments. Drugs such as demecolcine act by enhancing the depolymerisation of already formed microtubules. Some of these drugs have multiple effects on the cytoskeleton, for example Latrunculin both prevents actin polymerization as well as enhancing its rate of depolymerization. Typically the microtubule targeting drugs can be found in the clinic where they are used therapeutically in the treatment of some forms of cancer. As a result of the lack of specificity for specific type of actin the use of these drugs in animals results in unacceptable off target effects. Despite this the actin targeting compounds are still useful tools that can be used on a cellular level to help further our understanding of how this complex part of the cells internal machinery operates. For example, Phalloidin which has been conjugated with a fluorescent probe can be used for visualizing the filamentous actin in fixed samples.

Amanita sphaerobulbosa, commonly known as the Asian abrupt-bulbed Lepidella, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Amanitaceae. First described by mycologist Tsuguo Hongo in 1969, it is found in Southern Asia. The species was formerly consider synonymous with the North American lookalike Amanita abrupta, but that species has narrower spores, a persistent partial veil, and lacks the refractive contents found in the hyphae and inflated cells of A. sphaerobulbosa.