Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, which became rare following occupational exposure limits established around 1950. Berylliosis is an occupational lung disease.
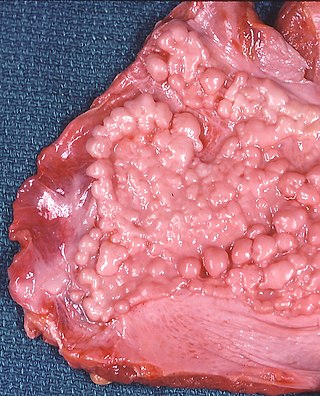
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart disease.

A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.

Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.
Neuroendocrine hyperplasia is rare and poorly understood lung condition which is characterized by an abnormal growth of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells in the lungs. It is a non-progressive disease of the interstitial tissues of the lungs. Prior to the findings of the hyperplasia of neuroendocrine cells it was known as tachypnea of infancy, as most children outgrow the need for oxygen supplementation within two to seven years. It is characterized by tachypnea, hypoxemia, and retractions. It is typically diagnosed in infants and children younger than one year of age. There is no currently recognized treatment, infants and children are given oxygen supplementation until they outgrow the need; since neuroendocrine cells do not multiply or get larger in size while the lungs continue to grow. This allows the lung disease to have less effect on lung function with age, although they will always have the same amount of neuroendocrine cells as they were born with.

Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris, aspiration, herbicides or fluorocarbons and some systemic diseases. If unresolved, continued inflammation can result in irreparable damage such as pulmonary fibrosis.

Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.

Acute interstitial pneumonitis is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.

Alveolar lung diseases, are a group of diseases that mainly affect the alveoli of the lungs.
Occupational lung diseases comprise a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiolitis obliterans, inhalation injury, interstitial lung diseases, infections, lung cancer and mesothelioma. These can be caused directly or due to immunological response to an exposure to a variety of dusts, chemicals, proteins or organisms. Occupational cases of interstitial lung disease may be misdiagnosed as COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or a myriad of other diseases; leading to a delay in identification of the causative agent.
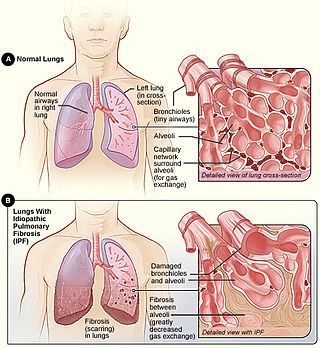
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic scarring lung disease characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.

Bird fancier's lung (BFL), also known as bird breeder's lung, is a type of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. It can cause shortness of breath, fever, dry cough, chest pain, anorexia and weight loss, fatigue, and progressive pulmonary fibrosis. It is triggered by exposure to avian proteins present in the dry dust of droppings or feathers of a variety of birds. The lungs become inflamed, with granuloma formation. It mostly affects people who work with birds or own many birds.

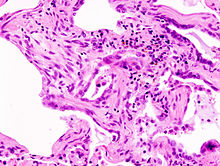
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.

Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways. There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.

Respiratory bronchiolitis is a lung disease associated with tobacco smoking. In pathology, it is defined by the presence of "smoker's macrophages". When manifesting significant clinical symptoms it is referred to as respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD).
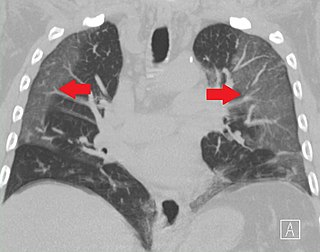
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.