
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.

The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

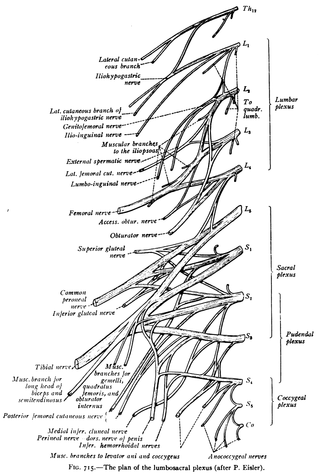
A nerve plexus is a plexus of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve plexuses, except in the thoracic region, as well as other forms of autonomic plexuses, many of which are a part of the enteric nervous system. The nerves that arise from the plexuses have both sensory and motor functions. These functions include muscle contraction, the maintenance of body coordination and control, and the reaction to sensations such as heat, cold, pain, and pressure. There are several plexuses in the body, including:

The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum.
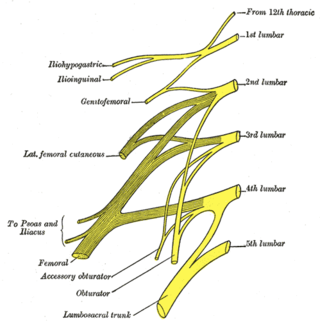
The lumbar nerves are the five pairs of spinal nerves emerging from the lumbar vertebrae. They are divided into posterior and anterior divisions.

The perforating cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the sacral plexus that provides sensory innervation to the skin of the buttocks.
A nerve root is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:

The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back.
Pelvic splanchnic nerves or nervi erigentes are splanchnic nerves that arise from sacral spinal nerves S2, S3, S4 to provide parasympathetic innervation to the organs of the pelvic cavity.

The ventral ramus is the anterior division of a spinal nerve. The ventral rami supply the antero-lateral parts of the trunk and the limbs. They are mainly larger than the dorsal rami.

The lumbar ganglia are paravertebral ganglia located in the inferior portion of the sympathetic trunk. The lumbar portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 4 lumbar ganglia. The lumbar splanchnic nerves arise from the ganglia here, and contribute sympathetic efferent fibers to the nearby plexuses. The first two lumbar ganglia have both white and gray rami communicates.
Sacral nerve stimulation, also termed sacral neuromodulation, is a type of medical electrical stimulation therapy.

The cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. C1 carries predominantly motor fibres, but also a small meningeal branch that supplies sensation to parts of the dura around the foramen magnum.
The sacral spinal nerve 5 (S5) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment.

The sacral spinal nerve 4 (S4) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment.

The sacral spinal nerve 2 (S2) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment.

The sacral spinal nerve 1 (S1) is a spinal nerve of the sacral segment.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.













