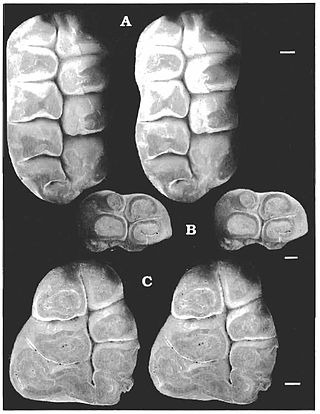
Catopsalis is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of North America. This animal was a relatively large member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. Most multituberculates were much smaller.

Miacidae is a former paraphyletic family of extinct primitive placental mammals that lived in North America, Europe and Asia during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, about 65–33.9 million years ago. These mammals were basal to order Carnivora, the crown-group within the Carnivoraformes.
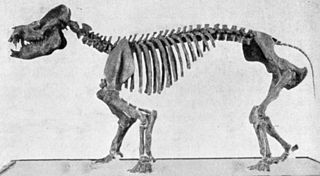
Coryphodon is an extinct genus of pantodonts of the family Coryphodontidae.

Cimolestes is a genus of early eutherians with a full complement of teeth adapted for eating insects and other small animals. Paleontologists have disagreed on its relationship to other mammals, in part because quite different animals were assigned to the genus, making Cimolestes a grade taxon of animals with similar features rather than a genus of closely related ones. Fossils have been found in North America, South America, Europe and Africa. Cimolestes first appeared during the Late Cretaceous of North America. According to some paleontologists, Cimolestes died out at the start of the Paleocene, while others report the genus from the early Eocene.

Patriofelis is an extinct genus of large, cat-like predatory placental mammals from extinct subfamily Oxyaeninae within extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene. It was around 1.2 to 1.8 metres long, not including the tail, and weighed about 40–90 kg, making it around the same size as a modern cougar. It had short legs with broad feet, suggesting that it may have been a poor runner, but a quite good swimmer. As its close relative Oxyaena was a reasonably good climber, it is possible Patriofelis could climb as well. It is found in particular in the Bridger Basin of southwestern Wyoming and at John Day Fossil Beds National Monument, Oregon, both in the United States.

Vulpavus is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.

Tritemnodon was an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived in North America during the early Eocene. Fossils of Tritemnodon agilis have been found in Utah and Wyoming. It was the size of a wolf.

Tillodontia is an extinct suborder of eutherian mammals known from the Early Paleocene to Late Eocene of China, the Late Paleocene to Middle Eocene of North America where they display their maximum species diversity, the Middle Eocene of Pakistan, and the Early Eocene of Europe. Leaving no descendants, they are most closely related to the pantodonts, another extinct group. The tillodonts were medium- to large-sized animals that probably feed on roots and tubers in temperate to subtropical habitats.

The Nacimiento Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in the San Juan Basin of western New Mexico. It has an age of 61 to 65.7 million years, corresponding to the early and middle Paleocene. The formation has yielded an abundance of fossils from shortly after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event that provide clues to the recovery and diversification of mammals following the extinction event.

Sinopa is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct family Sinopidae within extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived in North America and Asia from the early to middle Eocene.

Palaeonictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Palaeonictinae within extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived in Europe and North America from the late Paleocene to the early Eocene.
Schowalteria is a genus of extinct mammal from the Cretaceous of Canada. It is the earliest known representative of order Taeniodonta, a specialised lineage of eutherian mammals otherwise found in Paleocene and Eocene deposits. It is notable for its large size, being among the largest of Mesozoic mammals, as well as its speciation towards herbivory, which in some respects exceeds that of its later relatives.

Palaeanodonta is an extinct clade of stem-pangolins. They were insectivorous (myrmecophagous), possibly fossorial, and lived from the middle Paleocene to early Oligocene in North America, Europe and Asia. While the taxonomic grouping of Palaeanodonta has been debated, it is widely thought that they are a sister group to pangolins.

Protictis is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America from early Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Palaeonictinae is an extinct subfamily of placental mammals from extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived from the late Paleocene to early Eocene of Europe and North America.

Metacheiromyidae is an extinct paraphyletic family of myrmecophagous placental mammals within extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.

Epoicotheriinae is an extinct paraphyletic subfamily of insectivorous placental mammals within extinct paraphyletic family Epoicotheriidae in extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the early Eocene to early Oligocene. Epoicotheriins were fossorial mammals. Late Eocene/early Oligocene genera were highly specialized animals that were convergent with the talpids, golden moles and marsupial mole in the structure of their skulls and forelimbs, and would have had a similar lifestyle as subterranean burrowers.

Conoryctidae is an extinct family of mammals from extinct order Taeniodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the early Paleocene to early Eocene.

Conoryctinae is an extinct subfamily of taeniodonts from extinct family Conoryctidae, that lived in North America from the early Paleocene to early Eocene.



















