| Quaternary prevention | |
|---|---|
| Purpose | identify patients at risk of overmedication |
The quaternary prevention, concept coined by the Belgian general practitioner Marc Jamoulle, [1] are the actions taken to identify a patient at risk of overmedicalisation, to protect them from new medical invasion, and to suggest interventions which are ethically acceptable. [2] [3]
Quaternary prevention is the set of health activities to mitigate or avoid the consequences of unnecessary or excessive intervention of the health system. [4]
Marc Jamoulle divided medical situations into four quadrants based on if the patient was experiencing illness (i.e. if the patient experienced subjective poor health) and if the doctor had identified disease (constructed based on diagnostic criteria), with a different type of prevention happening in each:
Jamoulle noted that when the patient was experiencing illness but no specific disease had been identified that patient was particularly vulnerable to their condition being made worse by invasive or harmful diagnostic medical intervention.
This original explanation is more limited than the more general term listed in the Wonca International Dictionary for General/Family Practice, "action taken to identify patient at risk of overmedicalisation, to protect him from new medical invasion, and to suggest to him interventions, which are ethically acceptable". [5]

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medical psychology or medico-psychology is the application of psychological principles to the practice of medicine, primarily drug-oriented, for both physical and mental disorders.
Internal medicine, also known as general internal medicine in Commonwealth nations, is a medical specialty for medical doctors focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of internal diseases. Medical practitioners of internal medicine are referred to as internists, or physicians in Commonwealth nations. Internists possess specialized skills in managing patients with undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes. They provide care to both hospitalized (inpatient) and ambulatory (outpatient) patients and often contribute significantly to teaching and research. Internists are qualified physicians who have undergone postgraduate training in internal medicine, and should not be confused with "interns”, a term commonly used for a medical doctor who has obtained a medical degree but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised.

Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.

A clinic is a health facility that is primarily focused on the care of outpatients. Clinics can be privately operated or publicly managed and funded. They typically cover the primary care needs of populations in local communities, in contrast to larger hospitals which offer more specialized treatments and admit inpatients for overnight stays.
Medicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions, and thus become the subject of medical study, diagnosis, prevention, or treatment. Medicalization can be driven by new evidence or hypotheses about conditions; by changing social attitudes or economic considerations; or by the development of new medications or treatments.
Health psychology is the study of psychological and behavioral processes in health, illness, and healthcare. The discipline is concerned with understanding how psychological, behavioral, and cultural factors contribute to physical health and illness. Psychological factors can affect health directly. For example, chronically occurring environmental stressors affecting the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, cumulatively, can harm health. Behavioral factors can also affect a person's health. For example, certain behaviors can, over time, harm or enhance health. Health psychologists take a biopsychosocial approach. In other words, health psychologists understand health to be the product not only of biological processes but also of psychological, behavioral, and social processes.

A primary care physician (PCP) is a physician who provides both the first contact for a person with an undiagnosed health concern as well as continuing care of varied medical conditions, not limited by cause, organ system, or diagnosis. The term is primarily used in the United States. In the past, the equivalent term was 'general practitioner' in the US; however in the United Kingdom and other countries the term general practitioner is still used. With the advent of nurses as PCPs, the term PCP has also been expanded to denote primary care providers.
In health care, diagnosis codes are used as a tool to group and identify diseases, disorders, symptoms, poisonings, adverse effects of drugs and chemicals, injuries and other reasons for patient encounters. Diagnostic coding is the translation of written descriptions of diseases, illnesses and injuries into codes from a particular classification. In medical classification, diagnosis codes are used as part of the clinical coding process alongside intervention codes. Both diagnosis and intervention codes are assigned by a health professional trained in medical classification such as a clinical coder or Health Information Manager.
Behavioral medicine is concerned with the integration of knowledge in the biological, behavioral, psychological, and social sciences relevant to health and illness. These sciences include epidemiology, anthropology, sociology, psychology, physiology, pharmacology, nutrition, neuroanatomy, endocrinology, and immunology. The term is often used interchangeably, but incorrectly, with health psychology. The practice of behavioral medicine encompasses health psychology, but also includes applied psychophysiological therapies such as biofeedback, hypnosis, and bio-behavioral therapy of physical disorders, aspects of occupational therapy, rehabilitation medicine, and physiatry, as well as preventive medicine. In contrast, health psychology represents a stronger emphasis specifically on psychology's role in both behavioral medicine and behavioral health.
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician, physician assistant, registered dietitian, veterinarian, veterinary technician, optometrist, pharmacist, pharmacy technician, medical assistant, physical therapist, occupational therapist, dentist, midwife, psychologist, audiologist, healthcare scientist, or who perform services in allied health professions. Experts in public health and community health are also health professionals.

The natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people from its pathological onset ("inception") until its resolution. The inception of a disease is not a firmly defined concept. The natural history of a disease is sometimes said to start at the moment of exposure to causal agents. Knowledge of the natural history of disease ranks alongside causal understanding in importance for disease prevention and control. Natural history of disease is one of the major elements of descriptive epidemiology.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to medicine:
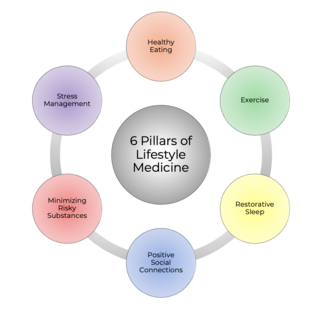
Lifestyle medicine (LM) is a branch of medicine focused on preventive healthcare and self-care dealing with prevention, research, education, and treatment of disorders caused by lifestyle factors and preventable causes of death such as nutrition, physical inactivity, chronic stress, and self-destructive behaviors including the consumption of tobacco products and drug or alcohol abuse. The goal of LM is to improve individuals' health and wellbeing by applying the 6 pillars of lifestyle medicine (nutrition, regular physical activity, restorative sleep, stress management, avoidance of risky substances, and positive social connection) to prevent chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity. By focusing on these 6 areas to improve health, LM can prevent 80% of chronic illnesses and non-communicable diseases (NCD).
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.

Iatrogenesis is the causation of a disease, a harmful complication, or other ill effect by any medical activity, including diagnosis, intervention, error, or negligence. First used in this sense in 1924, the term was introduced to sociology in 1976 by Ivan Illich, alleging that industrialized societies impair quality of life by overmedicalizing life. Iatrogenesis may thus include mental suffering via medical beliefs or a practitioner's statements. Some iatrogenic events are obvious, like amputation of the wrong limb, whereas others, like drug interactions, can evade recognition. In a 2013 estimate, about 20 million negative effects from treatment had occurred globally. In 2013, an estimated 142,000 persons died from adverse effects of medical treatment, up from an estimated 94,000 in 1990.

A doctor's visit, also known as a physician office visit or a consultation, or a ward round in an inpatient care context, is a meeting between a patient with a physician to get health advice or treatment plan for a symptom or condition, most often at a professional health facility such as a doctor's office, clinic or hospital. According to a survey in the United States, a physician typically sees between 50 and 100 patients per week, but it may vary with medical specialty, but differs only little by community size such as metropolitan versus rural areas.
Schooliosis, a pun on "school" and "scoliosis", is a term for a type of medical misdiagnosis. The word was coined by Petr Skrabanek and James McCormick.
The inverse benefit law states that the ratio of benefits to harms among patients taking new drugs tends to vary inversely with how extensively a drug is marketed. Two Americans, Howard Brody and Donald Light, have defined the inverse benefit law, inspired by Tudor Hart's inverse care law.

Barbara Starfield was an American pediatrician. She was an advocate for primary health care worldwide. Her academic and professional life was almost fully dedicated to the Johns Hopkins University.