
The Malpighiales comprise one of the largest orders of flowering plants, containing about 36 families and more than 16,000 species, about 7.8% of the eudicots. The order is very diverse, containing plants as different as the willow, violet, poinsettia, manchineel, rafflesia and coca plant, and are hard to recognize except with molecular phylogenetic evidence. It is not part of any of the classification systems based only on plant morphology. Molecular clock calculations estimate the origin of stem group Malpighiales at around 100 million years ago (Mya) and the origin of crown group Malpighiales at about 90 Mya.

The Salicaceae is the willow family of flowering plants. The traditional family included the willows, poplar, aspen, and cottonwoods. Genetic studies summarized by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) have greatly expanded the circumscription of the family to contain 56 genera and about 1220 species, including the Scyphostegiaceae and many of the former Flacourtiaceae.

The Flacourtiaceae is a defunct family of flowering plants whose former members have been scattered to various families, mostly to the Achariaceae and Salicaceae. It was so vaguely defined that hardly anything seemed out of place there and it became a dumping ground for odd and anomalous genera, gradually making the family even more heterogeneous. In 1975, Hermann Sleumer noted that "Flacourtiaceae as a family is a fiction; only the tribes are homogeneous."
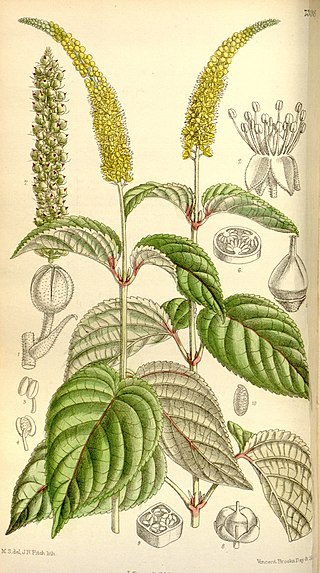
Abatia is a genus of about ten species of Central and South American trees in the family Salicaceae. Previously, it was treated in the family Flacourtiaceae, or tribe Abatieae of the family Passifloraceae or Samydaceae by G. Bentham & J.D. Hooker and Hutchinson.

Richard Spruce was an English botanist specializing in bryology. One of the great Victorian botanical explorers, Spruce spent 15 years exploring the Amazon from the Andes to its mouth, and was one of the first Europeans to visit many of the places where he collected specimens. Spruce discovered and named a number of new plant species, and corresponded with some of the leading botanists of the nineteenth century.
Astrocasia is a plant genus of the family Phyllanthaceae first described as a genus in 1905. It is included in the subtribe Astrocasiinae. It is native to Mesoamerica, northern South America, and the western part of the West Indies. Plants are mostly dioecious, except for Astrocasia diegoae which is monoecious, and some individuals of A. neurocarpa and A. tremula.
- Astrocasia austinii(Standl.) G.L.Webster - Izabal
- Astrocasia diegoaeJ.Jiménez Ram. & Mart.Gord. - Guerrero
- Astrocasia jacobinensis(Müll.Arg.) G.L.Webster - Bahia, Bolivia
- Astrocasia neurocarpa(Müll.Arg.) I.M.Johnst. ex Standl. - Oaxaca, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, Tamaulipas
- Astrocasia peltataStandl. - Costa Rica, Nayarit, Jalisco
- Astrocasia tremula (Griseb.) G.L.Webster - Mexico, Central America, West Indies, northern South America

Samydaceae is a family of tropical and subtropical woody plants, its best known genus being Casearia. It has always been of uncertain placement, in the past usually being submerged in the family Flacourtiaceae.
Dipentodon is a genus of flowering plants in the family Dipentodontaceae. Its only species, Dipentodon sinicus, is a small, deciduous tree native to southern China, northern Myanmar, and northern India. It has been little studied and until recently its affinities remained obscure.

Huerteales is the botanical name for an order of flowering plants. It is one of the 17 orders that make up the large eudicot group known as the rosids in the APG III system of plant classification. Within the rosids, it is one of the orders in Malvidae, a group formerly known as eurosids II and now known informally as the malvids. This is true whether Malvidae is circumscribed broadly to include eight orders as in APG III, or more narrowly to include only four orders. Huerteales consists of four small families, Petenaeaceae, Gerrardinaceae, Tapisciaceae, and Dipentodontaceae.

Gerrardina is a genus of two species of trees, shrubs, and scrambling shrubs found in southeastern Africa. Until recently, the genus was placed in the polyphyletic family Flacourtiaceae, but it was abnormal there due to its apical placentation, small embryos, and mucilaginous foliar epidermis. Analyses of DNA data indicated that the genus did not fit in any known plant family and not clearly in any then-recognized order, and a new family, Gerrardinaceae, was thus created for it. Later analyses of additional DNA data and data from wood anatomy indicated that the family should be placed in the order Huerteales.

Pineda is a genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It contains two species of shrubs: Pineda incana, which is native to the Andes of Ecuador and Peru, and Pineda ovata, which is native to the Andes of Bolivia.

Hasseltia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It contains four species of small to medium-sized trees native to the neotropics, ranging from Mexico south to Brazil and Bolivia. The genus is named for the Dutch physician and botanist Johan Conrad van Hasselt.
Macrohasseltia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of tree: Macrohasseltia macroterantha, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Macrohasseltia is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Olmediella, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.

Olmediella is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Olmediella betschleriana, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Olmediella is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Bennettiodendron, Carrierea, Idesia, Itoa, Macrohasseltia, Poliothyrsis, and even the willows (Salix) and cottonwoods (Populus) themselves.
Aphaerema was formerly a genus of flowering plants in the Flacourtiaceae, consisting of one species of small shrubs, Aphaerema spicata, which is native to Brazil and Argentina. Later studies indicated that Aphaerema should be classified in the willow family, Salicaceae, and combined with the genus Abatia. Unfortunately, because the name Abatia spicata was already used, the species was given the new name Abatia angeliana, in honor of Brazilian botanist João Angely. Aphaerema is one of the few groups of Salicaceae with opposite leaves.
Hasseltiopsis is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Salicaceae. It consists of one species of trees: Hasseltiopsis dioica, which is native to Central America. Formerly placed in the heterogeneous family Flacourtiaceae, Hasseltiopsis is now classified in Salicaceae, along with close relatives Prockia, Pineda, Neosprucea, and Banara.
Priamosia was formerly a genus of flowering plants in the Flacourtiaceae, consisting of one species of shrubs, Priamosia domingensis, which is native to the Dominican Republic and Haiti. Later studies indicated that Priamosia should be classified in the willow family, Salicaceae, and combined with the genus Xylosma. Priamosia was previously separated from the genus Xylosma because it has only four stamens, while Xylosma has eight or more.
Christian Leberecht von Prøck (1718-1780) was a Danish baron. He served as Governor-General of the Danish West Indies colonies from 1756–1766. In 1768, Pröck became a diocese commander over Iceland and the Faroe Islands. He died on 4 September 1780 in Copenhagen.
Ophiobotrys zenkeri is a species of tree native to tropical Africa from Ivory Coast to Gabon and is the only member of the genus Ophiobotrys. Formerly classified in the Flacourtiaceae, phylogenetic analyses based on DNA data indicate that this species, along with its close relatives in the Asian genera Osmelia and Pseudosmelia, are better placed in a broadly circumscribed Salicaceae. Ophiobotrys differs from its close relatives in having 5 sepals, 5(-6) stamens, one divided style, and terminal inflorescences.

Billardiera drummondii is a slender climber in the Pittosporaceae family, native to the south-west of Western Australia, which grows in Eucalypt woodland on coastal soils. Its flowers are blue to purple and seen in January.












