
The Comoros archipelago consists of four main islands aligned along a northwest–southeast axis at the north end of the Mozambique Channel, between Mozambique and the island of Madagascar. Still widely known by their French names, the islands officially have been called by their Swahili names by the Comorian government. They are Grande Comore (Njazidja), Mohéli (Mwali), Anjouan (Nzwani), and Mayotte (Mahoré). The islands' distance from each other—Grande Comore is some 200 kilometers from Mayotte, forty kilometers from Mohéli, and eighty kilometers from Anjouan—along with a lack of good harbor facilities, make transportation and communication difficult. Comoros are sunny islands.
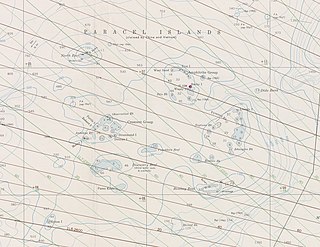
The Paracel Islands, also known as the Xisha Islands and the Hoang Sa Archipelago, are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.

Rossel Island is the easternmost island of the Louisiade Archipelago, within the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. Tree Islet is situated 1.5 miles (2.4 km) to the north-west, while Wule Island is situated 1.5 miles (2.4 km) westward.

The Chesterfield Islands are a French archipelago of New Caledonia located in the Coral Sea, 550 km (300 nmi) northwest of Grande Terre, the main island of New Caledonia. The archipelago is 120 km long and 70 km broad, made up of 11 uninhabited islets and many reefs. The land area of the islands is less than 10 km2.

Pana Tinani is an island in the Louisiade Archipelago in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea.

Pocklington Reef is a coral reef and a mostly submerged atoll in the far southeast of Papua New Guinea.

Parama Island is an island close off the south coast of Papua New Guinea. It is located 17 km east of Daru, the provincial capital of Western Province, at the southernmost extreme of the Fly River delta, and at the northeastern corner of the Torres Strait. It is the northernmost of the Torres Strait Islands, and at the same time the southernmost of the Fly River delta. Bampton Point, its southernmost point, marks the southwestern corner of the Gulf of Papua. The Coral Sea is southeast. Torres Strait is south and southwest, specifically the Great Northeast Channel, which separates Parama Island from the closest Australian (Queensland) island, Bramble Cay, 48 km ESE.

The Deboyne Islands are an atoll, composed of a group of reefs and islands in the north of the Louisiade Archipelago, Papua New Guinea.

The Duchateau Islands are an island group in the Coral Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea. They lie to the east of Panarairai Island in the Louisiade Archipelago.

The Tizard Bank, 10°15′N114°30′E is a partially sunken atoll and one of the significant maritime features of the north-western part of the Spratly Islands. It is claimed by the People's Republic of China, the Republic of China, and Vietnam, and various parts of it are occupied by these states.
The Calvados Chain are a group of islands in the Solomon Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea within the Louisiade Archipelago.

Yeina Island is an island of volcanic origin in the Southeast Louisiade Archipelago in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea.
The Dumoulin Islands are an uninhabited group of islands in Louisiade Archipelago.

The Jomard Islands are an uninhabited island group in the Coral Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea, It lies to the east of Montemont Islands in the Louisiade Archipelago.

Bramble Haven is an atoll in the Louisiade Archipelago. Its islands on the northern section are grouped as the Duperre Islands.
The Sloss Islands are an uninhabited archipelago in Louisiade Archipelago.

The Engineer Islands are an archipelago in the Solomon Sea belonging to Papua New-Guinea.
The Laseinie Islands are an archipelago in the Solomon Sea. Politically they belong to Bwanabwana Rural LLG of Samarai-Murua District of Milne Bay Province, in the southeastern region of Papua New Guinea. They are located southeast of the D'Entrecasteaux Islands. They are part of the Louisiade Archipelago.















