
Bougainvillea glabra, the lesser bougainvillea or paperflower, is the most common species of bougainvillea used for bonsai. The epithet 'glabra' comes from Latin and means "bald".

Aeonium haworthii, also known as Haworth's aeonium or pinwheel, is a species of succulent flowering plant in the family Crassulaceae. It is grown as a houseplant in temperate regions. It has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit, as has the cultivar 'Variegatum'.

Salix aegyptiaca, known as the Persian willow, is a large shrub or small tree from the genus of willow (Salix) with red branches that are tomentose in the first two years and leaves up to 15 centimeters long. The natural range of the species is in the Caucasus and in western Asia. It is cultivated in many countries.
Salix capusii is a large shrub from the genus of the willow (Salix) with chestnut-brown branches and 4 to 5 centimeters long, gray-blue leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Pakistan, and China.

Salix appendiculata is a plant from the willow genus (Salix). They can be found in France, Italy, Central and Eastern Europe, and on the Balkan Peninsula.

Salix caesia is a small shrub in the genus Salix, the willows. It is widespread, mainly in Asia.
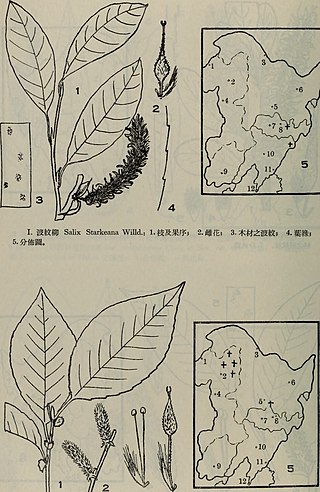
Salix starkeana is a small, prostrate shrub from the genus of willows (Salix) with red-brown to purple-red, bare branches and olive-green leaf tops. The natural range of the species is in Europe and in northern Asia.
Salix caspica is a plant from the willow genus (Salix) within the willow family (Salicaceae). The natural range extends from eastern European Russia to far western China.
Salix annulifera is a small shrub from the genus of the willow (Salix) with up to 8 centimeter long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in China.
Salix anticecrenata is a low, pillow-shaped shrub from the genus of willow (Salix) with about 1.5 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in Nepal and China.
Salix chienii is a large shrub or small tree in the willow genus Salix with initially light green and tomentose hairy and later reddish brown and balding branches. The leaf blades have lengths of 2 to 3.5 sometimes 5.5 centimeters. The natural range of the species is in China.
Salix chikungensis is a shrub in the willow genus Salix with tomentose hairy and later balding branches. The leaf blades have lengths of 6 to 8.5 centimeters. The natural range of the species is in China.

Salix clathrata is a prostrate shrub in the willow genus Salix with spread, heavily branched branches. The leaf blades have lengths of 1.5 to rarely 3 centimeters. The natural range of the species is in China.
Salix delavayana is a shrub or small tree from the genus willow (Salix) with mostly 3 to 8 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in the south of China and in Tibet.
Salix dibapha is a shrub from the genus of willow (Salix) with mostly 4 to 6 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in China.
Salix dissa is a low shrub from the genus willow (Salix) with usually 1 to 3 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in China.
Salix divergentistyla is a shrub or tree from the genus of willow (Salix) with mostly 3 to 4.5 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in Tibet.
Salix donggouxianica is a shrub from the genus willow (Salix) with usually 3.5 to 4.5 centimeters long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in the northeast of China.

Salix erioclada is a species from the genus of willows (Salix) and grows as a shrub or small tree. The leaf blades have a length of about 5 centimeters. The natural range of the species is in China.

Salix ernestii is a species in the genus of willow (Salix) and grows as a shrub. The leaf blades are about 11 centimeters long. The natural range of the species is in China.









