
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula H2O2. In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used both as a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry.

In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure R−O−O−R, where R is any element. The O−O group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxy group. The nomenclature is somewhat variable, and the term was introduced by Thomas Thomson in 1804 for an oxide with the greatest quantity of oxygen.
In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula O−2. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−). The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O2, which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) is a diradical containing two unpaired electrons, and superoxide results from the addition of an electron which fills one of the two degenerate molecular orbitals, leaving a charged ionic species with a single unpaired electron and a net negative charge of −1. Both dioxygen and the superoxide anion are free radicals that exhibit paramagnetism. Superoxide was historically also known as "hyperoxide".

Titanic acid is a general name for a family of chemical compounds of the elements titanium, hydrogen, and oxygen, with the general formula [TiOx(OH)4−2x]n. Various simple titanic acids have been claimed, mainly in the older literature. No crystallographic and little spectroscopic support exists for these materials. Some older literature refers to TiO2 as titanic acid, and the dioxide forms an unstable hydrate when TiCl4 hydrolyzes.

An oxidizing agent is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent. In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens.

Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, CrO2−
4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, Cr
2O2−
7. They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible.

Calcium peroxide or calcium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaO2. It is the peroxide (O22−) salt of Ca2+. Commercial samples can be yellowish, but the pure compound is white. It is almost insoluble in water.
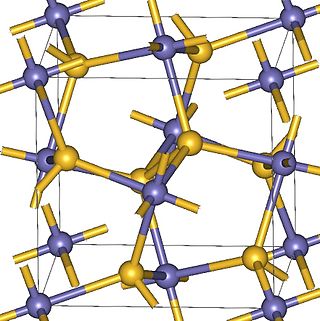
Magnesium peroxide (MgO2) is an odorless fine powder peroxide with a white to off-white color. It is similar to calcium peroxide because magnesium peroxide also releases oxygen by breaking down at a controlled rate with water. Commercially, magnesium peroxide often exists as a compound of magnesium peroxide and magnesium hydroxide.

Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is a common inorganic chemical reagent, most commonly used as an oxidizing agent in various laboratory and industrial applications. As with all hexavalent chromium compounds, it is acutely and chronically harmful to health. It is a crystalline ionic solid with a very bright, red-orange color. The salt is popular in laboratories because it is not deliquescent, in contrast to the more industrially relevant salt sodium dichromate.

Potassium superoxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KO2. It is a yellow paramagnetic solid that decomposes in moist air. It is a rare example of a stable salt of the superoxide anion. It is used as a CO2 scrubber, H2O dehumidifier, and O2 generator in rebreathers, spacecraft, submarines, and spacesuits.

Sodium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2O2. This yellowish solid is the product of sodium ignited in excess oxygen. It is a strong base. This metal peroxide exists in several hydrates and peroxyhydrates including Na2O2·2H2O2·4H2O, Na2O2·2H2O, Na2O2·2H2O2, and Na2O2·8H2O. The octahydrate, which is simple to prepare, is white, in contrast to the anhydrous material.
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written NaH2BO4, Na2H4B2O8, or, more properly, [Na+]2[B2O4(OH)4]2−. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS.
Potassium hypomanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K3MnO4. Also known as potassium manganate(V), this bright blue solid is a rare example of a salt with the hypomanganate or manganate(V) anion, where the manganese atom is in the +5 oxidation state. It is an intermediate in the production of potassium permanganate and the industrially most important Mn(V) compound.

Chromium compounds are compounds containing the element chromium (Cr). Chromium is a member of group 6 of the transition metals. The +3 and +6 states occur most commonly within chromium compounds, followed by +2; charges of +1, +4 and +5 for chromium are rare, but do nevertheless occasionally exist.

In chemistry, a photoinitiator is a molecule that creates reactive species when exposed to radiation. Synthetic photoinitiators are key components in photopolymers.
Dioxygen complexes are coordination compounds that contain O2 as a ligand. The study of these compounds is inspired by oxygen-carrying proteins such as myoglobin, hemoglobin, hemerythrin, and hemocyanin. Several transition metals form complexes with O2, and many of these complexes form reversibly. The binding of O2 is the first step in many important phenomena, such as cellular respiration, corrosion, and industrial chemistry. The first synthetic oxygen complex was demonstrated in 1938 with cobalt(II) complex reversibly bound O2.

Elephant's toothpaste is a foamy substance caused by the rapid decomposition of hydrogen peroxide using potassium iodide (KI) or yeast and warm water as a catalyst. How rapidly the reaction proceeds will depend on the concentration of hydrogen peroxide.

Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide or chromium oxide peroxide or more accurately chromium(VI) oxide diperoxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrO5 or more accurately CrO(O2)2. It is an unstable dark blue compound. This compound contains one oxo ligand and two peroxo ligands, making a total of five oxygen atoms per chromium atom.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.

Metal peroxides are metal-containing compounds with ionically- or covalently-bonded peroxide (O2−
2) groups. This large family of compounds can be divided into ionic and covalent peroxide. The first class mostly contains the peroxides of the alkali and alkaline earth metals whereas the covalent peroxides are represented by such compounds as hydrogen peroxide and peroxymonosulfuric acid (H2SO5). In contrast to the purely ionic character of alkali metal peroxides, peroxides of transition metals have a more covalent character.















