| Part of a series on |
| Sikhism |
|---|
 |
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 10,000-15,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Punjabi • Indonesian |
Sikhism in Indonesia is a small religious minority in Indonesia. There are about 10,000 to 15,000 Sikhs in Indonesia. [1]
| Part of a series on |
| Sikhism |
|---|
 |
 | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 10,000-15,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Punjabi • Indonesian |
Sikhism in Indonesia is a small religious minority in Indonesia. There are about 10,000 to 15,000 Sikhs in Indonesia. [1]

Hindus or Sanatani are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism or Sanātana Dharma. Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to religion:

Southeast Asia is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the parts of Southeast Asia that lie south of the Equator.
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental, or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greater autonomy are usually not considered separatists. Some discourse settings equate separatism with religious segregation, racial segregation, or sex segregation, while other discourse settings take the broader view that separation by choice may serve useful purposes and is not the same as government-enforced segregation. There is some academic debate about this definition, and in particular how it relates to secessionism, as has been discussed online.

Hinduism in Southeast Asia had a profound impact on the region's cultural development and its history. As the Indic scripts were introduced from the Indian subcontinent, people of Southeast Asia entered the historical period by producing their earliest inscriptions around the 1st to 5th century CE. Today, Hindus in Southeast Asia are mainly Overseas Indians and Balinese. There are also Javanese and Balamon Cham minority in Cambodia and south central Vietnam who also practice Hinduism.

Laskar Jihad was an Islamist and anti-Christian Indonesian militia, which was founded and led by Jafar Umar Thalib. At present, the militia is believed to have disbanded.

The Eastern religions are the religions which originated in East, South and Southeast Asia and thus have dissimilarities with Western, African and Iranian religions. Eastern religions include:

Recent archaeological and other evidence suggests Hinduism has had some cultural, economic, political and religious influence in the Philippines. Among these is the 9th century Laguna Copperplate Inscription found in 1989, deciphered in 1992 to be Kawi script with Sanskrit words; the golden Agusan statue discovered in another part of Philippines in 1917 has also been linked to Hinduism.

Southeast Asian music encapsulates numerous musical traditions and styles in many countries of Southeast Asia. This subregion consists of eleven countries, namely, Brunei, Cambodia, East Timor, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam, which accommodate hundreds of ethnic groups. Thousands of styles of music are present as a result of regional groups speaking many languages all over the subregion of Asia. Regionalism is usually accepted and celebrated, however, it is sometimes suppressed by the people, even though countries from southeast Asia are trying to construct national cultures. Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Christianity are the paramount faiths in Southeast Asia. Throughout history to the present time, instrumental and vocal music has been centralized and focused on the religious life of subregional Asia. Urbanization has helped to assimilate musical and religious practices. Although modernization has put a significant threat on the distinctive regional music traditions, most countries in the region have maintained their own unique style and nature of music that encapsulates various periods of development in music, culture, and belief.

Indian Indonesians are Indonesians whose ancestors originally came from the Indians subcontinent. Therefore, this term can be regarded as a blanket term for not only Indonesian Indians but also Indonesians with other South Asian ancestries. According to the Indian Ministry of External Affairs, there were about 120,000 people of Indian origin as well as 9,000 Indian nationals living and working in Indonesia as of January 2012. Most of them were concentrated in the province of North Sumatra and urban areas such as Banda Aceh, Surabaya, Medan, and Jakarta. However, it is quite impossible to get correct statistical figures on the Indian Indonesian population, because some of them have merged and assimilated with the indigenous population to become indistinguishable from native Indonesians.
Asia is the largest and most populous continent and the birthplace of many religions including Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, Islam, Jainism, Judaism, Shinto, Sikhism, Taoism, and Zoroastrianism. All major religious traditions are practiced in the region and new forms are constantly emerging. Asia is noted for its diversity of culture. Islam and Hinduisms are the largest religion in Asia with approximately 1.2-1.3 billion adherents each.
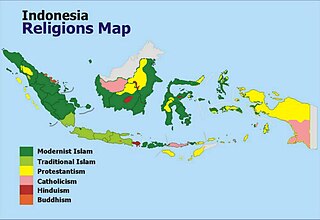
Several different religions are practised in Indonesia. Indonesia is officially a presidential republic and a unitary state without an established state religion. Indonesia has the world's largest Muslim population and the first principle of Indonesia's philosophical foundation, Pancasila, requires its citizens to state the belief in "the one and almighty God". Although, as explained by the Constitutional Court, this first sila of Pancasila is an explicit recognition of divine substances and meant as a principle on how to live together in a religiously diverse society. However, blasphemy is a punishable offence and the Indonesian government has a discriminatory attitude towards its numerous tribal religions, atheist and agnostic citizens. In addition, the Aceh province officially applies Sharia law and is notorious for its discriminatory practices towards religious and sexual minorities. There are also Islamic fundamentalist movements in several parts of the country with overwhelming Muslim majorities.
Growth of religion involves the spread of individual religions and the increase in the numbers of religious adherents around the world. In sociology, desecularization is the proliferation or growth of religion, most commonly after a period of previous secularization. Statistics commonly measure the absolute number of adherents, the percentage of the absolute growth per-year, and the growth of converts in the world.

Sikhism is a recognised minority religion in Thailand, with about 100,000 adherents. The religion was brought by migrants from India who began to arrive in the late 19th century. There are about twenty or Gurdwaras in the country, including the Gurdwara Sri Guru Singh Sabha in Bangkok.

Singaporean Sikhs numbered 12,051 at the country's 2020 census, forming the country's sixth largest religious group at 0.35% of the population. Sikhism in Singapore has its roots in the military and policing forces of the British Empire. Currently, there are 12,000–15,000 Sikhs in Singapore. There are 7 gurdwaras along with a missionary society, a welfare society, two youth organizations and two sports clubs. Most Sikhs are from the Jat community.

The Punjabi diaspora refers to the descendants of ethnic Punjabis who emigrated out of the Punjab region in the northern part of the South Asia to the rest of the world. Punjabis are one of the largest ethnic groups in both the Pakistani and Indian diasporas. The Punjabi diaspora numbers around the world has been given between 3-5 million, mainly concentrated in Britain, Canada, United States, Western Europe, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Australia and New Zealand.
Indians in Brunei consist of Bruneians of Indian descent as well as expatriate professionals that have recently come to the country. According to the Government of India, there are 10,000 Indians living and working in the country.

Sikhism in Japan is a small, minority religion. There are gurdwaras located in Tokyo, Ibaraki and Kobe.

Indonesian horror are the films of the horror genre produced by the Indonesian film industry. Often inspired by local folklore and religious elements, Indonesian horror films have been produced in the country since the 1960s. After a hiatus during the Suharto era in the 1990s, when censorship affected production, Indonesian horror films continued being produced following Reformasi in 1998.