
The Royal Alexandra Interprovincial Bridge, also known as the Alexandra Bridge or Interprovincial Bridge, is a steel truss cantilever bridge spanning the Ottawa River between Ottawa, Ontario and Gatineau, Quebec. In addition to carrying vehicle traffic, a shared use pathway on the bridge for pedestrians and cyclists is maintained by the National Capital Commission.

The Sellwood Bridge is a deck arch bridge that spans the Willamette River in Portland, Oregon, in the United States. The current bridge opened in 2016 and replaced a 1925 span that had carried the same name. The original bridge was Portland's first fixed-span bridge and, being the only river crossing for miles in each direction, the busiest two-lane bridge in Oregon. The Sellwood Bridge links the Sellwood and Westmoreland neighborhoods of Portland on the east side with Oregon Route 43/Macadam Avenue on the west side. At its east end it leads to Tacoma Street. The bridge is owned and operated by Multnomah County. The original span of 1925 was a steel truss bridge, while its 2016 replacement is a deck-arch-type bridge.

The High Level Bridge is a bridge that spans the North Saskatchewan River in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.

The Pattullo Bridge is a through arch bridge that crosses the Fraser River and links the cities of New Westminster and Surrey in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia. It was named in honour of Thomas Dufferin Pattullo, the 22nd Premier of British Columbia. A key link between Surrey and the rest of Greater Vancouver, the Pattullo Bridge handles an average of 75,700 cars and 3840 trucks daily, or roughly 20% of vehicle traffic across the Fraser River as of 2013.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 216, better known by its official name of Anthony Henday Drive, is a 78-kilometre (48 mi) freeway that encircles Edmonton, Alberta. It is a heavily travelled commuter and truck bypass route with the southwest quadrant serving as a portion of the CANAMEX Corridor that links Canada to the United States and Mexico. Henday is one of the busiest highways in Western Canada, carrying over 95,000 vehicles per day in 2022 at its busiest point near West Edmonton Mall. Rush hour congestion is common on the four-lane section in southwest Edmonton, where traffic levels have risen due to rapid suburban development. Work began in fall 2019 to widen this section to six lanes by the end of 2023.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 63, commonly referred to as Highway 63, is a 434-kilometre (270 mi) highway in northern Alberta, Canada that connects the Athabasca oil sands and Fort McMurray to Edmonton via Highway 28. It begins as a two-lane road near the hamlet of Radway where it splits from Highway 28, running north through aspen parkland and farmland of north central Alberta. North of Boyle, it curves east to pass through the hamlet of Grassland and becomes divided west of Atmore where it again turns north, this time through heavy boreal forest and muskeg, particularly beyond Wandering River. Traffic levels significantly increase as Highway 63 bends through Fort McMurray, crossing the Athabasca River before connecting the city to the Syncrude and Suncor Energy plants further north. It ends approximately 16 km (10 mi) beyond a second crossing of the Athabasca River northeast of Fort McKay.

The Birmingham Bridge is a bowstring arch bridge that is located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and spans the Monongahela River.

The Traffic Bridge is the name given to two truss bridges constructed across the South Saskatchewan River, connecting Victoria Avenue to 3rd Avenue South and Spadina Crescent in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. The original bridge opened on October 10, 1907, and was the first bridge to carry motor vehicle traffic in Saskatoon, replacing an unreliable ferry service. The promised construction of the bridge was considered a prime factor in the amalgamation of the towns of Saskatoon, Nutana and Riversdale into one city named Saskatoon. The Traffic Bridge was the only road bridge in Saskatoon until 1916, when the University Bridge was completed. In 2010, the bridge was permanently closed due to severe corrosion and was demolished by 2016.

The University Bridge spans the South Saskatchewan River between Clarence Avenue and College Drive on the east shore with 25th Street on the west in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan Canada. The bridge is also known as the 25th Street Bridge and is a major commuter route between the two halves of Saskatoon. Between its opening in 1916 and the opening of the Circle Drive Bridge in 1983, it was the northernmost vehicular river crossing in the city. It is named for the fact that it provides access to the University of Saskatchewan.

The Lamar Boulevard Bridge is a historic arch bridge carrying Texas State Highway Loop 343 over Lady Bird Lake in downtown Austin, Texas, United States. The bridge features six open-spandrel concrete arches spanning 659 feet (201 m) and carries tens of thousands of vehicles daily across the lake. Completed in 1942, the Lamar Boulevard Bridge was the second permanent bridge to cross the Colorado River, and one of the last Art Deco-style open-spandrel concrete arch bridges built in Texas. The bridge was named an Austin Landmark in 1993 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1994.

Blackfriars Bridge in London, Ontario, Canada is a wrought iron bowstring arch through truss bridge, crossing the North Thames River. The bridge was constructed in 1875 and carries single-lane vehicles, bicycles and pedestrians from Blackfriars Street to Ridout Street North.
The timeline of Edmonton history is a chronology of significant events in the history of Edmonton, Alberta.

105 Street is an arterial road in Downtown Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It starts across the North Saskatchewan River from Downtown, as one-way streets Walterdale Hill and Queen Elizabeth Park Road, which join and continue north on Walterdale Bridge. At 100 Avenue, 105 Street becomes a two-way street, and continues through Downtown past MacEwan University.
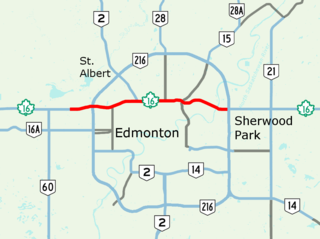
Yellowhead Trail is a 24.6-kilometre (15.3 mi) expressway segment of the Yellowhead Highway in northern Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It carries a significant amount of truck traffic to and from the industrial areas of north Edmonton and serves as a key commuter route for the bedroom communities of Stony Plain, Spruce Grove, and Sherwood Park, carrying nearly 80,000 vehicles per weekday in 2015. A suburban bypass of the route was completed when the northeast leg of Anthony Henday Drive (Highway 216) opened in late 2016, providing an alternate route through north Edmonton.
Walterdale is a former industrial and residential neighbourhood in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada within the North Saskatchewan River valley. It is located on the south shore of the river in an area now occupied by Kinsmen Park within a river valley neighbourhood named River Valley Walterdale.

The Tawatinâ Bridge is an extradosed LRT bridge crossing the North Saskatchewan River in Edmonton, Alberta. Below the concrete box girder spans is a suspended eight-metre-wide shared-use path, which was opened to the public on December 12, 2021. It is part of Edmonton Transit Service's Valley Line extension, which opened on November 4, 2023. The Tawatinâ Bridge consists of two railway tracks.

The James D. Pfluger Pedestrian and Bicycle Bridge is a shared use bridge for pedestrians and cyclists spanning Lady Bird Lake in downtown Austin, Texas. Opened in 2001, the bridge connects the north and south sides of the Ann and Roy Butler Hike-and-Bike Trail and features an unusual "double curve" design. The bridge runs parallel to the Lamar Boulevard Bridge, which carries road traffic across the lake roughly 200 feet (61 m) to the west.

The East River Bridge is a multi-span bridge in Sheet Harbour, Nova Scotia that carries Trunk 7 and the Marine Drive scenic route over the Northeast Arm of Sheet Harbour. The bridge is 183 m (600 ft) in length and was constructed from September 2014 to December 2015. It was opened on December 17, 2015 to pedestrians, with a bridge walk commemorating the closing of the old bridge and the opening of the new bridge. The bridge was opened to vehicles the day after. It replaced a green steel arch bridge of the same name that was built in 1956 immediately north of the current bridge. The previous bridge had a span of 213 m (699 ft) and shared engineering ties with the Angus L. MacDonald Bridge in Halifax. Nova Scotia was considering repairs to the old bridge, but they ultimately elected to construct a new bridge instead. The current bridge was designed without overhead arches, unlike its predecessor, as the construction cost would have been doubled.
Calgary Trail and Gateway Boulevard are a pair of major arterial roadways in Edmonton, Alberta. Gateway Boulevard carries northbound traffic while Calgary Trail carries southbound traffic. From south of 31 Avenue, they form a two-way freeway separated by a median; for this portion, the roadway maintains the separate names for northbound and southbound traffic. Near 31 Avenue, Calgary Trail and Gateway Boulevard separate and become parallel one-way arterial roadways to Saskatchewan Drive, at the edge of the North Saskatchewan River valley. Designated as part of Highway 2 south of Whitemud Drive, it is Edmonton's main southern entrance and is both a major commuter route, connecting to the Edmonton International Airport and Leduc, as well as a regional connection to Red Deer and Calgary.

The Samuel De Champlain Bridge, colloquially known as the Champlain Bridge, is a cable-stayed bridge design by architect Poul Ove Jensen and built to replace the original Champlain Bridge over the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec, between Nuns' Island in the borough of Verdun in Montreal and the suburban city of Brossard on the South Shore. A second, connected bridge links Nuns' Island to the main Island of Montreal. The bridge is the busiest bridge in the country with more cars flowing into it than any other bridge.


























