An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so electrons flow from the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "+" is the cathode.
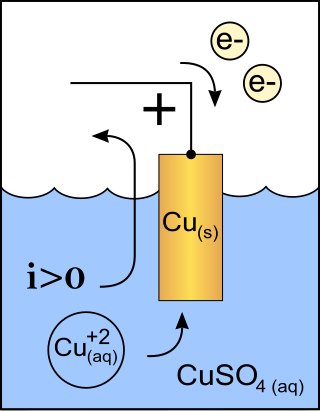
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic CCD for Cathode Current Departs. A conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is opposite to that of the conventional current flow. Consequently, the mnemonic cathode current departs also means that electrons flow into the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode.

Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.

An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit. Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery.

An electrochemical cell is a device that generates electrical energy from chemical reactions. Electrical energy can also be applied to these cells to cause chemical reactions to occur. Electrochemical cells that generate an electric current are called voltaic or galvanic cells and those that generate chemical reactions, via electrolysis for example, are called electrolytic cells.

In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity."

A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. In comparison with other commercial rechargeable batteries, Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, higher energy density, higher energy efficiency, a longer cycle life, and a longer calendar life. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991: within the next 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold.

A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell, is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulates and stores energy through a reversible electrochemical reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from button cells to megawatt systems connected to stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid, zinc–air, nickel–cadmium (NiCd), nickel–metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and lithium-ion polymer.
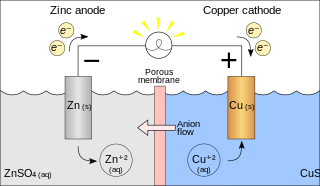
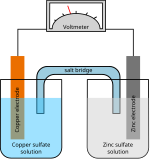
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation–reduction reactions. A common apparatus generally consists of two different metals, each immersed in separate beakers containing their respective metal ions in solution that are connected by a salt bridge or separated by a porous membrane.

An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that utilizes an external source of electrical energy to force a chemical reaction that would otherwise not occur. The external energy source is a voltage applied between the cell's two electrodes; an anode and a cathode, which are immersed in an electrolyte solution. This is in contrast to a galvanic cell, which itself is a source of electrical energy and the foundation of a battery. The net reaction taking place in a galvanic cell is a spontaneous reaction, i.e., the Gibbs free energy remains -ve, while the net reaction taking place in an electrolytic cell is the reverse of this spontaneous reaction, i.e., the Gibbs free energy is +ve.

An alkaline battery is a type of primary battery where the electrolyte has a pH value above 7. Typically these batteries derive energy from the reaction between zinc metal and manganese dioxide.

A zinc–air battery is a metal–air electrochemical cell powered by the oxidation of zinc with oxygen from the air. During discharge, a mass of zinc particles forms a porous anode, which is saturated with an electrolyte. Oxygen from the air reacts at the cathode and forms hydroxyl ions which migrate into the zinc paste and form zincate, releasing electrons to travel to the cathode. The zincate decays into zinc oxide and water returns to the electrolyte. The water and hydroxyl from the anode are recycled at the cathode, so the water is not consumed. The reactions produce a theoretical voltage of 1.65 Volts, but is reduced to 1.35–1.4 V in available cells.

A zinc–carbon battery (or carbon zinc battery in U.S. English) is a dry cell primary battery that provides direct electric current from the electrochemical reaction between zinc (Zn) and manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the presence of an ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) electrolyte. It produces a voltage of about 1.5 volts between the zinc anode, which is typically constructed as a cylindrical container for the battery cell, and a carbon rod surrounded by a compound with a higher Standard electrode potential (positive polarity), known as the cathode, that collects the current from the manganese dioxide electrode. The name "zinc-carbon" is slightly misleading as it implies that carbon is acting as the oxidizing agent rather than the manganese dioxide.
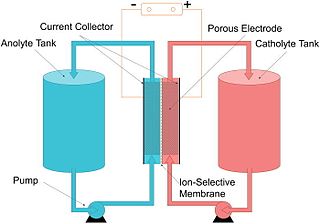
A flow battery, or redox flow battery, is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides and in opposite direction of a membrane. Ion transfer inside the cell occurs through the membrane while both liquids circulate in their own respective space. Cell voltage is chemically determined by the Nernst equation and ranges, in practical applications, from 1.0 to 2.43 volts. The energy capacity is a function of the electrolyte volume and the power is a function of the surface area of the electrodes.

A mercury battery is a non-rechargeable electrochemical battery, a primary cell. Mercury batteries use a reaction between mercuric oxide and zinc electrodes in an alkaline electrolyte. The voltage during discharge remains practically constant at 1.35 volts, and the capacity is much greater than that of a similarly sized zinc-carbon battery. Mercury batteries were used in the shape of button cells for watches, hearing aids, cameras and calculators, and in larger forms for other applications.

A rechargeable alkaline battery, also known as alkaline rechargeable or rechargeable alkaline manganese (RAM), is a type of alkaline battery that is capable of recharging for repeated use. The formats include AAA, AA, C, D, and snap-on 9-volt batteries. Rechargeable alkaline batteries are manufactured fully charged and have the ability to hold their charge for years, longer than nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, which self-discharge. Rechargeable alkaline batteries can have a high recharging efficiency and have less environmental impact than disposable cells.

The Leclanché cell is a battery invented and patented by the French scientist Georges Leclanché in 1866. The battery contained a conducting solution (electrolyte) of ammonium chloride, a cathode of carbon, a depolarizer of manganese dioxide (oxidizer), and an anode of zinc (reductant). The chemistry of this cell was later successfully adapted to manufacture a dry cell.

Batteries provided the primary source of electricity before the development of electric generators and electrical grids around the end of the 19th century. Successive improvements in battery technology facilitated major electrical advances, from early scientific studies to the rise of telegraphs and telephones, eventually leading to portable computers, mobile phones, electric cars, and many other electrical devices.

An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell.
The lithium–air battery (Li–air) is a metal–air electrochemical cell or battery chemistry that uses oxidation of lithium at the anode and reduction of oxygen at the cathode to induce a current flow.