Related Research Articles
A cryptocurrency exchange, or a digital currency exchange (DCE), is a business that allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets, such as conventional fiat money or other digital currencies. Exchanges may accept credit card payments, wire transfers or other forms of payment in exchange for digital currencies or cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency exchange can be a market maker that typically takes the bid–ask spreads as a transaction commission for its service or, as a matching platform, simply charges fees.

Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency. Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. The cryptocurrency was invented in 2008 by an unknown entity under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The currency began use in 2009, when its implementation was released as open-source software. The word "bitcoin" was defined in a white paper published on October 31, 2008. It is a compound of the words bit and coin.

A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It is a decentralized system for verifying that the parties to a transaction have the money they claim to have, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries, such as banks, when funds are being transferred between two entities.
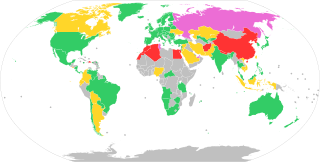
The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies substantially from one jurisdiction to another, and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Whereas, in the majority of countries the usage of cryptocurrency isn't in itself illegal, its status and usability as a means of payment varies, with differing regulatory implications.
Circle began as a peer-to-peer payments technology company that now manages stablecoin USDC, a cryptocurrency the value of which is pegged to the U.S. dollar. It was founded by Jeremy Allaire and Sean Neville in October 2013. Circle is headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. USDC, the second largest stablecoin worldwide, is designed to hold at or near a stable price of $1. The majority of its stablecoin collateral is held in short-term U.S. government securities.
Monero is a cryptocurrency which uses a blockchain with privacy-enhancing technologies to obfuscate transactions to achieve anonymity and fungibility. Observers cannot decipher addresses trading Monero, transaction amounts, address balances, or transaction histories.
Kraken is a United States–based cryptocurrency exchange, founded in 2011. It was one of the first bitcoin exchanges to be listed on Bloomberg Terminal and was valued at US$10.8 billion in mid-2022. The company has been the subject of several regulatory investigations since 2018, and has agreed to cumulative fines of over $30 million.

Digital Currency Group (DCG) is a venture capital company focusing on the digital currency market. It is located in Stamford, Connecticut. The company has five subsidiaries: CoinDesk, Foundry, Genesis, Grayscale Investments, and Luno.
Bitfinex is a cryptocurrency exchange owned and operated by iFinex Inc, and is registered in the British Virgin Islands. Bitfinex was founded in 2012. It was originally a peer-to-peer Bitcoin exchange, and later added support for other cryptocurrencies.
A cryptocurrency bubble is a phenomenon where the market increasingly considers the going price of cryptocurrency assets to be inflated against their hypothetical value. The history of cryptocurrency has been marked by several speculative bubbles.
Binance Holdings Ltd., branded Binance, is a global company that operates the largest cryptocurrency exchange in terms of daily trading volume of cryptocurrencies. Binance was founded in 2017 by Changpeng Zhao, a developer who had previously created high frequency trading software. Binance was initially based in China, then moved its headquarters to Singapore shortly before the Chinese government imposed regulations on cryptocurrency trading. Binance subsequently left Singapore in late 2021 and after that, had no official company headquarters.
Cryptocurrency and crime describes notable examples of cybercrime related to theft of cryptocurrencies and some of the methods or security vulnerabilities commonly exploited. Cryptojacking is a form of cybercrime specific to cryptocurrencies that has been used on websites to hijack a victim's resources and use them for hashing and mining cryptocurrency.
OKX is a global cryptocurrency spot and derivatives exchange and the second biggest crypto exchange by trading volume, serving over 50 million people globally. It was founded by Star Xu in 2017, who is also the CEO as of 2023. The President is Hong Fang and the CMO is Haider Rafique. OKX is owned by OK Group, which also owns the crypto exchange Okcoin.

Changpeng Zhao, commonly known as CZ, is a Chinese-born Canadian businessman, investor, and software engineer. Zhao is the co-founder and CEO of Binance, the world's largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume as of July 2022.
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency where the value of the digital asset is supposed to be pegged to a reference asset, which is either fiat money, exchange-traded commodities, or another cryptocurrency.
Cryptoeconomics is an evolving economic paradigm for a cross-disciplinary approach to the study of digital economies and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Cryptoeconomics integrates concepts and principles from traditional economics, cryptography, computer science, and game theory disciplines. Just as traditional economics provides a theoretical foundation for traditional financial services, cryptoeconomics provides a theoretical foundation for DeFi services bought and sold via fiat cryptocurrencies, and executed by smart contracts.
Paxos Trust Company is a New York–based financial institution and technology company specializing in blockchain. The company's product offerings include a cryptocurrency brokerage service, asset tokenization services, and settlement services. ItBit, a bitcoin exchange run by Paxos, was the first bitcoin exchange to be licensed by the New York State Department of Financial Services, granting the company the ability to be the custodian and exchange for customers in the United States.
Bitso began as a global cryptocurrency exchange founded in Mexico. It was founded in 2014 by Ben Peters, Pablo Gonzalez and Daniel Vogel. Daniel Vogel is the current chief executive officer. Bitso was the first Latin American company and one of the few crypto-currency platforms to be regulated by the Gibraltar Financial Services Commission under its Distributed Ledger Technology Framework.
FTX Trading Ltd., commonly known as FTX, is a bankrupt company that formerly operated a fraud-ridden cryptocurrency exchange and crypto hedge fund. The exchange was founded in 2019 by Sam Bankman-Fried and Gary Wang and, at its peak in July 2021, had over one million users and was the third-largest cryptocurrency exchange by volume. FTX is incorporated in Antigua and Barbuda and headquartered in the Bahamas. FTX is closely associated with FTX.US, a separate exchange available to US residents.

Nobitex is Iran's largest crypto exchange. 87% of all funds, domestic and international, that transferred in Iranian exchanges in 2022 - equivalent to US$2.6 billion were don at nobitex.
References
- ↑ "Iran's muddled relationship with cryptocurrency is self-inflicted". Atlantic Council. 2020-06-18. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ↑ Ratna, Tanvi. "Iran Has a Bitcoin Strategy to Beat Trump". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ↑ Erdbrink, Thomas (2019-01-29). "How Bitcoin Could Help Iran Undermine U.S. Sanctions (Published 2019)". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ↑ "Iranians Warned To Be Wary As Daily Crypto-Currency Trade Reaches $20 Million". Iran International. 2020-12-04. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ↑ Lerner, Barry (June 2018). "Regulation of Cryptocurrency". www.loc.gov. Archived from the original on 2020-12-27. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ↑ "Iran uses crypto mining to lessen impact of sanctions, study finds". Reuters. 21 May 2021.
- ↑ Berwick, Angus; Wilson, Tom; Berwick, Angus; Wilson, Tom (2022-11-07). "Crypto exchange Binance helped Iranian firms trade $8 billion despite sanctions". Reuters. Retrieved 2023-07-10.
- ↑ "Nobitex responded to the Reuters report regarding the relationship with Binance". ILNA. 2022-11-07. Retrieved 2023-07-07.