
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres.
Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goitre. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome.

Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine.
Liver function tests, also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin, and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function. Most liver diseases cause only mild symptoms initially, but these diseases must be detected early. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Some tests are associated with functionality, some with cellular integrity, and some with conditions linked to the biliary tract. Because some of these tests do not measure function, it is more accurate to call these liver chemistries or liver tests rather than liver function tests. Several biochemical tests are useful in the evaluation and management of patients with hepatic dysfunction. These tests can be used to detect the presence of liver disease. They can help distinguish among different types of liver disorders, gauge the extent of known liver damage, and monitor the response to treatment. Some or all of these measurements are also carried out on individuals taking certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, to ensure that these medications are not adversely impacting the person's liver.

Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme. It is also called alanine aminotransferase and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) and was first characterized in the mid-1950s by Arthur Karmen and colleagues. ALT is found in plasma and in various body tissues but is most common in the liver. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle. Serum ALT level, serum AST level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.

Prostate-specific antigen (PSA), also known as gamma-seminoprotein or kallikrein-3 (KLK3), P-30 antigen, is a glycoprotein enzyme encoded in humans by the KLK3 gene. PSA is a member of the kallikrein-related peptidase family and is secreted by the epithelial cells of the prostate gland.

Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.
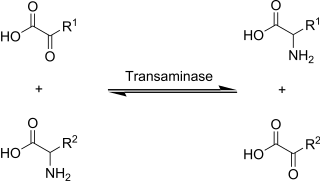
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.

Primary hyperparathyroidism is a medical condition where the parathyroid gland produce excess amounts of parathyroid hormone (PTH). The symptoms of the condition relate to the resulting elevated serum calcium (hypercalcemia), which can cause digestive symptoms, kidney stones, psychiatric abnormalities, and bone disease.
The anion gap is a value calculated from the results of multiple individual medical lab tests. It may be reported with the results of an electrolyte panel, which is often performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel.

The McDonald criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). These criteria are named after neurologist W. Ian McDonald who directed an international panel in association with the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) of America and recommended revised diagnostic criteria for MS in April 2001. These new criteria intended to replace the Poser criteria and the older Schumacher criteria. They have undergone revisions in 2005, 2010 and 2017.

Glycogen storage disease type 0 is a disease characterized by a deficiency in the glycogen synthase enzyme (GSY). Although glycogen synthase deficiency does not result in storage of extra glycogen in the liver, it is often classified as a glycogen storage disease because it is another defect of glycogen storage and can cause similar problems. There are two isoforms (types) of glycogen synthase enzyme; GSY1 in muscle and GSY2 in liver, each with a corresponding form of the disease. Mutations in the liver isoform (GSY2), causes fasting hypoglycemia, high blood ketones, increased free fatty acids and low levels of alanine and lactate. Conversely, feeding in these patients results in hyperglycemia and hyperlactatemia.
Hy's law is a rule of thumb that a patient is at high risk of a fatal drug-induced liver injury if given a medication that causes hepatocellular injury with jaundice. The law is based on observations by Hy Zimmerman, a major scholar of drug-induced liver injury. Some have suggested the principle be called a hypothesis or observation.
In medicine, the presence of elevated transaminases, commonly the transaminases alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), may be an indicator of liver dysfunction. Other terms include transaminasemia, transaminitis, and elevatedliver enzymes. Normal ranges for both ALT and AST vary by gender, age, and geography and are roughly 8-40 U/L. Mild transaminesemia refers to levels up to 250 U/L. Drug-induced increases such as that found with the use of anti-tuberculosis agents such as isoniazid are limited typically to below 100 U/L for either ALT or AST. Muscle sources of the enzymes, such as intense exercise, are unrelated to liver function and can markedly increase AST and ALT. Cirrhosis of the liver or fulminant liver failure secondary to hepatitis commonly reach values for both ALT and AST in the >1000 U/L range. Elevated transaminases that persist less than six months are termed "acute" in nature, and those values that persist for six months or more are termed "chronic" in nature.

Serine—pyruvate aminotransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGXT gene.

Aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GOT1 gene.
Maternal obesity refers to obesity of a woman during pregnancy. Parental obesity refers to obesity of either parent during pregnancy.
The AST/ALT ratio or De Ritis ratio is the ratio between the concentrations of the enzymes aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase, aka alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the blood of a human or animal. It is measured with a blood test and is sometimes useful in medical diagnosis for elevated transaminases to differentiate between causes of liver damage, or hepatotoxicity.
Latent iron deficiency (LID), also called iron-deficient erythropoiesis, is a medical condition in which there is evidence of iron deficiency without anemia. It is important to assess this condition because individuals with latent iron deficiency may develop iron-deficiency anemia. Additionally, there is some evidence of a decrease in vitality and an increase in fatigue among individuals with LID.
Indium lung is a rare occupational lung disease caused by exposure to respirable indium in the form of indium tin oxide. It is classified as an interstitial lung disease.











