In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination of the two. Virtual machines differ and are organized by their function, shown here:
ARM is a family of RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for computer processors. Arm Ltd. develops the ISAs and licenses them to other companies, who build the physical devices that use the instruction set. It also designs and licenses cores that implement these ISAs.
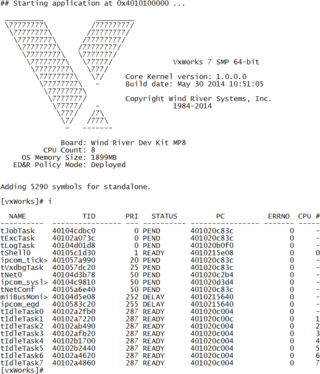
VxWorks is a real-time operating system developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and, in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.

An embedded operating system is an operating system for embedded computer systems. Embedded operating systems are a computer system designed to increase functionality and reliability for achieving a specific task. Depending on the method used for Computer multitasking, this type of operating system might be considered a real-time operating system (RTOS).
Enea AB is a global information technology company with its headquarters in Kista, Sweden that provides real-time operating systems and consulting services. Enea, which is an abbreviation of Engmans Elektronik Aktiebolag, also produces the OSE operating system.
Adeos is a nanokernel hardware abstraction layer (HAL), or hypervisor, that operates between computer hardware and the operating system (OS) that runs on it. It is distinct from other nanokernels in that it is not only a low level layer for an outer kernel. Instead, it is intended to run several kernels together, which makes it similar to full virtualization technologies. It is free and open-source software released under a GNU General Public License (GPL).
A hypervisor is a type of computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Unlike an emulator, the guest executes most instructions on the native hardware. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system–level virtualization, where all instances must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the same kernel.

QEMU is a free and open-source emulator. It emulates a computer's processor through dynamic binary translation and provides a set of different hardware and device models for the machine, enabling it to run a variety of guest operating systems. It can interoperate with Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) to run virtual machines at near-native speed. QEMU can also do emulation for user-level processes, allowing applications compiled for one architecture to run on another.
The MicroBlaze is a soft microprocessor core designed for Xilinx field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA). As a soft-core processor, MicroBlaze is implemented entirely in the general-purpose memory and logic fabric of Xilinx FPGAs.
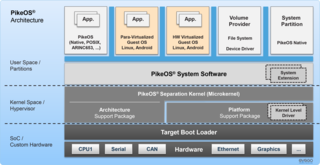
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) featuring a separation kernel-based hypervisor. This hypervisor supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is designed to facilitate the development of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT) by adhering to the high standards of quality, safety, and security across different industries. In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is an option for critical real-time applications, ensuring safety and security.
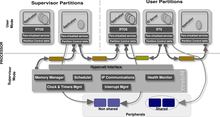
Integrated modular avionics (IMA) are real-time computer network airborne systems. This network consists of a number of computing modules capable of supporting numerous applications of differing criticality levels.
Lynx Software Technologies, Inc. is a San Jose, California software company founded in 1988. Lynx specializes in secure virtualization and open, reliable, certifiable real-time operating systems (RTOSes). Originally known as Lynx Real-Time Systems, the company changed its name to LynuxWorks in 2000 after acquiring, and merging with, ISDCorp, an embedded systems company with a strong Linux background. In May 2014, the company changed its name to Lynx Software Technologies.

Segger Microcontroller, founded in 1992, is a private company involved in the embedded systems industry. It provides products used to develop and manufacture four categories of embedded systems: real-time operating systems (RTOS) and software libraries (middleware), debugging and trace probes, programming tools, and in-system programmers. The company is headquartered in Monheim am Rhein, Germany, with remote offices in Gardner, Massachusetts; Milpitas, California; and Shanghai, China.
ARINC 653 is a software specification for space and time partitioning in safety-critical avionics real-time operating systems (RTOS). It allows the hosting of multiple applications of different software levels on the same hardware in the context of an Integrated Modular Avionics architecture.
SYSGO GmbH is a German information technologies company that supplies operating systems and services for embedded systems with high safety and security-related requirements, using Linux. For security-critical applications, the company offers the Hypervisor and RTOS PikeOS, an operating system for multicore processors and the foundation for intelligent devices in the Internet of Things (IoT).
LynxSecure is a least privilege real-time separation kernel hypervisor from Lynx Software Technologies designed for safety and security critical applications found in military, avionic, industrial, and automotive markets.
An embedded hypervisor is a hypervisor that supports the requirements of embedded systems.
Open Kernel Labs is a privately owned company that develops microkernel-based hypervisors and operating systems for embedded systems. The company was founded in 2006 by Steve Subar and Gernot Heiser as a spinout from NICTA. It was headquartered in Chicago, while research and development was located in Sydney, Australia. The company was acquired by General Dynamics in September 2012.

The ARM Cortex-R is a family of 32-bit and 64-bit RISC ARM processor cores licensed by Arm Ltd. The cores are optimized for hard real-time and safety-critical applications. Cores in this family implement the ARM Real-time (R) profile, which is one of three architecture profiles, the other two being the Application (A) profile implemented by the Cortex-A family and the Microcontroller (M) profile implemented by the Cortex-M family. The ARM Cortex-R family of microprocessors currently consists of ARM Cortex-R4(F), ARM Cortex-R5(F), ARM Cortex-R7(F), ARM Cortex-R8(F), ARM Cortex-R52(F), ARM Cortex-R52+(F), and ARM Cortex-R82(F).