External links
- "Poumons". www.embryology.ch (in French). Archived from the original on 2019-09-27. Retrieved 2007-11-07.
| Proctodeum | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Surface ectoderm |
| Gives rise to | Lower anal canal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | proctodeum |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A proctodeum is the back ectodermal part of an alimentary canal. It is created during embryogenesis by a folding of the outer body wall. It will form the lower part of the anal canal, below the pectinate line, which will be lined by stratified squamous non-keratinized (zona hemorrhagica) and stratified squamous keratinized (zona cutanea) epithelium. The junction between them is Hilton's white line.

The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin.

Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with little extracellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves.

An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.

Squamous metaplasia is a benign non-cancerous change (metaplasia) of surfacing lining cells (epithelium) to a squamous morphology.

The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment of the bowel, it functions to regulate release of excrement by two muscular sphincter complexes. The anus is the aperture at the terminal portion of the anal canal.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.
Keratomalacia is an eye disorder that results from vitamin A deficiency. Vitamin A is required to maintain specialized epithelia.

The squamous part of temporal bone, or temporal squama, forms the front and upper part of the temporal bone, and is scale-like, thin, and translucent.
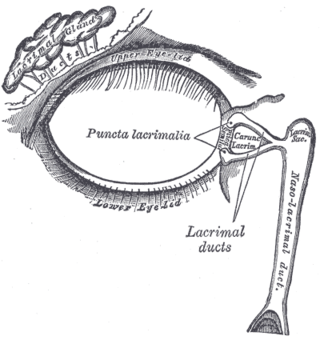
The lacrimal canaliculi are the small channels in each eyelid that drain lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal puncta to the lacrimal sac. This forms part of the lacrimal apparatus that drains lacrimal fluid from the surface of the eye to the nasal cavity.

The cervical canal is the spindle-shaped, flattened canal of the cervix which connects the vagina to the main cavity of the uterus in most mammals.

A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina.
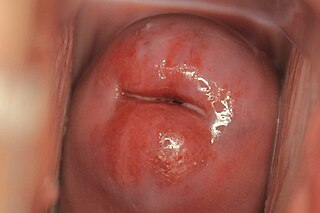
Cervical ectropion is a condition in which the cells from the 'inside' of the cervical canal, known as glandular cells, are present on the 'outside' of the vaginal portion of the cervix. The cells on the 'outside' of the cervix are typically squamous epithelial cells. Where the two cells meet is called the transformation zone, also known as the stratified squamous epithelium. Cervical ectropion can be grossly indistinguishable from early cervical cancer and must be evaluated by a physician to determine risks and prognosis. It may be found incidentally when a vaginal examination is done. The area may look red because the glandular cells are red. While many women are born with cervical ectropion, it can be caused by a number of reasons, such as:
An eruption cyst, or eruption hematoma, is a bluish swelling that occurs on the soft tissue over an erupting tooth. It is usually found in children. The fluid in the cyst is sometimes clear creating a pale-coloured cyst although often they are blue. An eruption cyst is a developmental soft-tissue cyst of odontogenic origin that forms over an erupting tooth. most commonly seen anterior to first molar

A squamous cell papilloma is a generally benign papilloma that arises from the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin, lip, oral cavity, tongue, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, cervix, vagina or anal canal. Squamous cell papillomas are typically associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) while sometimes the cause is unknown.

The anocutaneous line, also called the Hilton white line or intersphincteric groove, is a boundary in the anal canal.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.
Also called Zuska's disease, subareolar abscess is a subcutaneous abscess of the breast tissue beneath the areola of the nipple. It is a frequently aseptic inflammation and has been associated with squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts.

Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lung is a histologic type of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It is the second most prevalent type of lung cancer after lung adenocarcinoma and it originates in the bronchi. Its tumor cells are characterized by a squamous appearance, similar to the one observed in epidermal cells. Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung is strongly associated with tobacco smoking, more than any other forms of NSCLC.

Anatomical terminology is used to describe microanatomical structures. This helps describe precisely the structure, layout and position of an object, and minimises ambiguity. An internationally accepted lexicon is Terminologia Histologica.
A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body, the organs, internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body, and the lining of the moveable joint cavities. There are two basic types of tissue membranes: connective tissue and epithelial membranes.