
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek kutos, "hollow vessel". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.

In immunology, a memory B cell (MBC) is a type of B lymphocyte that forms part of the adaptive immune system. These cells develop within germinal centers of the secondary lymphoid organs. Memory B cells circulate in the blood stream in a quiescent state, sometimes for decades. Their function is to memorize the characteristics of the antigen that activated their parent B cell during initial infection such that if the memory B cell later encounters the same antigen, it triggers an accelerated and robust secondary immune response. Memory B cells have B cell receptors (BCRs) on their cell membrane, identical to the one on their parent cell, that allow them to recognize antigen and mount a specific antibody response.

In cell biology, a phagosome is a vesicle formed around a particle engulfed by a phagocyte via phagocytosis. Professional phagocytes include macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs).

CD23, also known as Fc epsilon RII, or FcεRII, is the "low-affinity" receptor for IgE, an antibody isotype involved in allergy and resistance to parasites, and is important in regulation of IgE levels. Unlike many of the antibody receptors, CD23 is a C-type lectin. It is found on mature B cells, activated macrophages, eosinophils, follicular dendritic cells, and platelets.
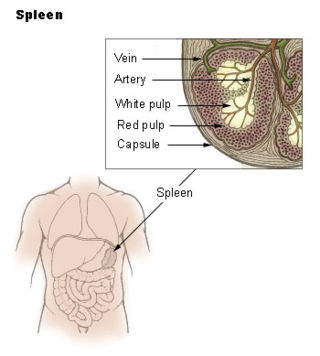
The marginal zone is the region at the interface between the non-lymphoid red pulp and the lymphoid white-pulp of the spleen.

Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes during a normal immune response; most of the germinal center B cells (BGC) are removed by tingible body macrophages. There are several key differences between naive B cells and GC B cells, including level of proliferative activity, size, metabolic activity and energy production. The B cells develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen. The initiation of germinal center formation involves the interaction between B and T cells in the interfollicular area of the lymph node, CD40-CD40L ligation, NF-kB signaling and expression of IRF4 and BCL6.

White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen, that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid tissue.

Complement receptor type 2 (CR2), also known as complement C3d receptor, Epstein-Barr virus receptor, and CD21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR2 gene.
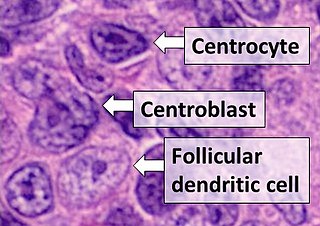
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell, but are of mesenchymal origin. Possible functions of FDC include: organizing lymphoid tissue's cells and microarchitecture, capturing antigen to support B cell, promoting debris removal from germinal centers, and protecting against autoimmunity. Disease processes that FDC may contribute include primary FDC-tumor, chronic inflammatory conditions, HIV-1 infection development, and neuroinvasive scrapie.

Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM3) also known as CD50, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ICAM3 gene. The protein is constitutively expressed on the surface of leukocytes, which are also called white blood cells and are part of the immune system. ICAM3 mediates adhesion between cells by binding to specific integrin receptors. It plays an important role in the immune cell response through its facilitation of interactions between T cells and dendritic cells, which allows for T cell activation. ICAM3 also mediates the clearance of cells undergoing apoptosis by attracting and binding macrophages, a type of cell that breaks down infected or dying cells through a process known as phagocytosis, to apoptotic cells.

G-protein coupled receptor 183 also known as Epstein-Barr virus-induced G-protein coupled receptor 2 (EBI2) is a protein (GPCR) expressed on the surface of some immune cells, namely B cells and T cells; in humans it is encoded by the GPR183 gene. Expression of EBI2 is one critical mediator of immune cell localization within lymph nodes, responsible in part for the coordination of B cell, T cell, and dendritic cell movement and interaction following antigen exposure. EBI2 is a receptor for oxysterols. The most potent activator is 7α,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7α,25-OHC), with other oxysterols exhibiting varying affinities for the receptor. Oxysterol gradients drive chemotaxis, attracting the EBI2-expressing cells to locations of high ligand concentration. The GPR183 gene was identified due to its upregulation during Epstein-Barr virus infection of the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line BL41, hence its name: EBI2.
Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIb is a low affinity inhibitory receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin gamma (IgG). FCGR2B participates in the phagocytosis of immune complexes and in the regulation of antibody production by B lymphocytes.

Marginal-zone B cells are noncirculating mature B cells that in humans segregate anatomically into the marginal zone (MZ) of the spleen and certain other types of lymphoid tissue. The MZ B cells within this region typically express low-affinity polyreactive B-cell receptors (BCR), high levels of IgM, Toll-like receptors (TLRs), CD21, CD1, CD9, CD27 with low to negligible levels of secreted-IgD, CD23, CD5, and CD11b that help to distinguish them phenotypically from follicular (FO) B cells and B1 B cells.
Within the immune system, Follicular B cells are a type of B cell that reside in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles of secondary and tertiary lymphoid organs, including spleen and lymph nodes. Antibody responses against proteins are believed to involve follicular B cell pathways in secondary lymphoid organs.

Follicular helper T cells (also known as T follicular helper cells and abbreviated as TFH), are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the periphery within B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5. Upon cellular interaction and cross-signaling with their cognate follicular (Fo B) B cells, TFH cells trigger the formation and maintenance of germinal centers through the expression of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and the secretion of IL-21 and IL-4. TFH cells also migrate from T cell zones into these seeded germinal centers, predominantly composed of rapidly dividing B cells mutating their Ig genes. Within germinal centers, TFH cells play a critical role in mediating the selection and survival of B cells that go on to differentiate either into long-lived plasma cells capable of producing high affinity antibodies against foreign antigen, or germinal center-dependent memory B cells capable of quick immune re-activation in the future if ever the same antigen is re-encountered. TFH cells are also thought to facilitate negative selection of potentially autoimmune-causing mutated B cells in the germinal center. However, the biomechanisms by which TFH cells mediate germinal center tolerance are yet to be fully understood.
FDC-SP or follicular dendritic cell-secreted protein, is a small, secreted protein, located on chromosome 4 in humans. It is thought to play an immune role in the junctional epithelium at the gingival crevice in the human mouth. It is very similar in structure to statherin, a protein contained in saliva.

Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma (FDCS) is an extremely rare neoplasm. While the existence of FDC tumors was predicted by Lennert in 1978, the tumor wasn't fully recognized as its own cancer until 1986 after characterization by Monda et al. It accounts for only 0.4% of soft tissue sarcomas, but has significant recurrent and metastatic potential and is considered an intermediate grade malignancy. The major hurdle in treating FDCS has been misdiagnosis. It is a newly characterized cancer, and because of its similarities in presentation and markers to lymphoma, both Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin subtypes, diagnosis of FDCS can be difficult. With recent advancements in cancer biology better diagnostic assays and chemotherapeutic agents have been made to more accurately diagnose and treat FDCS.
Lymph node stromal cells are essential to the structure and function of the lymph node whose functions include: creating an internal tissue scaffold for the support of hematopoietic cells; the release of small molecule chemical messengers that facilitate interactions between hematopoietic cells; the facilitation of the migration of hematopoietic cells; the presentation of antigens to immune cells at the initiation of the adaptive immune system; and the homeostasis of lymphocyte numbers. Stromal cells originate from multipotent mesenchymal stem cells.

A centroblast generally refers to an activated B cell that is enlarged and is rapidly proliferating in the germinal center of a lymphoid follicle. They are specifically located in the dark zone of the germinal center. Centroblasts form from naive B cells being exposed to follicular dendritic cell cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-15, 8D6, and BAFF. Stimulation from helper T cells is also required for centroblast development. Interaction between CD40 ligand on an activated T helper cell and the B cell CD40 receptor induces centroblasts to express activation-induced cytidine deaminase, leading to somatic hypermutation, allowing the B cell receptor to potentially gain stronger affinity for an antigen. In the absence of FDC and helper T cell stimulation, centroblasts are unable to differentiate and will undergo CD95-mediated apoptosis.
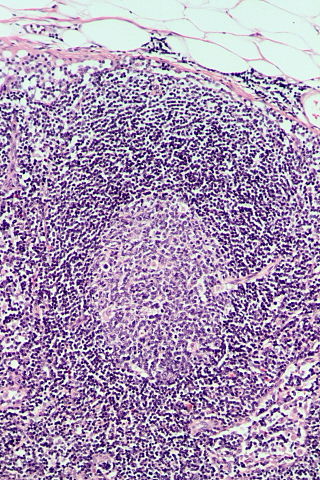
Follicular hyperplasia (FH) is a type of lymphoid hyperplasia and is classified as a lymphadenopathy, which means a disease of the lymph nodes. It is caused by a stimulation of the B cell compartment and by abnormal cell growth of secondary follicles. This typically occurs in the cortex without disrupting the lymph node capsule. The follicles are pathologically polymorphous, are often contrasting and varying in size and shape. Follicular hyperplasia is distinguished from follicular lymphoma in its polyclonality and lack of bcl-2 protein expression, whereas follicular lymphoma is monoclonal, and expresses bcl-2.
















