
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV). The syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Around late 2017, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.

Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS, and COVID-19. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus is a species of coronavirus that infects humans, bats and certain other mammals. It is an enveloped positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that enters its host cell by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. It is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and subgenus Sarbecovirus.

Coronaviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. The group includes the subfamilies Letovirinae and Orthocoronavirinae; the members of the latter are known as coronaviruses.

Avian coronavirus (IBV) is a coronavirus that infects birds, causing the associated disease avian infectious bronchitis (IB). It is a highly infectious avian pathogen that affects the respiratory tract, gut, kidney and reproductive systems of chickens.
Viral pneumonia is a pneumonia caused by a virus. Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in one or both of the lungs. The pulmonary alveoli fill with fluid or pus making it difficult to breathe. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Viruses are the most common cause of pneumonia in children, while in adults bacteria are a more common cause.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus is a strain of virus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets.
Betaarterivirus suid 1, formerly Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), is a virus that causes a disease of pigs, called porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS), also known as blue-ear pig disease. This economically important, panzootic disease causes reproductive failure in breeding stock and respiratory tract illness in young pigs. Initially referred to as "mystery swine disease" and "mystery reproductive syndrome", it was first reported in 1987 in North America (2) and Central Europe (3). The disease costs the United States swine industry around $644 million annually, and recent estimates in Europe found that it costs almost 1.5b€ every year.

Canine coronavirus (CCoV) is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which is a member of the species Alphacoronavirus 1. It causes a highly contagious intestinal disease worldwide in dogs. The infecting virus enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. It was discovered in 1971 in Germany during an outbreak in sentry dogs. The virus is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus and subgenus Tegacovirus.
An emergent virus is a virus that is either newly appeared, notably increasing in incidence/geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious diseases and raise public health challenges globally, given their potential to cause outbreaks of disease which can lead to epidemics and pandemics. As well as causing disease, emergent viruses can also have severe economic implications. Recent examples include the SARS-related coronaviruses, which have caused the 2002-2004 outbreak of SARS (SARS-CoV-1) and the 2019–20 pandemic of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Other examples include the human immunodeficiency virus which causes HIV/AIDS; the viruses responsible for Ebola; the H5N1 influenza virus responsible for avian flu; and H1N1/09, which caused the 2009 swine flu pandemic. Viral emergence in humans is often a consequence of zoonosis, which involves a cross-species jump of a viral disease into humans from other animals. As zoonotic viruses exist in animal reservoirs, they are much more difficult to eradicate and can therefore establish persistent infections in human populations.

Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a species of coronavirus which infects mice. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the CEACAM1 receptor. It has, like other coronaviruses from genus Betacoronavirus, subgenus Embecovirus, an additional hemagglutinin esterase (HE) gene.
Reverse zoonosis, also known as zooanthroponosis, and sometimes anthroponosis, refers to pathogens reservoired in humans that are capable of being transmitted to non-human animals.
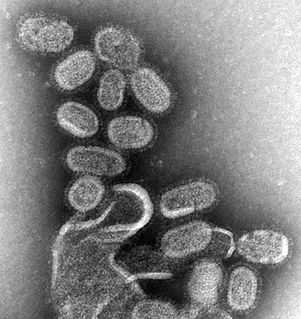
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by an influenza virus. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and commonly include: high fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle and joint pain, headache, coughing, and feeling tired. These symptoms typically begin two days after exposure to the virus and most last less than a week, although the coughing may last for more than two weeks. In children, there may be diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not common in adults. Diarrhea and vomiting occur more commonly in gastroenteritis, which is an unrelated disease sometimes referred to as "stomach flu" or the "24-hour flu". Complications of influenza may include viral pneumonia, secondary bacterial pneumonia, sinus infections, and worsening of previous health problems such as asthma or heart failure.

Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss of appetite, body aches, and nausea, typically in connection with a sudden onset of illness. In most cases, the symptoms are caused by cytokines released by immune system activation, and are thus relatively non-specific.
Bovine coronavirus is a coronavirus which is a member of the species Betacoronavirus 1. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminic acid recepter. Infection causes calf enteritis and contributes to the enzootic pneumonia complex in calves. It can also cause winter dysentery in adult cattle. It can infect both domestic and wild ruminants and has a worldwide distribution. Transmission is horizontal, via oro-fecal or respiratory routes. It has, like other coronaviruses from genus Betacoronavirus, subgenus Embecovirus, an additional shorter spike-like surface protein called hemagglutinin esterase (HE).

Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), or EMC/2012 (HCoV-EMC/2012), is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the DPP4 receptor. The species is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and subgenus Merbecovirus.

Human coronavirus HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1) is a species of coronavirus in humans. It causes an upper respiratory disease with symptoms of the common cold, but can advance to pneumonia and bronchiolitis. It was first discovered in January 2004 from one man in Hong Kong. Subsequent research revealed it has global distribution and earlier genesis.

Human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) is a member of the species Betacoronavirus 1, which infects humans and cattle. The infecting coronavirus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminic acid receptor. OC43 is one of seven known coronaviruses to infect humans. It is one of the viruses responsible for the common cold. It has, like other coronaviruses from genus Betacoronavirus, subgenus Embecovirus, an additional shorter spike protein called hemagglutinin esterase (HE).
Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) is a species of coronavirus which infects humans and bats. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. Along with Human coronavirus OC43, it is one of the viruses responsible for the common cold. HCoV-229E is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus and subgenus Duvinacovirus.

The history of coronaviruses is a reflection of the discovery of the diseases caused by coronaviruses and identification of the viruses. It starts with the first report of a new type of upper-respiratory tract disease among chickens in North Dakota, US, in 1931. The causative agent was identified as a virus in 1933. By 1936, the disease and the virus were recognised as unique from other viral disease. The became known as infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), but later officially renamed as Avian coronavirus.










