
Cygwin is a Unix-like environment and command-line interface for Microsoft Windows. Cygwin's purpose is expressed in its motto: "Get that Linux feeling – on Windows".

A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window.
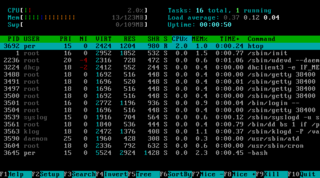
ANSI escape sequences are a standard for in-band signaling to control cursor location, color, font styling, and other options on video text terminals and terminal emulators. Certain sequences of bytes, most starting with an ASCII escape character and a bracket character, are embedded into text. The terminal interprets these sequences as commands, rather than text to display verbatim.

A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal and predated the use of a computer screen by decades.

The F Virtual Window Manager is a virtual window manager for the X Window System. Originally a twm derivative, FVWM has evolved into a powerful and highly configurable environment for Unix-like systems.

In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an early form of human–computer interaction, before the advent of modern conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Like GUIs, they may use the entire screen area and accept mouse and other inputs. They may also use color and often structure the display using special graphical characters such as ┌ and ╣, referred to in Unicode as the "box drawing" set. The modern context of use is usually a terminal emulator.

Konsole is a free and open-source terminal emulator graphical application which is part of KDE Applications and ships with the KDE desktop environment. Konsole was originally written by Lars Doelle. It ls licensed under the GPL-2.0-or-later and the GNU Free Documentation License.
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console and network file transfer application. It supports several network protocols, including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can also connect to a serial port. The name "PuTTY" has no official meaning.

Terminal (Terminal.app) is the terminal emulator included in the macOS operating system by Apple. Terminal originated in NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP, the predecessor operating systems of macOS.

In computing, xterm is the standard terminal emulator for the X Window System. It allows users to run programs which require a command-line interface.

QEMU is a free and open-source emulator. It emulates the machine's processor through dynamic binary translation and provides a set of different hardware and device models for the machine, enabling it to run a variety of guest operating systems. It can interoperate with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to run virtual machines at near-native speed. QEMU can also do emulation for user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one architecture to run on another.

GNOME Terminal is a terminal emulator for the GNOME desktop environment written by Havoc Pennington and others. Terminal emulators allow users to access a UNIX shell while remaining on their graphical desktop.
An SSH client is a software program which uses the secure shell protocol to connect to a remote computer. This article compares a selection of notable clients.
In computer security, executable-space protection marks memory regions as non-executable, such that an attempt to execute machine code in these regions will cause an exception. It makes use of hardware features such as the NX bit, or in some cases software emulation of those features. However, technologies that emulate or supply an NX bit will usually impose a measurable overhead while using a hardware-supplied NX bit imposes no measurable overhead.

FVWM-Crystal is a theme framework for the FVWM window manager. It uses GUI tools to edit the look of windows, instead of the use of editing a text file in FVWM. It creates a desktop environment using FVWM as its window manager and main core.

ZOC is a popular computer-based terminal emulator and Telnet software client for the Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh macOS operating systems that supports telnet, modem, SSH 1 and 2, ISDN, serial, TAPI, Rlogin and other means of communication. Its terminal emulator supports Xterm emulation with full colors, meta-keys and local printing, VT102, VT220 and several types of ANSI as well as Wyse, TVI, TN3270, and Sun's CDE. It supports full keyboard remapping, scripting in REXX and other languages, and support for named pipes.

SecureCRT is a commercial SSH and Telnet client and terminal emulator by VanDyke Software. Originally a Windows product, VanDyke later added a Mac OS X version in 2010 with release v6.6 and a Linux version in 2011 with release v6.7.

The Linux console is a system console internal to the Linux kernel. A system console is the device which receives all kernel messages and warnings and which allows logins in single user mode. The Linux console provides a way for the kernel and other processes to send text output to the user, and to receive text input from the user. The user typically enters text with a computer keyboard and reads the output text on a computer monitor. The Linux kernel supports virtual consoles – consoles that are logically separate, but which access the same physical keyboard and display. The Linux console are implemented by the VT subsystem of the Linux kernel, and do not rely on any user space software. This is in contrast to a terminal emulator, which is a user space process that emulates a terminal, and is typically used in a graphical display environment.
A terminal multiplexer is a software application that can be used to multiplex several separate pseudoterminal-based login sessions inside a single terminal display, terminal emulator window, PC/workstation system console, or remote login session, or to detach and reattach sessions from a terminal. It is useful for dealing with multiple programs from a command line interface, and for separating programs from the session of the Unix shell that started the program, particularly so a remote process continues running even when the user is disconnected.

devpts is a virtual filesystem directory available in the Linux kernel since version 2.1.93. It is normally mounted at /dev/pts and contains solely devices files which represent slaves to the multiplexing master located at /dev/ptmx which in turn is used to implement terminal emulators.












