
The Indian National Satellite System or INSAT, is a series of multipurpose geostationary satellites launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to satisfy telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue operations. Commissioned in 1983, INSAT is the largest domestic communication system in the Indo-Pacific Region. It is a joint venture of the Department of Space, Department of Telecommunications, India Meteorological Department, All India Radio and Doordarshan. The overall coordination and management of INSAT system rests with the Secretary-level INSAT Coordination Committee.

The GSAT satellites are India's indigenously developed communications satellites, used for digital audio, data and video broadcasting. As of 5 December 2018, 20 GSAT satellites manufactured by ISRO have been launched, out of which 14 are in service.
MEASAT Satellite Systems Sdn. Bhd., formerly Binariang Satellite Systems Sdn. Bhd., is a Malaysian communications satellite operator that owns and operates the MEASAT and AFRICASAT spacecraft. The company provides satellite services to leading Malaysian broadcasters Direct-To-Home, (DTH) platforms and telecom operators. With capacity across six communication satellites, the company provides satellite services to over 150 countries.
Tata Play is an Indian Subscription based Satellite television (DTH) service provider using MPEG-4 digital compression technology, transmitting using INSAT-4A GSAT-10 and GSAT-24 satellites. Incorporated in 2005, it currently offers 630+ channels, 543 SD channels and 91 HD channels and services, along with many other value added services. Tata Play is the largest DTH service provider in India. As of March 2023, according to TRAI Tata Play serves 21.3 million subscribers which is 32.65% of total DTH users in India.

The Master Control Facility (MCF) is a facility set up by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in the city of Hassan in the Indian state of Karnataka. Established in 1982, this facility is responsible for monitoring and controlling geostationary and geosynchronous satellites launched by ISRO. This was the only Master Control Facility of ISRO till another one was established in Bhopal in 2005.

INSAT 3E is a defunct communication satellite built by Indian Space Research Organisation. It was launched on September 28, 2003, from the European Space Agency's spaceport in French Guiana on board the Ariane rocket. The satellite had a launch mass of 2750 kilograms. It is the 4th satellite launched in the INSAT-3 series for INSAT. It was designed for providing high-speed communication, Television, VSAT & Tele-education services and was an important landmark in Indian Space Programme.
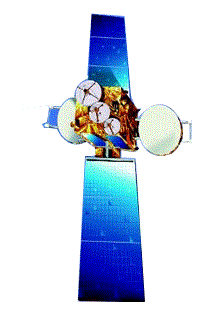
INSAT-3C is a multipurpose satellite built by ISRO and launched by Arianespace in Jan 2002. INSAT-3C is the second satellite of the INSAT-3 series. All the transponders provide coverage over India. Insat-3C is controlled from the Master Control Facility at Hassan in Karnataka. It will provide voice, video and digital data services to India and neighboring countries.

INSAT-4A was the first one in the INSAT-4 Satellites series, providing services in the Ku and C band frequency bands. At the time of launch, it was the heaviest satellite India had produced. The Ku transponders cover the Indian main land and C-Band transponders cover an extended area. It has a dozen Ku transponders and another dozen of C-band transponders. This spacecraft was placed at 83°E along with INSAT-2E and INSAT-3B, by Ariane launch vehicle (ARIANE5-V169).
Direct-to-Home (DTH) television is a method of receiving satellite television by means of signals transmitted from direct-broadcast satellites. The Government of India (GoI) permitted the reception and distribution of satellite television signals in November 2000. The first DTH service in the country was launched by Dish TV on 2 October 2003. DD Free Dish, the first free DTH service in India, was launched by public broadcaster Prasar Bharati in December 2004.
INSAT-4CR was a communications satellite operated by ISRO as part of the Indian National Satellite System. Launched in September 2007, it replaced the INSAT-4C satellite which had been lost in a launch failure the previous year. The satellite was initially stationed in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 74 degrees east, with expected operational life of at least ten years, however this may have been reduced by the underperformance of the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle which placed it into orbit. INSAT-4CR is planned to be replaced by GSAT-31, which was launched on February 6, 2019.
GSAT-14 is an Indian communications satellite launched in January 2014. It replaced the GSAT-3 satellite, which was launched in 2004. GSAT-14 was launched by a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk.II, which incorporated an Indian-built cryogenic engine on the third stage.
GSAT-10 is an Indian communication satellite which was launched by Ariane-5ECA carrier rocket in September 2012. It has 12 KU Band, 12 C Band and 6 lower extended c band transponders, and included a navigation payload to augment GAGAN capacity. Following its launch and on-orbit testing, it was placed in Geosynchronous orbit at 83.0° East, from where it will provide communication services in India.

INSAT-4E, also known as GSAT-6, is a member of the INSAT family and is a multimedia communication satellite that will offer a Satellite Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (S-DMB) service across several digital multimedia terminals or consoles which can be used to provide information services to vehicles on the fly and to the mobile phones. The satellite can be used for other social and strategic applications.
GSAT-7 or INSAT-4F is a multi-band military communications satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation. The Indian Navy is the user of the multi-band communication spacecraft, which has been operational since September 2013. According to defense experts, the satellite will enable the navy to extend its blue water capabilities and stop relying on foreign satellites like Inmarsat, which provide communication services to its ships.
GSAT-16 is the 11th Indian communication satellite, meant to increase the number of transponders available for satellite-based telecommunication, television, and VSAT services in India. GSAT-16 is similar to GSAT-15 with each satellite weighing 3,150 kg and having power generation capacity of 6.8 kW.
INSAT-4B was an Indian communications satellite which forms part of the Indian National Satellite System. Launched in 2007, it was placed in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 93.48° East.
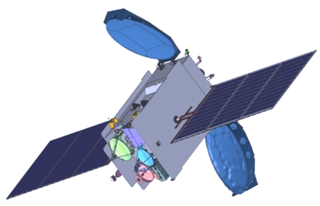
GSAT-17 is an Indian communications satellite. Built by ISRO and operated by INSAT, it carries 24 C-band, 2 lower C-band, 12 upper C-band, 2 CxS, and 1 SxC transponders. It additionally carries a dedicated transponder for data relay (DRT) and search-and-rescue (SAR) services. At the time of launch, GSAT-17 was the heaviest satellite built by ISRO.

GSAT-31 is a high-throughput telecommunication satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
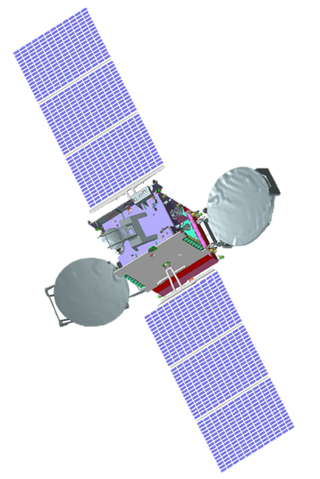
GSAT-30 is a telecommunications satellite developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
CMS-02 is an Indian Communication Satellite built by ISRO. The CMS-02 satellite is funded, owned and operated by New Space India Limited. Cost of spacecraft was around ₹400 crore. The entire capacity onboard CMS-02 satellite will be leased to Tata Play. The satellite was placed into orbit by using Ariane 5 rocket.










