
The Staggers Rail Act of 1980 is a United States federal law that deregulated the American railroad industry to a significant extent, and it replaced the regulatory structure that had existed since the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887.

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 36,000 employees, 33,400 miles (53,800 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

CSX Transportation, known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad company operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Operating about 21,000 route miles (34,000 km) of track, it is the leading subsidiary of CSX Corporation, a Fortune 500 company headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida.

Ferromex is a private rail consortium that operates the largest railway in Mexico with combined mileage of 12,100 kilometres (7,500 mi) and is often classed with North American Class I railroads.

The United States Railroad Administration (USRA) was the name of the nationalized railroad system of the United States between December 28, 1917, and March 1, 1920. It was the largest American experiment with nationalization, and was undertaken against a background of war emergency following American entry into World War I. During its brief existence, the USRA made major investments in the United States railroad system, and introduced standardized locomotive and railroad car classes, known as USRA standard. After the end of World War I, while some in the United States advocated for continuing nationalization, ultimately the railroads were returned to their previous owners in early 1920.

The Surface Transportation Board (STB) of the United States is an independent federal agency that serves as an adjudicatory board. The board was created in 1996 following the abolition of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) and absorbed regulatory powers relevant to the railroad industry previously under the ICC's purview.

The Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad is a wholly owned U.S. subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Kansas City. Before its purchase, it was the largest Class II railroad in the United States, operating across South Dakota and southern Minnesota in the Northern Plains of the United States. Portions of the railroad also extended into Wyoming, Nebraska, Iowa, and Illinois. It interchanged with all seven U.S. Class I railroads.

The San Diego and Arizona Eastern Railway Company is a short-line American railroad founded in 1906 as the San Diego and Arizona Railway (SD&A) by sugar magnate, developer, and entrepreneur John D. Spreckels. Dubbed "The Impossible Railroad" by many engineers of its day due to the immense logistical challenges involved, the line was established in part to provide San Diego with a direct rail link to the east by connecting with the Southern Pacific Railroad lines in El Centro, California.

Pan Am Railways, Inc. (PAR) is a subsidiary of CSX Corporation that operates Class II regional railroads covering northern New England from Mattawamkeag, Maine, to Rotterdam Junction, New York. Pan Am Railways is primarily made up of former Class II regional railroads such as Boston and Maine Corporation, Maine Central Railroad Company, Portland Terminal Company, and Springfield Terminal Railway Company. It was formerly known as Guilford Transportation Industries and was also known as Guilford Rail System. Guilford bought the name, colors, and logo of Pan American World Airways in 1998.

Rail transportation in the United States consists primarily of freight shipments along a well integrated network of standard gauge private freight railroads that also extend into Canada and Mexico. The United States has the largest rail transport network of any country in the world, about 160,000 miles (260,000 km).

The Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 is a United States federal law that was designed to regulate the railroad industry, particularly its monopolistic practices. The Act required that railroad rates be "reasonable and just," but did not empower the government to fix specific rates. It also required that railroads publicize shipping rates and prohibited short haul or long haul fare discrimination, a form of price discrimination against smaller markets, particularly farmers in Western or Southern Territory compared to the official Eastern states. The Act created a federal regulatory agency, the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC), which it charged with monitoring railroads to ensure that they complied with the new regulations.

The Meridian and Bigbee Railroad is a Class III railroad that operates over 168 miles (270 km) of track between Meridian, Mississippi and Burkville, Alabama. Additionally, the M&B has trackage rights over CSX from Burkville to Montgomery, Alabama. MNBR operates with a 286,000-pound railcar loading capacity.
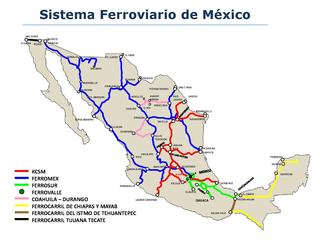
Mexico has a freight railway system owned by the national government and operated by various entities under concessions (charters) granted by the national government. The railway system provides freight and passenger service throughout the country, connecting major industrial centers with ports and with rail connections at the United States border. Passenger rail services were limited to a number of tourist trains between 1997, when Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México suspended service, and 2008, when Ferrocarril Suburbano de la Zona Metropolitana de México inaugurated Mexico's first commuter rail service between Mexico City and the State of Mexico. This is not including the Mexico City Metro, which started service in 1969.

The Kansas City Terminal Railway is a Class III terminal railroad that serves as a joint operation of the trunk railroads that serve the Kansas City metropolitan area, the United States' second largest rail hub after Chicago. It is operated by the Kaw River Railroad.

Stillwater Central Railroad is a shortline railroad operating in Oklahoma.

A shortline railroad is a small or mid-sized railroad company that operates over a relatively short distance relative to larger, national railroad networks. The term is used primarily in the United States and Canada. In the former, railroads are categorized by operating revenue, and most shortline railroads fall into the Class III or Class II categorization defined by the Surface Transportation Board.

The Chicago Rock Island & Pacific Railroad LLC is an American Class III railroad operating in Mississippi, Kansas and Oklahoma. It uses the name and the most recent corporate identity of the first Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad (1852–1980).

Canadian Pacific Kansas City Limited, doing business as CPKC, is a Class I railroad in North America that resulted from the merger of Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and Kansas City Southern (KCS) on April 14, 2023. It is the first and currently the only single-line railway connecting Canada, Mexico, and the United States, operating approximately 32,000 kilometres (20,000 mi) of rail across the three countries. CPKC is headquartered in Calgary and led by Keith Creel as President and CEO.




















