A beefsteak, often called just steak, is a flat cut of beef with parallel faces, usually cut perpendicular to the muscle fibers. In common restaurant service a single serving has a raw mass ranging from 120 to 600 grams. Beef steaks are usually grilled, pan-fried, or broiled. The more tender cuts from the loin and rib are cooked quickly, using dry heat, and served whole. Less tender cuts from the chuck or round are cooked with moist heat or are mechanically tenderized.

Chateaubriand is a dish that traditionally consists of a large front cut fillet of tenderloin grilled between two lesser pieces of meat that are discarded after cooking. While the term originally referred to the preparation of the dish, Auguste Escoffier named the specific front cut of the tenderloin the Chateaubriand.

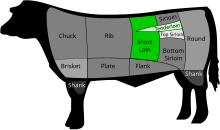
A beef tenderloin, known as an eye fillet in Australasia, filet in France, filet mignon in Brazil, and fillet in the United Kingdom and South Africa, is cut from the loin of beef.
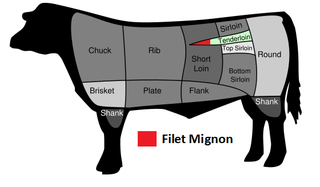
Filet mignon is a cut of meat taken from the smaller end of the tenderloin, or psoas major of a cow. In French, it mostly refers to cuts of pork tenderloin.

In American butchery, the sirloin steak is cut from the sirloin, the subprimal posterior to the short loin where the T-bone, porterhouse, and club steaks are cut. The sirloin is divided into several types of steak. The top sirloin is the most prized of these and is specifically marked for sale under that name. The bottom sirloin, which is less tender and much larger, is typically marked for sale simply as "sirloin steak". The bottom sirloin, in turn, connects to the sirloin tip roast.

The strip steak is a cut of beef steaks from the short loin of a cow. It consists of a muscle that does little work, the longissimus, making the meat particularly tender, although not as tender as the nearby psoas major or tenderloin. Unlike the tenderloin, the longissimus is a sizable muscle, allowing it to be cut into larger portions.

A pork chop, like other meat chops, is a loin cut taken perpendicular to the spine of the pig and is usually a rib or part of a vertebra. Pork chops are unprocessed and leaner than other cuts. Chops are commonly served as an individual portion, and can be accompanied with applesauce, vegetables, and other sides. Pork is one of the most commonly consumed meats in the world. In the United States, pork chops are the most commonly consumed meat cut from the pork loin and account for 10% of total pork consumption.

Pork ribs are a cut of pork popular in Western and Asian cuisines. The ribcage of a domestic pig, meat and bones together, is cut into usable pieces, prepared by smoking, grilling, or baking – usually with a sauce, often barbecue – and then served.

The tri-tip is a triangular cut of beef from the bottom sirloin subprimal cut, consisting of the tensor fasciae latae muscle. Untrimmed, the tri-tip weighs around 5 pounds. In the US, the tri-tip is taken from NAMP cut 185C.

A round steak is a beef steak from the "round", the rear leg of the cow. The round is divided into cuts including the eye (of) round, bottom round, and top round, with or without the "round" bone (femur), and may include the knuckle, depending on how the round is separated from the loin. This is a lean cut and it is moderately tough. Lack of fat and marbling makes round dry out when cooked with dry-heat cooking methods like roasting or grilling. Round steak is commonly prepared with slow moist-heat methods including braising, to tenderize the meat and maintain moisture. The cut is often sliced thin, then dried or smoked at low temperature to make jerky.

During butchering, beef is first divided into primal cuts, pieces of meat initially separated from the carcass. These are basic sections from which steaks and other subdivisions are cut. Since the animal's legs and neck muscles do the most work, they are the toughest; the meat becomes more tender as distance from hoof and horn increases.

Bistecca alla fiorentina is an Italian steak dish made of young steer (vitellone) or heifer (scottona) that is one of the most famous dishes in Tuscan cuisine. It is loin steak on the bone cooked on a grill until rare (50 °C).
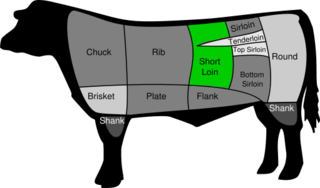
Short loin is the American name for a cut of beef that comes from the back of the cattle. It contains part of the spine and includes the top loin and the tenderloin. This cut yields types of steak including porterhouse, strip steak, and T-bone. The T-bone is a cut that contains less of the tenderloin than does the porterhouse. Webster's Dictionary defines it as "a portion of the hindquarter of beef immediately behind the ribs that is usually cut into steaks." The short loin is considered a tender beef.

Top sirloin is a cut of beef from the primal loin or subprimal sirloin. Top sirloin steaks differ from sirloin steaks in that the bone and the tenderloin and bottom round muscles have been removed; the remaining major muscles are the gluteus medius and biceps femoris.

A primal cut or cut of meat is a piece of meat initially separated from the carcass of an animal during butchering. Examples of primals include the round, loin, rib, and chuck for beef or the ham, loin, Boston butt, and picnic for pork.

A meat chop is a cut of meat cut perpendicular to the spine, and usually containing a rib or riblet part of a vertebra and served as an individual portion. The most common kinds of meat chops are pork and lamb. A thin boneless chop, or one with only the rib bone, may be called a cutlet, though the difference is not always clear. The term "chop" is not usually used for beef, but a T-bone steak is essentially a loin chop, a rib steak and a rib cutlet.

Loin chops can refer to either a commercial cut of pork, or lamb.

A steak is a thick cut of meat generally sliced across the muscle fibers, sometimes including a bone. It is normally grilled or fried. Steak can be diced, cooked in sauce, such as in steak and kidney pie, or minced and formed into patties, such as hamburgers.

Baseball steak is a center cut of beef taken from the top sirloin cap steak. Baseball steaks differ from sirloin steaks in that the bone and the tenderloin and bottom round muscles have been removed; and the cut is taken from biceps femoris. A baseball steak is essentially a center cut top sirloin cap steak. This cut of beef is very lean, and is considered very flavorful.