General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was established by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).

Wireless Markup Language (WML), based on XML, is an obsolete markup language intended for devices that implement the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) specification, such as mobile phones. It provides navigational support, data input, hyperlinks, text and image presentation, and forms, much like HTML. It preceded the use of other markup languages used with WAP, such as XHTML and HTML itself, which achieved dominance as processing power in mobile devices increased.
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include multimedia content to and from a mobile phone over a cellular network. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia message. The MMS standard extends the core SMS capability, allowing the exchange of text messages greater than 160 characters in length. Unlike text-only SMS, MMS can deliver a variety of media, including up to forty seconds of video, one image, a slideshow of multiple images, or audio.

NTT DoCoMo's i-mode is a mobile internet service popular in Japan. Unlike Wireless Application Protocols, i-mode encompasses a wider variety of internet standards, including web access, e-mail, and the packet-switched network that delivers the data. i-mode users also have access to other various services such as: sports results, weather forecasts, games, financial services, and ticket booking. Content is provided by specialised services, typically from the mobile carrier, which allows them to have tighter control over billing.
A mobile browser is a web browser designed for use on a mobile device such as a mobile phone, PDA, smartphone, or tablet. Mobile browsers are optimized to display web content most effectively on small screens on portable devices. Some mobile browsers, especially older versions, are designed to be small and efficient to accommodate the low memory capacity and low bandwidth of certain wireless handheld devices. Traditional smaller feature phones use stripped-down mobile web browsers; however, most current smartphones have full-fledged browsers that can handle the latest web technologies, such as CSS 3, JavaScript, and Ajax.
WapTV now Miniweb was the name given to the company which originated the WTVML as a content format for the delivery of Interactive TV applications using Internet Servers. The system is an Interactive television technology platform comprising a mobile browser, a markup language, and a significant collection of associated software tools and services.
OMA SpecWorks, previously the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA), is a standards organization which develops open, international technical standards for the mobile phone industry. It is a nonprofit Non-governmental organization (NGO), not a formal government-sponsored standards organization as is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU): a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.

The Nokia 7110 is a GSM mobile phone announced in February 1999 and released in October 1999. It was the first mobile phone to run Series 40 and to come with a WAP browser.

A mobile phone feature is a capability, service, or application that a mobile phone offers to its users. Mobile phones are often referred to as feature phones, and offer basic telephony. Handsets with more advanced computing ability through the use of native code try to differentiate their own products by implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers. This has led to great innovation in mobile phone development over the past 20 years.
Nokia Browser for Symbian was the default web browser for the S60 and Symbian mobile phone platform. The browser is based on a port of Apple Inc.'s open-source WebCore and JavaScriptCore frameworks which form the WebKit rendering engine that Apple uses in its Safari Web browser.

The mobile web comprises mobile browser-based World Wide Web services accessed from handheld mobile devices, such as smartphones or feature phones, through a mobile or other wireless network.

The Nokia 6030, introduced in Q1 2005, is a GSM dual band handset operating on frequencies 900 and 1800 MHz, with automatic switching between frequencies. It is small in size with dimensions of 104 x 44 x 18 mm and weighs 90 grams. It also has 3MB Shared Memory.
Content adaptation is the action of transforming content to adapt to device capabilities. Content adaptation is usually related to mobile devices, which require special handling because of their limited computational power, small screen size, and constrained keyboard functionality.
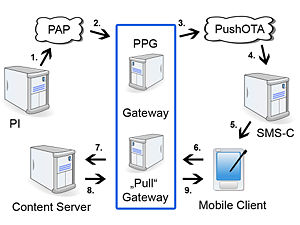
A WAP gateway sits between mobile devices using the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) and the World Wide Web, passing pages from one to the other much like a proxy. This translates pages into a form suitable for the mobiles, for instance using the Wireless Markup Language (WML). This process is hidden from the phone, so it may access the page in the same way as a browser accesses HTML, using a URL, provided the mobile phone operator has not specifically prevented this. WAP gateway software encodes and decodes requests and responses between the smartphones, microbrowser and internet. It decodes the encoded WAP requests from the microbrowser and send the HTTP requests to the internet or to a local application server. It also encodes the WML and HDML data returning from the web for transmission to the microbrowser in the handset.
Alternate air ticket purchasing order systems allow for alternative ways of purchasing air tickets and GDS Connectivity not involving Internet or personal TA contact.

ThunderHawk is a discontinued web browser from Bitstream available for a full range of operating systems in high end and mass-market mobile phones and personal digital assistants. It is basically meant for mobile operators and original equipment manufacturers and not meant to download for normal users.
On-Device Portals (ODPs) allow mobile phone users to easily browse, purchase and use mobile content and services. An ODP platform enables operators to provide a consistent and branded on-device experience across their broadening portfolio of services and typically provides on-device catalogs of content for purchase, deep links to WAP portals, customer care functionality and rich media services such as full track music, TV and video.
The Nokia 3600 slide is a mobile phone by Nokia that was released in August 2008. The phone runs the Series 40 3rd Edition platform. This is classed as the 'low end version' of the Nokia 6600 slide, its major difference being the lack of 3G support.
Mobile web analytics studies the behaviour of mobile website users in a similar way to traditional web analytics. In a commercial context, mobile web analytics refers to the data collected from the users who access a website from a mobile phone. It helps to determine which aspects of the website work best for mobile traffic and which mobile marketing campaigns work best for the business, including mobile advertising, mobile search marketing, text campaigns, and desktop promotion of mobile sites and services.

Vision was a mobile browser developed by Novarra Inc. that ran on Java Platform, Micro Edition. It was first released in 2002, and the final release was in 2009.