Articles related to anatomy include:

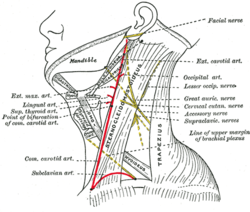
The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges.

The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back.

The paired submandibular glands are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. They each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as the parotid secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3mm.

The digastric muscle is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle bellies include the suspensory muscle of duodenum, omohyoid, occipitofrontalis.
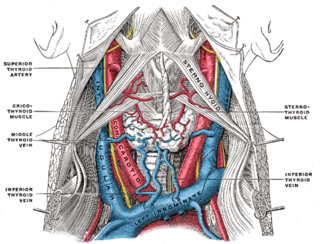
The internal jugular vein is a paired jugular vein that collects blood from the brain and the superficial parts of the face and neck. This vein runs in the carotid sheath with the common carotid artery and vagus nerve.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.

The hyoglossus is a thin and quadrilateral intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It originates from the hyoid bone; it inserts onto the side of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. It acts to depress and retract the tongue.
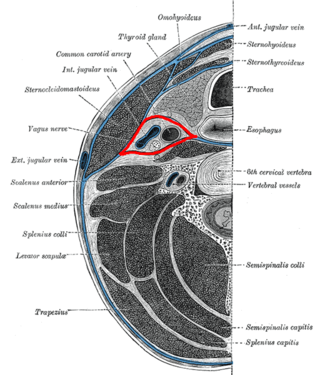
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve, ansa cervicalis, and sympathetic trunk. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein.

The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery opposite the facial artery. Its path is below the posterior belly of digastric to the occipital region. This artery supplies blood to the back of the scalp and sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles in the back and neck.
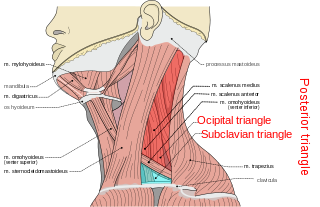
The posterior triangle is a region of the neck.
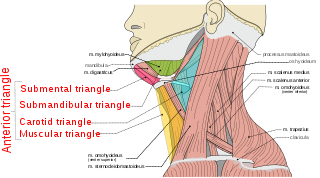
The anterior triangle is a region of the neck.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.

The submental triangle is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The parapharyngeal space, is a potential space in the head and the neck. It has clinical importance in otolaryngology due to parapharyngeal space tumours and parapharyngeal abscess developing in this area. It is also a key anatomic landmark for localizing disease processes in the surrounding spaces of the neck; the direction of its displacement indirectly reflects the site of origin for masses or infection in adjacent areas, and consequently their appropriate differential diagnosis.