Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1951 to 1955. Apart from two years between 1922 and 1924, he was a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1900 to 1964 and represented a total of five constituencies. Ideologically an adherent to economic liberalism and imperialism, he was for most of his career a member of the Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955. He was a member of the Liberal Party from 1904 to 1924.
Sir Edward Howard Marsh was a British polymath, translator, arts patron and civil servant. He was the sponsor of the Georgian school of poets and a friend to many poets, including Rupert Brooke and Siegfried Sassoon. In his career as a civil servant he worked as private secretary to a succession of the United Kingdom's most powerful ministers, particularly Winston Churchill. He was a discreet but influential figure within Britain's homosexual community.

Sir Martin John Gilbert was a British historian and honorary Fellow of Merton College, Oxford. He was the author of 88 books, including works on Winston Churchill, the 20th century, and Jewish history including the Holocaust. He was a member of the Chilcot Inquiry into Britain's role in the Iraq War.

Alan McCrae Moorehead, was a war correspondent and author of popular histories, most notably two books on the nineteenth-century exploration of the Nile, The White Nile (1960) and The Blue Nile (1962). Australian-born, he lived in England, and Italy, from 1937.

The River War: An Historical Account of the Reconquest of the Soudan (1899), by Winston Churchill, is a history of the conquest of the Sudan between 1896 and 1899 by Anglo-Egyptian forces led by Lord Kitchener. He defeated the Sudanese Dervish forces, led by Khalifa Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, heir to the self-proclaimed Mahdi Muhammad Ahmad, who had vowed to conquer Egypt and drive out the Ottomans. The first, two-volume, edition includes accounts of Churchill's own experiences as a British Army officer during the war, and his views on its conduct.
Richard M. Langworth CBE is an author based in Moultonborough, New Hampshire, United States, and Eleuthera, Bahamas, who specialises in automotive history and Winston Churchill. He was editor of The Packard Cormorant from 1975 to 2001 and is a Trustee of the Packard Motorcar Foundation in Detroit, Michigan. His works have won awards from the Antique Automobile Club of America, Society of Automotive Historians, Old Cars Weekly, Packard Club and Graphic Arts Association of New Hampshire.

The Story of the Malakand Field Force: An Episode of Frontier War was an 1898 book written by Winston Churchill; it was his first published work of non-fiction.

My Early Life, also known in the US as A Roving Commission: My Early Life, is a 1930 book by Winston Churchill. It is an autobiography from his birth in 1874 to around 1902. The book closes with mention of his marriage in 1908, stating that he lived happily ever after.

The Sunday Dispatch was a prominent British newspaper, published between 27 September 1801 and 18 June 1961. It was ultimately discontinued due to its merger with the Sunday Express.

The siege of Malakand was the 26 July – 2 August 1897 siege of the British garrison in the Malakand region of colonial British India's North West Frontier Province. The British faced a force of Pashtun tribesmen whose tribal lands had been bisected by the Durand Line, the 1,519 mile (2,445 km) border between Afghanistan and British India drawn up at the end of the Anglo-Afghan wars to help hold back what the British feared to be the Russian Empire's spread of influence towards the Indian subcontinent.

General Sir Bindon Blood, was a British Army commander who served in Egypt, Afghanistan, India, and South Africa.

Lays of Ancient Rome is an 1842 collection of narrative poems, or lays, by Thomas Babington Macaulay. Four of these recount heroic episodes from early Roman history with strong dramatic and tragic themes, giving the collection its name. Macaulay also included two poems inspired by recent history: Ivry (1824) and The Armada (1832).
The First Mohmand campaign was a British military campaign against the Mohmands from 1897 to 1898.

The Second World War is a history of the period from the end of the First World War to July 1945, written by Winston Churchill. Churchill labelled the "moral of the work" as follows: "In War: Resolution, In Defeat: Defiance, In Victory: Magnanimity, In Peace: Goodwill".

Winston Churchill, in addition to his careers of soldier and politician, was a prolific writer under the variant of his full name 'Winston S. Churchill'. After being commissioned into the 4th Queen's Own Hussars in 1895, Churchill gained permission to observe the Cuban War of Independence, and sent war reports to The Daily Graphic. He continued his war journalism in British India, at the Siege of Malakand, then in the Sudan during the Mahdist War and in southern Africa during the Second Boer War.
Ian Hamilton's March is a book written by Winston Churchill. It is a description of his experiences accompanying the British army during the Second Boer War, continuing after the events described in London to Ladysmith via Pretoria.
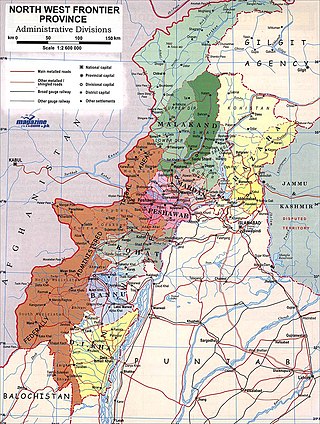
The Malakand Agency was one of the agencies in the North West Frontier Province of British India and later of Pakistan until 2010. It included the princely states of Chitral, Dir and Swat, and an area around the Malakand Pass known as the Malakand Protected Area. The largest city in the area was Mingora, while the three state capitals were Chitral, Dir, and Saidu Sharif. In 1970, following the abolition of the princely states, the agency became the Malakand Division, which was divided into districts, one of which was the Malakand Protected Area, known as Malakand District. In 2000 the Malakand Division was abolished. Despite the constitutional changes since 1970, the expression Malakand Agency is still used, sometimes of the entire area of the former Agency, but more often of Malakand District.

Batkhela is a city, tehsil and the district headquarter of the Malakand District within the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. According to the 2017 Census of Pakistan, the population of Batkhela was recorded at 68,200. Batkhela is considered as one of the most popular business cities in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. A water canal that pours into a small dam in the Jabban area near Batkhela is the main source of electricity production here.

The World Crisis is Winston Churchill's account of the First World War, published in six volumes. Published between 1923 and 1931: in many respects it prefigures his better-known multivolume The Second World War. The World Crisis is analytical and, in some parts, a justification by Churchill of his role in the war. Churchill denied it was a "history," describing the work in Vol. 2 as "a contribution to history of which note should be taken together with other accounts."

The early life of Winston Churchill covers the period from his birth on 30 November 1874 to 31 May 1904 when he formally crossed the floor of the House of Commons, defecting from the Conservative Party to sit as a member of the Liberal Party.