
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development.

A reusable launch vehicle has parts that can be recovered and reflown, while carrying payloads from the surface to outer space. Rocket stages are the most common launch vehicle parts aimed for reuse. Smaller parts such as rocket engines and boosters can also be reused, though reusable spacecraft may be launched on top of an expendable launch vehicle. Reusable launch vehicles do not need to make these parts for each launch, therefore reducing its launch cost significantly. However, these benefits are diminished by the cost of recovery and refurbishment.

A solid rocket booster (SRB) is a large solid propellant motor used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from initial launch through the first ascent. Many launch vehicles, including the Atlas V, SLS and space shuttle, have used SRBs to give launch vehicles much of the thrust required to place the vehicle into orbit. The space shuttle used two space shuttle SRBs, which were the largest solid propellant motors ever built and the first designed for recovery and reuse. The propellant for each solid rocket motor on the space shuttle weighed approximately 500,000 kilograms.

Space burial is the launching of human remains into space. Missions may go into orbit around the Earth or to extraterrestrial bodies such as the Moon, or farther into space.
Orbital Sciences Corporation was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other government customers. In 2014, Orbital merged with Alliant Techsystems to create a new company called Orbital ATK, Inc., which in turn was purchased by Northrop Grumman in 2018. The remnants of the former Orbital Sciences Corporation today are a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman, known as Northrop Grumman Space Systems.

Falcon 1 was a small-lift launch vehicle that was operated from 2006 to 2009 by SpaceX, an American aerospace manufacturer. On 28 September 2008, Falcon 1 became the first privately-developed fully liquid-fueled launch vehicle to go into orbit around the Earth.
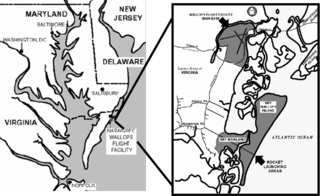
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

Falcon 9 is a partially reusable heavy-lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, manufactured and launched by American aerospace company SpaceX.
UP Aerospace, Inc. is a private spaceflight corporation headquartered in Denver, Colorado. UP Aerospace provides sub-orbital transportation for corporate, military and educational payloads, via their SpaceLoft XL sounding rocket launch vehicles.
Celestis, Inc. is a company that launches cremated human remains into space, a procedure known as a space burial. It is a subsidiary of the private space company Space Services Inc. The company purchases launches as a secondary payload on various launch vehicles, and launches samples of a person's cremated remains. Launching an individual's entire cremated remains would be prohibitively expensive for most people, so Celestis launches small portions of 1-7 grams.
The Conestoga was a launch vehicle design funded by Space Services Inc. of America (SSIA) of Houston, Texas. Conestoga originally consisted of surplus LGM-30 Minuteman stages with additional strap-on boosters, as required for larger payloads. It was the world's first privately funded commercial rocket, but was launched only three times before the program was shut down.

Antares, known during early development as Taurus II, is an expendable launch system developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation and the Pivdenne Design Bureau to launch the Cygnus spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of NASA's COTS and CRS programs. Able to launch payloads heavier than 8,000 kg (18,000 lb) into low Earth orbit, Antares is currently the largest rocket operated by Northrop Grumman. Antares launches from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport and made its inaugural flight on April 21, 2013.

RatSat or DemoSat was an aluminum mass simulator on the fourth flight of the Falcon 1 rocket, launched on 28 September 2008. Ratsat remained bolted to the second stage of the carrier rocket after reaching low Earth orbit. It is an aluminium alloy chamber in hexagonal prism shape with 1.5 m (5 ft) length.

SpaceX manufactures launch vehicles to operate its launch provider services and to execute its various exploration goals. SpaceX currently manufactures and operates the Falcon 9 Full Thrust family of medium-lift launch vehicles and the Falcon Heavy family of heavy-lift launch vehicles – both of which powered by SpaceX Merlin engines and employing VTVL technologies to reuse the first stage. As of 2020, the company is also developing the fully reusable Starship launch system, which will replace the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy.

Orbital-3, also known as Orb-3, was an attempted flight of Cygnus, an automated cargo spacecraft developed by United States-based company Orbital Sciences, on 28 October 2014. The mission was intended to launch at 22:22:38 UTC that evening. This flight, which would have been its fourth to the International Space Station and the fifth of an Antares launch vehicle, resulted in the Antares rocket exploding seconds after liftoff.

The Falcon 9 v1.0 was the first member of the Falcon 9 launch vehicle family, designed and manufactured by SpaceX in Hawthorne, California. Development of the medium-lift launcher began in 2005, and it first flew on June 4, 2010. The Falcon 9 v1.0 then launched four Dragon cargo spacecraft: one on an orbital test flight, then one demonstration and two operational resupply missions to the International Space Station under a Commercial Resupply Services contract with NASA.

OA-4, previously known as Orbital-4, was the fourth successful flight of the Orbital ATK uncrewed resupply spacecraft Cygnus and its third flight to the International Space Station (ISS) under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) contract with NASA. With the Antares launch vehicle undergoing a redesign following its failure during the Orb-3 launch, OA-4 was launched by an Atlas V launch vehicle. Following three launch delays due to inclement weather beginning on 3 December 2015, OA-4 was launched at 21:44:57 UTC on 6 December 2015. With a liftoff weight of 7,492 kg (16,517 lb), OA-4 became the heaviest payload ever launched on an Atlas V. The spacecraft rendezvoused with and was berthed to the ISS on 9 December 2015. It was released on 19 February 2016 after 72 days at the International Space Station. Deorbit occurred on 20 February 2016 at approximately 16:00 UTC.

Electron is a two-stage, partially recoverable orbital launch vehicle developed by Rocket Lab, an American aerospace company with a wholly owned New Zealand subsidiary. Electron was developed to service the commercial small satellite launch market. Its Rutherford engines are the first electric-pump-fed engine to power an orbital-class rocket. Electron is often flown with a kickstage or Rocket Lab's Photon spacecraft. Although the rocket was designed to be expendable, Rocket Lab has recovered the first stage twice and is working towards the capability of reusing the booster. The Flight 26 (F26) booster has featured the first helicopter catch recovery attempt.
Space Vector Corporation (SVC) is a United States-based company that provides aerospace products and services to government and commercial customers. Space Vector is headquartered in Chatsworth, California and is a privately held small business. Its primary products are flight safety and system batteries, GPS tracking systems, custom avionics and structures, attitude control systems, pneumatic components, and separation systems. Space Vector also provides launch services as a prime contractor under the Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) Sounding Rocket Program (SRP-3) which includes performing vehicle integration activities, end-to-end system testing, payload integration, launch operations, and mission analysis and design.

A super heavy-lift launch vehicle is a rocket that can lift to low Earth orbit a "super heavy payload", which is defined as more than 50 metric tons (110,000 lb) by the United States and as more than 100 metric tons (220,000 lb) by Russia. It is the most capable launch vehicle classification by mass to orbit, exceeding that of the heavy-lift launch vehicle classification.














