
The ME Association is a UK health charitable organization that provides information, advocacy, and services to persons and families affected by ME/CFS, and raises funds for research into ME/CFS. It has been reported to be one of the two largest UK charities for ME/CFS.
Malcolm Hooper is a British pharmacist and emeritus professor of medicinal chemistry at the University of Sunderland. He is best known for his advocacy related to Gulf War syndrome.
Rintatolimod, sold under the tradename Ampligen, is a medication intended for treatment of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). There is some evidence it may improve some ME/CFS symptoms.

Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) has a long history with an evolution in medical understanding, diagnoses and social perceptions.
Management of ME/CFS focusses on symptoms management, as no treatments that address the root cause of the illness are available. Pacing, or regulating one's activities to avoid triggering worse symptoms, is the most common management strategy for post-exertional malaise. Clinical management varies widely, with many patients receiving combinations of therapies.

Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is an illness with a history of controversy. Although it is classified as an organic disease, it was historically assumed to be psychosocial, and a minority of medical professionals still hold this view. The pathophysiology of ME/CFS remains unclear, there exists many competing diagnostic criteria, and some proposed treatments are controversial. There is a lack of awareness about the condition, which has led to substantiated accusations of patient neglect and harm.

Clinical descriptions of ME/CFS vary. Different groups have produced sets of diagnostic criteria that share many similarities. The biggest differences between criteria are whether post-exertional malaise (PEM) is required, and the number of symptoms needed.
Graded exercise therapy (GET) is a programme of physical activity that starts very slowly and gradually increases over time, intended as a treatment for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). Most public health bodies, including the CDC and NICE, consider it ineffective, and its safety is disputed. However, GET still enjoys support among a minority of clinicians and organizations.
Daniel Peterson is an American physician in private practice in the state of Nevada, and has been described as a "pioneer" in the treatment of Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). He graduated from the University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York, in 1976 and was an intern and resident at the University of Utah Medical Center from 1976 to 1979. In 1979, he became a diplomate of the American Board of Internal Medicine. He is president of Sierra Internal Medicine of Incline Village, established in 1981.
The Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Advisory Committee (CFSAC) was formed in response to the use of funds by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the study of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). The CFSAC was charted under the Public Health Service Act of the US and funded by the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The CFSAC advises the Secretary of Health and Human Services on issues related to its mandate, including issues related to access and care for individuals with CFS, research, public health, clinical care and education regarding CFS. In November, 2008, support for CFSAC activities was changed to the Office on Women's Health, a division of the Office of Public Health and Science. It held it first meeting in 2003.

Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a serious long-term illness. People with ME/CFS experience a profound fatigue that does not go away with rest, sleep issues and problems with memory or concentration. They are able to do much less than before they became ill. Further common symptoms include dizziness, nausea and pain. The hallmark symptom is a worsening of the illness hours to days after minor physical or mental activity. This "crash" can last less than a day to several months.
The term functional somatic syndrome (FSS) refers to a group of chronic diagnoses with no identifiable organic cause. This term was coined by Hemanth Samkumar. It encompasses disorders such as fibromyalgia, chronic widespread pain, temporomandibular disorder, irritable bowel syndrome, lower back pain, tension headache, atypical face pain, non-cardiac chest pain, insomnia, palpitation, dyspepsia and dizziness. General overlap exists between this term, somatization and somatoform. The status of ME/CFS as a functional somatic syndrome is contested. Although the aetiology remains unclear, there are consistent findings of biological abnormalities, and major health bodies such as the NAM, WHO, and NIH, classify it as an organic disease.
Rosamund Vallings is a medical doctor, known as one of the leading authorities on Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) in New Zealand.
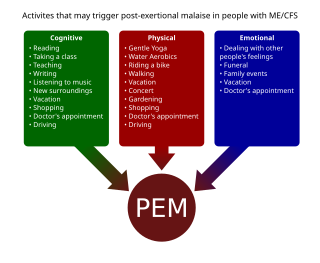
Post-exertional malaise (PEM), sometimes referred to as post-exertional symptom exacerbation (PESE) or post-exertional neuroimmune exhaustion (PENE), is a worsening of symptoms that occurs after minimal exertion. It is the hallmark symptom of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and common in long COVID and fibromyalgia. PEM is often severe enough to be disabling, and is triggered by ordinary activities that healthy people tolerate. Typically, it begins 12–48 hours after the activity that triggers it, and lasts for days, but this is highly variable and may persist much longer. Management of PEM is symptom-based, and patients are recommended to pace their activities to avoid triggering PEM.
Idiopathic chronic fatigue (ICF) or chronic idiopathic fatigue or insufficient/idiopathic fatigue is a term used for cases of unexplained fatigue that have lasted at least six consecutive months and which do not meet the criteria for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Such fatigue is widely understood to have a profound effect on the lives of patients who experience it.

DecodeME is an ongoing genome-wide association study searching for genetic risk factors for ME/CFS. With a planned recruitment of 25,000 patients, it is expected to be the largest such study to date. Recruitment closed on 15 November 2023 and results are expected in 2024.
The Open Medicine Foundation (OMF) is a US-based charity that funds research into the illnesses myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), fibromyalgia, post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome, and long COVID.
Andrew Melvin Ramsay (1901–1990) was a British physician, who is known for his research and advocacy on myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME), a chronic disease causing muscle weakness and cognitive dysfunction. Ramsay worked as a consultant at the Royal Free Hospital in London during a mysterious 1955 disease outbreak of what later became known as ME. He studied the disease and similar outbreaks elsewhere. Work by Ramsay showed that although ME seldom caused death, the disease could be highly disabling.
Carmen Scheibenbogen is a German immunologist who is the acting director of the Institute for Medical Immunology of the Charité university hospital in Berlin. She specialises in hematology, oncology and immunology. She leads the Outpatient Clinic for Immunodeficiency and the Fatigue Centre at the Charité hospital. She is one of the few doctors specialised in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) in Germany, and also researches long COVID.
The PACE trial was a large and controversial trial which compared the effects of cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), graded exercise therapy (GET), adaptive pacing therapy, and specialist medical care for people with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).






