
The Malpighiales comprise one of the largest orders of flowering plants, containing about 36 families and more than 16,000 species, about 7.8% of the eudicots. The order is very diverse, containing plants as different as the willow, violet, poinsettia, manchineel, rafflesia and coca plant, and are hard to recognize except with molecular phylogenetic evidence. It is not part of any of the classification systems based only on plant morphology. Molecular clock calculations estimate the origin of stem group Malpighiales at around 100 million years ago (Mya) and the origin of crown group Malpighiales at about 90 Mya.

The Celastrales are an order of flowering plants found throughout the tropics and subtropics, with only a few species extending far into the temperate regions. The 1200 to 1350 species are in about 100 genera. All but seven of these genera are in the large family Celastraceae. Until recently, the composition of the order and its division into families varied greatly from one author to another.

Violales is a botanical name of an order of flowering plants and takes its name from the included family Violaceae; it was proposed by Lindley (1853). The name has been used in several systems, although some systems used the name Parietales for similar groupings. In the 1981 version of the influential Cronquist system, order Violales was placed in subclass Dilleniidae with a circumscription consisting of the families listed below. Some classifications such as that of Dahlgren placed the Violales in the superorder Violiflorae.

The Flacourtiaceae is a defunct family of flowering plants whose former members have been scattered to various families, mostly to the Achariaceae and Salicaceae. It was so vaguely defined that hardly anything seemed out of place there and it became a dumping ground for odd and anomalous genera, gradually making the family even more heterogeneous. In 1975, Hermann Sleumer noted that "Flacourtiaceae as a family is a fiction; only the tribes are homogeneous."

The Passifloraceae are a family of flowering plants, containing about 750 species classified in around 27 genera.
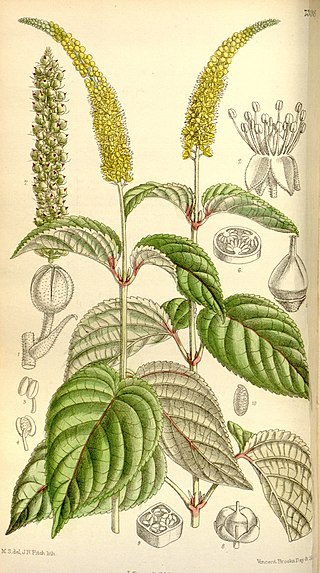
Abatia is a genus of about ten species of Central and South American trees in the family Salicaceae. Previously, it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae, or tribe Abatieae of the family Passifloraceae or Samydaceae by G. Bentham & J.D. Hooker and Hutchinson.

The Monimiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It is closely related to the families Hernandiaceae and Lauraceae. It consists of shrubs, small trees, and a few lianas of the tropics and subtropics, mostly in the southern hemisphere. The largest center of diversity is New Guinea, with about 75 species. Lesser centres of diversity are Madagascar, Australia, and the neotropics. Africa has one species, Xymalos monospora, as does Southern Chile. Several species are distributed through Malesia and the southwest Pacific.
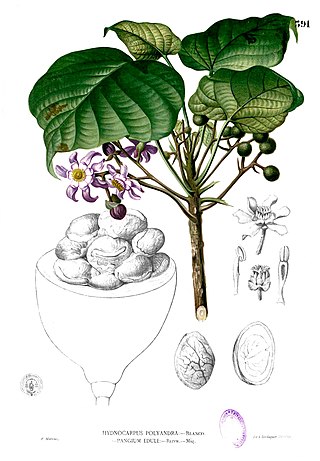
Achariaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of 31 genera and about 155 species of tropical herbs, shrubs, and trees. The APG IV system has greatly expanded the scope of the family by including many genera previously classified in Flacourtiaceae. Molecular data strongly support the inclusion of this family in the order Malpighiales.

Samydaceae is a family of tropical and subtropical woody plants, its best known genus being Casearia. It has always been of uncertain placement, in the past usually being submerged in the family Flacourtiaceae.
Dipentodon is a genus of flowering plants in the family Dipentodontaceae. Its only species, Dipentodon sinicus, is a small, deciduous tree native to southern China, northern Myanmar, and northern India. It has been little studied and until recently its affinities remained obscure.

Pineda is a genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It contains two species of shrubs: Pineda incana, which is native to the Andes of Ecuador and Peru, and Pineda ovata, which is native to the Andes of Bolivia.

Macrohasseltia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of tree: Macrohasseltia macroterantha, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Macrohasseltia is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Olmediella, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.

Olmediella is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Olmediella betschleriana, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Olmediella is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Macrohasseltia, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.
Aphaerema was formerly a genus of flowering plants in the Flacourtiaceae, consisting of one species of small shrubs, Aphaerema spicata, which is native to Brazil and Argentina. Later studies indicated that Aphaerema should be classified in the willow family, Salicaceae, and combined with the genus Abatia. Because the name Abatia spicata was already used, the species was given the new name Abatia angeliana, in honor of Brazilian botanist João Angely. Aphaerema is one of the few groups of Salicaceae with opposite leaves.
Hasseltiopsis is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Hasseltiopsis dioica, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Hasseltiopsis is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Prockia, Pineda, Neosprucea, and Banara.
Ahernia is a genus of a single species, Ahernia glandulosa, a tree in the family Achariaceae, native to Hainan and Luzon island of the Philippines. Previously it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae before being placed in Achariaceae. Ahernia is closely related to the American genera Hasseltia, Macrothumia, and Pleuranthodendron, but differs in its axillary racemes and more numerous (10–15) petals. Ahernia glandulosa is found in low elevation primary forests and is known in the Tagalog language as butun or sanglai. It grows 8–15 m (26–49 ft) tall.
Irenodendron is a genus of three species of shrubs and trees in the willow family Salicaceae native to northern South America. These species were previously treated as a section of the genus Laetia in the family Flacourtiaceae, but the genus Laetia and its relatives were moved to the Salicaceae based on analyses of DNA data. Irenodendron was later hypothesized to be more closely related to the genera Ryania, Trichostephanus, and Piparea due to the presence of an apically divided style, and wood with dark heartwood and large rays; it differs from those genera in having cup-shaped bracts under the flowers and in lacking staminodes.

Macrothumia is a genus in the willow family Salicaceae with a single species Macrothumia kuhlmannii. It is a tree native to the states of Bahia, Espírito Santo, and Minas Gerais inBrazil. Formerly classified in the genus Banara in the family Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in Ahernia, Hasseltia, and Pleuranthodendron are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Macrothumia differs from its close relatives in having a congested fascicle- or umbel-like inflorescence and a large fruit. The genus name is derived from the Greek word μακροθυμία, which means long-suffering and enduring patience.
Tetrathylacium is a genus of two species of shrubs and small trees in the family Salicaceae native to the southern Central America and northern South America. Previously it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae but was moved along with its close relatives to the Salicaceae based on analyses of DNA data. Tetrathylacium is rather unique in the Samydaceae in having tightly arranged panicles of spikes, four sepals and stamens, and non-arillate seeds. The stems are often inhabited by ants, and T. macrophyllum is suspected to have locust pollination.















