USS New London was a screw steamer of the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was outfitted with a Parrott rifle and 32-pounders, and was assigned as a gunboat in the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America.

USS Sciota was a Unadilla-class gunboat built on behalf of the United States Navy for service during the Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat, with both a 20-pounder rifle for horizontal firing, and two howitzers for shore bombardment, and assigned to the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Stars and Stripes was a 407-ton steamer acquired by the U.S. Navy and put to use by the Union during the American Civil War.

USS Albatross was a screw steamer rigged as a three-masted schooner acquired by the Union Navy during the beginning of the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a gunboat with heavy guns and used in the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Kennebec was a Unadilla-class gunboat built for the U.S. Navy following the outbreak of the American Civil War. She was named for the Kennebec River.

USS Norwich, a wooden, screw steamer built at Norwich, Connecticut in 1861, was purchased by the Union Navy at New York City 26 September 1861 from J. M. Huntington & Co.; and commissioned at the New York Navy Yard 28 December 1861, Lieutenant James M. Duncan in command.

USS Winona was a Unadilla-class gunboat built for service with the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Winona was heavily armed, with large guns for duels at sea, and 24-pounder howitzers for shore bombardment. Winona saw significant action in the Gulf of Mexico and in the waterways of the Mississippi River and was fortunate to return home safely after the war for decommissioning.
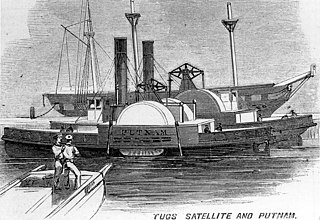
USS General Putnam – also known as the USS William G. Putnam – was acquired by the Union Navy during the first year of the American Civil War and outfitted as a gunboat and assigned to the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America. She also served as a tugboat and as a ship's tender when so required.
USS Clover was a steam gunboat acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Tulip was a 183-ton steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

USS Fuchsia was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Fox was a captured Confederate schooner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.

USS Thomas Freeborn was a steam tug acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Navy as a gunboat to patrol navigable waterways of the Confederacy to prevent the South from trading with other countries.
USS Tristram Shandy was a 444-ton steamer and blockade runner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Britannia was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat and patrol vessel in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS Annie was a schooner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a ship's tender in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. Her service during the Union naval blockade of Confederate waters peaked during the Second Chesapeake Affair (1863–64) as a "fresh reinforcement from the south" in the search and capture of the U.S.S Chesapeake.
USS Granite City was a Confederate blockade runner steamer captured in March 1863 by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was armed with cannon and by August 1863 was in service as a gunboat in support of the Navy blockade of Confederate waters. She was recaptured in January 1864 by Confederate forces, again became a blockade runner, and ultimately was abandoned as a wreck after running aground.
USS Wyandotte, originally USS Western Port, was a steamer acquired by the Navy as a gunboat for the Paraguay expedition in 1858. When the crisis of the American Civil War occurred, she operated in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.
USS T. A. Ward was a 284-ton schooner was purchased by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.
The third USS Virginia was a 581-ton blockade-running steamer captured by the United States Navy and put to use during the American Civil War. Virginia served the U.S. Navy primarily as a mortar gunboat. Her ordnance included six 24-pounder howitzers and a 12-pounder rifled gun.








