
The Warsaw Ghetto was the largest of the Nazi ghettos during World War II and the Holocaust. It was established in November 1940 by the German authorities within the new General Government territory of occupied Poland. At its height, as many as 460,000 Jews were imprisoned there, in an area of 3.4 km2 (1.3 sq mi), with an average of 9.2 persons per room, barely subsisting on meager food rations. Jews were deported from the Warsaw Ghetto to Nazi concentration camps and mass-killing centers. In the summer of 1942, at least 254,000 ghetto residents were sent to the Treblinka extermination camp during Großaktion Warschau under the guise of "resettlement in the East" over the course of the summer. The ghetto was demolished by the Germans in May 1943 after the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising had temporarily halted the deportations. The total death toll among the prisoners of the ghetto is estimated to be at least 300,000 killed by bullet or gas, combined with 92,000 victims of starvation and related diseases, the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, and the casualties of the final destruction of the ghetto.

Szmul Mordko Zygielbojm was a Polish socialist politician, Bund trade-union activist, and member of the National Council of the Polish government-in-exile.

The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising was the 1943 act of Jewish resistance in the Warsaw Ghetto in German-occupied Poland during World War II to oppose Nazi Germany's final effort to transport the remaining ghetto population to the gas chambers of the Majdanek and Treblinka extermination camps.

The Łódź Ghetto or Litzmannstadt Ghetto was a Nazi ghetto established by the German authorities for Polish Jews and Roma following the Invasion of Poland. It was the second-largest ghetto in all of German-occupied Europe after the Warsaw Ghetto. Situated in the city of Łódź, and originally intended as a preliminary step upon a more extensive plan of creating the Judenfrei province of Warthegau, the ghetto was transformed into a major industrial centre, manufacturing war supplies for Nazi Germany and especially for the Wehrmacht. The number of people incarcerated in it was increased further by the Jews deported from Nazi-controlled territories.

The Kraków Ghetto was one of five major metropolitan Nazi ghettos created by Germany in the new General Government territory during the German occupation of Poland in World War II. It was established for the purpose of exploitation, terror, and persecution of local Polish Jews. The ghetto was later used as a staging area for separating the "able workers" from those to be deported to extermination camps in Operation Reinhard. The ghetto was liquidated between June 1942 and March 1943, with most of its inhabitants deported to the Belzec extermination camp as well as to Płaszów slave-labor camp, and Auschwitz concentration camp, 60 kilometres (37 mi) rail distance.

Beginning with the invasion of Poland during World War II, the Nazi regime set up ghettos across German-occupied Eastern Europe in order to segregate and confine Jews, and sometimes Romani people, into small sections of towns and cities furthering their exploitation. In German documents, and signage at ghetto entrances, the Nazis usually referred to them as Jüdischer Wohnbezirk or Wohngebiet der Juden, both of which translate as the Jewish Quarter. There were several distinct types including open ghettos, closed ghettos, work, transit, and destruction ghettos, as defined by the Holocaust historians. In a number of cases, they were the place of Jewish underground resistance against the German occupation, known collectively as the ghetto uprisings.

Jewish resistance under Nazi rule took various forms of organized underground activities conducted against German occupation regimes in Europe by Jews during World War II. According to historian Yehuda Bauer, Jewish resistance was defined as actions that were taken against all laws and actions acted by Germans. The term is particularly connected with the Holocaust and includes a multitude of different social responses by those oppressed, as well as both passive and armed resistance conducted by Jews themselves.

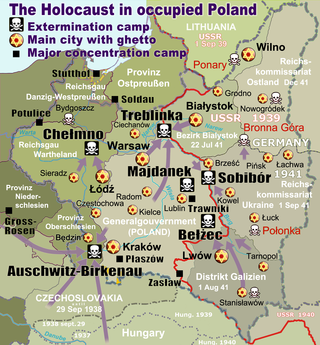
The Holocaust in Poland was the ghettoization, robbery, deportation, and murder of Jews in occupied Poland, organized by Nazi Germany. Three million Polish Jews were murdered, primarily at the Chelmno, Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka, and Auschwitz II–Birkenau extermination camps, representing half of all Jews murdered during the Europe-wide Holocaust.

Jewish partisans were fighters in irregular military groups participating in the Jewish resistance movement against Nazi Germany and its collaborators during World War II.

During the Holocaust, children were especially vulnerable to death under the Nazi regime. An estimated 1.5 million children, nearly all Jewish, were murdered during the Holocaust, either directly by or as a direct consequence of Nazi actions.

Michał Klepfisz was a chemical engineer, activist for the Bund, and member of the Jewish Morgenstern sports organization. During World War II he belonged to the Jewish Combat Organization, fighting the Nazi German forces in Poland. He was killed in the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising and was posthumously decorated by the Polish government in exile with a Silver Cross of the Virtuti Militari.

The Grossaktion Warsaw was the Nazi code name for the deportation and mass murder of Jews from the Warsaw Ghetto during the summer of 1942, beginning on 22 July. During the Grossaktion, Jews were terrorized in daily round-ups, marched through the ghetto, and assembled at the Umschlagplatz station square for what was called in the Nazi euphemistic jargon "resettlement to the East". From there, they were sent aboard overcrowded Holocaust trains to the extermination camp in Treblinka.

Polish Jews were the primary victims of the Nazi Germany-organized Holocaust in Poland. Throughout the German occupation of Poland, Jews were rescued from the Holocaust by Polish people, at risk to their lives and the lives of their families. According to Yad Vashem, Israel's official memorial to the victims of the Holocaust, Poles were, by nationality, the most numerous persons identified as rescuing Jews during the Holocaust. By January 2022, 7,232 people in Poland have been recognized by the State of Israel as Righteous among the Nations.

"The Little Smuggler" is a famous poem by the Polish poet Henryka Łazowertówna (1909–1942). Written in the Warsaw Ghetto during the Holocaust, it tells the story of a small child who supports his starving family by — illegally, under Nazi dispensation — bringing over food supplies from the "Aryan side", thereby allowing for his family's survival while at the same time risking his own life. Indeed, the last stanza of the poem gives expression to the heroic child's fear — not of his own death but that of his mother who, in the event of the loss of her child, would be left without her daily sustenance.

Vladka Meed was a member of Jewish resistance in Poland who famously smuggled dynamite into the Warsaw Ghetto, and also helped children escape out of the Ghetto.
Anna Braude Heller was a physician who worked in the Warsaw Ghetto during World War II.
The Gorlice Ghetto was established in 1940 after German occupation of the Polish city began on September 7, 1939. As one of many ghettos created by Nazi Germany in the General Government, its establishment meant further persecution and violence against the nearly 3,400 Jewish citizens that were settled in the area. As German forces quickly seized hundreds of the young, able men of Gorlice in order to use them for forced labor, many Jews began hiding for their lives as their businesses were taken and the rapid spread of disease plagued the city. The ghetto was officially dissolved on September 14, 1942, and carried with its downfall the transportation of hundreds of Jews to the concentration camp located in Bełżec.

In the best-known photograph taken during the 1943 Warsaw Ghetto Uprising, a boy holds his hands over his head while SS-Rottenführer Josef Blösche points a submachine gun in his direction. The boy and others hid in a bunker during the final liquidation of the ghetto, but they were caught and forced out by German troops. After the photograph was taken, all of the Jews in the photograph were marched to the Umschlagplatz and deported to Majdanek extermination camp or Treblinka. The exact location and the photographer are not known, and Blösche is the only person in the photograph who can be identified with certainty. The image is one of the most famous photographs of the Holocaust, and the boy came to represent children in the Holocaust, as well as all Jewish victims.
CENTOS was a Polish-Jewish children's-aid society. Founded in 1924, it became a "leading organization for Jewish childcare" in the Second Polish Republic and was highly active in the Warsaw Ghetto during The Holocaust in Poland.













