Diagnosis
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2017) |
Progressive massive fibrosis (PMF), characterized by the development of large conglomerate masses of dense fibrosis (usually in the upper lung zones), can complicate silicosis [1] and coal worker's pneumoconiosis. [2] Conglomerate masses may also occur in other pneumoconioses, such as talcosis, [3] berylliosis (CBD), [3] kaolin pneumoconiosis, [4] and pneumoconiosis from carbon compounds, [4] such as carbon black, graphite, and oil shale. Conglomerate masses can also develop in sarcoidosis, [5] but usually near the hilae and with surrounding paracicatricial emphysema.
The disease arises firstly through the deposition of silica or coal dust (or other dust) within the lung, and then through the body's immunological reactions to the dust.
According to the International Labour Office (ILO), PMF requires the presence of large opacity exceeding 1 cm (by x-ray). By pathology standards, the lesion in histologic section must exceed 2 cm to meet the definition of PMF. [6] In PMF, lesions most commonly occupy the upper lung zone, and are usually bilateral. The development of PMF is usually associated with a restrictive ventilatory defect on pulmonary function testing. PMF can be mistaken for bronchogenic carcinoma and vice versa. PMF lesions tend to grow very slowly, so any rapid changes in size, or development of cavitation, should prompt a search for either alternative cause or secondary disease.[ citation needed ]
The pathogenesis of PMF is complicated, but involves two main routes – an immunological route, and a mechanical route.[ citation needed ]
Immunologically, disease is caused primarily through the activity of lung macrophages, which phagocytose dust particles after their deposition. These macrophages seek to eliminate the dust particle through either the mucociliary mechanism, or through lymphatic vessels which drain the lungs. Macrophages also produce an inflammatory mediator known as interleukin-1 (IL-1), which is part of the immune systems first line defenses against infecting particles. IL-1 is responsible for 'activation' of local vasculature, causing endothelial cells to express certain cell adhesion molecules, which help the cells of the body's immune system to migrate into tissues. Macrophages exposed to dust have been shown to have markedly decreased chemotaxis. Production of inflammatory mediators – and the tissue damage that ensues as an effect of this, as well as reduced motility of cells, is fundamental to the pathogenesis of pneumoconiosis and the accompanying inflammation, fibrosis, and emphysema.[ citation needed ]
There are also some mechanical factors involved in the pathogenesis of Complex Pneumoconiosis that should be considered. The most notable indications are the fact that the disease tends to develop in the upper lobe of the lung – especially on the right, and its common occurrence in taller individuals.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2017) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2017) |
Progressive massive fibrosis increased during the period 1970–2016 among coal miners in central Appalachia who filed for black lung benefits. [7]

Pneumoconiosis is the general term for a class of interstitial lung disease where inhalation of dust has caused interstitial fibrosis. The three most common types are asbestosis, silicosis, and coal miner's lung. Pneumoconiosis often causes restrictive impairment, although diagnosable pneumoconiosis can occur without measurable impairment of lung function. Depending on extent and severity, it may cause death within months or years, or it may never produce symptoms. It is usually an occupational lung disease, typically from years of dust exposure during work in mining; textile milling; shipbuilding, ship repairing, and/or shipbreaking; sandblasting; industrial tasks; rock drilling ; or agriculture. It is one of the most common occupational diseases in the world.
Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis is a made up word coined in 1935 by the then president of the National Puzzlers' League, Everett M. Smith. It has sometimes been used as a synonym for the occupational disease known as silicosis, but it should not be as most silicosis is not related to mining of volcanic dusts, and no evidence of silicosis has been found in populations exposed to crystalline silica in volcanic ash. It is the longest word in the English language published in a dictionary, Oxford Dictionaries, which defines it as "an artificial long word said to mean a lung disease caused by inhaling very fine volcanic dust".
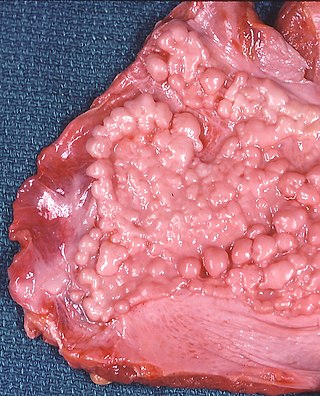
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart disease.

Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silicosis is characterized by shortness of breath, cough, fever, and cyanosis. It may often be misdiagnosed as pulmonary edema, pneumonia, or tuberculosis. Using workplace controls, silicosis is almost always a preventable disease.

Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue.
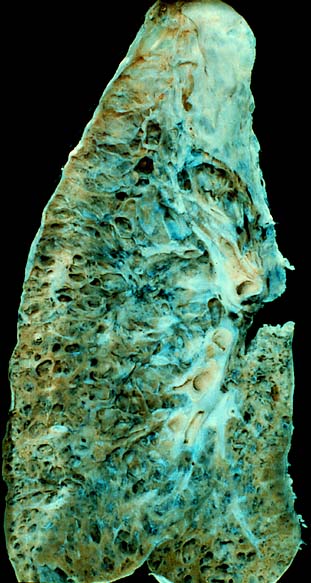
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
PMF may stand for:
Siderosis is the deposition of excess iron in body tissue. When used without qualification, it usually refers to an environmental disease of the lung, also known more specifically as pulmonary siderosis or Welder's disease, which is a form of pneumoconiosis.

Coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP), also known as black lung disease or black lung, is an occupational type of pneumoconiosis caused by long-term exposure to coal dust. It is common in coal miners and others who work with coal. It is similar to both silicosis from inhaling silica dust and asbestosis from inhaling asbestos dust. Inhaled coal dust progressively builds up in the lungs and leads to inflammation, fibrosis, and in worse cases, necrosis.

Bauxite pneumoconiosis, is a progressive form of pneumoconiosis usually caused by occupational exposure to bauxite fumes which contain aluminium and silica particulates.
Occupational lung diseases are work-related, lung conditions that have been caused or made worse by the materials a person is exposed to within the workplace. It includes a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiolitis obliterans, inhalation injury, interstitial lung diseases, infections, lung cancer and mesothelioma. These diseases can be caused directly or due to immunological response to an exposure to a variety of dusts, chemicals, proteins or organisms.
Caplan's syndrome is a combination of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and pneumoconiosis that manifests as intrapulmonary nodules, which appear homogeneous and well-defined on chest X-ray.

Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.
Rheumatoid lung disease is a disease of the lung associated with RA, rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid lung disease is characterized by pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis, lung nodules and pulmonary hypertension. Common symptoms associated with the disease include shortness of breath, cough, chest pain and fever. It is estimated that about one quarter of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop this disease, which are more likely to develop among elderly men with a history of smoking.
Equine multinodular pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic lung disease of horses. There is evidence that the disease is caused by infection with a gammaherpesvirus, equine herpesvirus 5. The disease affects usually adult horses reducing the ability to exercise as a result of the formation of nodular lesions in the lungs.

Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces (pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alveoli and they replace the spongy lung parenchyma. This reduces the total alveolar surface available for gas exchange leading to a reduction in oxygen supply for the blood. Emphysema usually affects the middle aged or older population because it takes time to develop with the effects of tobacco smoking, and other risk factors. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic risk factor that may lead to the condition presenting earlier.

Occupational dust exposure can occur in various settings, including agriculture, forestry, and mining. Dust hazards include those that arise from handling grain and cotton, as well as from mining coal. Wood dust, commonly referred to as "sawdust", is another occupational dust hazard that can pose a risk to workers' health.
Primary Source: Annals of the American Thoracic Society Source Reference: Almberg KS, et al "Progressive massive fibrosis resurgence identified in U.S. coal miners filing for black lung benefits, 1970–2016" Ann Am Thorac Soc 2018; DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201804-261OC
Occupational Lung Diseases, 3rd Edition, Morgan and Seaton https://web.archive.org/web/20060223051633/http://pim.medicine.dal.ca/il1.htm